International study led by researchers in Singapore reveals critical insights into timely interventions for maternal depression
2023-11-02
SINGAPORE – A large-scale international study spanning three continents, led by researchers from A*STAR’s Translational Neuroscience Programme of the Singapore Institute for Clinical Sciences (SICS) in Singapore, has found that maternal depressive symptoms begin from early pregnancy and can last up to two years after childbirth.
While health professionals often emphasise the postpartum stage after childbirth as a high-risk period for the onset of depression, findings from this latest study reveal a different reality – that maternal depressive symptoms can appear from early pregnancy ...
Paper argues reducing greenhouse gas emissions is not enough to combat climate change
2023-11-02
According to a new paper in Oxford Open Climate Change, published by Oxford University Press, the strategies humanity must pursue to reduce climate change will have to include more than reducing greenhouse gases. This comes from an analysis of climate data led by researcher James Hansen.
Scientists have known since the 1800s that infrared-absorbing (greenhouse) gases warm the Earth’s surface and that the abundance of greenhouse gases changes naturally as well as from human actions. Roger Revelle, who was one of the early scientists to study global warming, wrote in 1965 that industrialization meant that human ...
Research examines why mask usage in Japan persists
2023-11-02
Osaka, Japan – When you think of Japan in the age of COVID, you might imagine a crowd of people wearing masks. But why do so many Japanese people wear masks?
In an article published this month in the International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, a researcher from Osaka University analyzed mask use before and after the government of Japan downgraded the legal status of COVID-19. Results showed that many people continue to wear masks for socio-psychological reasons – including reasons related to ‘relief’ and ‘norm’.
Of course, the obvious motivation for mask use is disease prevention. In the first ...
Exercise therapy based on smart data to improve patients' quality of life
2023-11-02
Regular and moderate physical activity can significantly improve the quality of life of people with internal diseases such as cancer and depression. Unfortunately, many people with internal disorders cannot sufficiently participate in exercise training for several reasons. For example, they often do not have access to appropriate exercise training programs, have a high therapeutic burden, fatigue, or simply no time to engage in physical activity. Accordingly, the Sports Medicine research group led by Professor Perikles Simon at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) investigates how physical activity can be promoted and integrated into patients' daily lives by applying digital tools ...
Alternative antibiotic selection can reduce the risk of healthcare-associated infections for patients with pneumonia
2023-11-02
Arlington, Va. — November 2, 2023 — A new study published today in the American Journal of Infection Control (AJIC) reveals that the use of doxycycline may help protect against Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) infection for some patients with pneumonia. Specifically, study authors found that for hospitalized patients with community-acquired pneumonia who had experienced C. diff infections in the prior year, the use of doxycycline, instead of the more commonly used azithromycin, reduced the development ...
Survey finds most Americans are unaware of many signs that someone is having a seizure
2023-11-02
Orlando, Fla - If you’ve ever seen a movie or TV show in which a character has a seizure, you probably have a fairly standard mental picture of someone falling to the ground in full body convulsions while foaming at the mouth. But that doesn’t necessarily reflect reality. A new national survey by Orlando Health finds that while most Americans recognize those classic symptoms of what’s called a generalized tonic-clonic seizure, the majority fail to recognize the subtle signs, all of which can be dangerous and have a profound ...
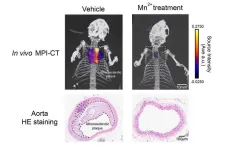
A “manganese bullet” targeting the top killer?
2023-11-02
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) continue to rank as the top killer in the modern world. This deadly disorder often starts with the buildup of lipid deposits or plaques within the blood vessel, silently setting the stage for atherosclerosis. Rupture of these atherosclerotic plaques, however, could clot blood vessels and lead to life-threatening conditions including heart attack or stroke.
Dyslipidemia, meaning having too much “bad” or atherogenic lipids in the blood, represents the most common cause of CVDs and ...
New NUS study provides insights into early breast cancer development in individuals with BRCA2 mutations
2023-11-02
A pioneering study led by Professor Ashok Venkitaraman from the Cancer Science Institute of Singapore (CSI Singapore) at the National University of Singapore and Dr Mona Shehata from the University of Cambridge (UK) has uncovered vital insights into the distinct effects of BRCA2 mutations on breast tissue cells, shedding light on early breast cancer development in people with BRCA2 mutations. The research was published in the prestigious journal Nature Communications on 25 August 2023.
Breast cancer is a serious concern for individuals with BRCA2 mutations, ...
Clinical intervention directed at social risks does not increase experiences of discrimination
2023-11-02
A growing recognition of the health impact of social risks – such as food insecurity and homelessness – has prompted researchers, healthcare providers and policymakers to consider ways to address these risk factors as part of holistic clinical care. However, some healthcare providers worry the same interventions designed to help patients and families with social risks might also make them feel singled out or like they are otherwise stigmatized.
Now, new results of a rigorous study from the University of Chicago Medicine published October 2023 in JAMA Pediatrics suggest well-designed interventions that address social risks can be provided ...
$13M NIH grant funds research aimed at revitalizing immune systems of older adults
2023-11-02
University of Arizona Health Sciences researchers received a $13.1 million grant from the National Institute on Aging to continue studies aimed at rejuvenating the immune system of older people in order to improve health throughout the lifespan.
Older adults are disproportionally affected by infection, cancer and certain types of autoimmune disease. This is influenced by the fact that as a person ages, their body produces fewer T cells and gets less proficient at maintaining them. T cells are a type of white blood cell essential to the immune ...
Study provides preliminary evidence in favor of a new type 1 diabetes treatment
2023-11-02
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that causes the body's immune system to attack and destroy insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Traditional management of type 1 diabetes has primarily involved replacing the missing insulin with injections which, though effective, can be expensive and burdensome. A new study led by researchers at the University of Chicago Medicine and Indiana University suggests that an existing drug could be repurposed to treat type 1 diabetes, potentially reducing dependence on insulin as the sole treatment.
The research centers on a medication known as α-difluoromethylornithine (DFMO), which inhibits an enzyme that plays a key role in cellular ...
New branch of oncology, cancer neuroscience, offers hope for hard-to-treat brain tumors
2023-11-02
Cancer cells hijack normal biological processes, allowing them to multiply. For example, tumors spur construction of new blood vessels, building themselves “highways” to supply nutrients.
Researchers have known about cancer’s blood vessel infiltration for decades, but it was only in the past few years that Stanford Medicine scientists and their colleagues discovered that tumors don’t just tap the body’s highway system; they can also infiltrate and exploit its “telecommunications.”
To ...
Less physical activity in adolescence likely rooted in biology
2023-11-02
AURORA, Colo. (Nov. 1, 2023) – The slowdown of physical activity during adolescence is not likely caused by lifestyle and environment but by energy demands placed on the body as it grows and sexually matures, according to a new study by researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus.
The study, published today in the Proceedings of the Royal Society B, examined the lifestyles of the physically active Tsimane people, an indigenous population of forager-horticulturalists in lowland Bolivia, to see similarities and differences to adolescents living in post-industrialized nations.
“We wanted to look at the role of environment and the role of biology,” ...
Adult coral can handle more heat and keep growing thanks to heat-evolved symbionts
2023-11-02
Adult fragments of a coral species can better tolerate bleaching and recover faster when treated with tougher heat-evolved symbionts, new research from the Australian Institute of Marine Science (AIMS) and the University of Melbourne indicates.
The study also found that treatment with the heat-evolved symbionts did not compromise the coral’s ability to grow. This differs from previous studies on Great Barrier Reef corals which found that naturally heat tolerant symbionts could enhance heat resistance in adult corals, but at a cost to its growth.
Symbionts are the tiny cells of algae that live inside the coral tissue, providing corals with energy to grow. The survival ...
Stronger, stretchier, self-healing plastic
2023-11-02
An innovative plastic, stronger and stretchier than the current standard type and which can be healed with heat, remembers its shape and partially biodegradable, has been developed by researchers at the University of Tokyo. They created it by adding the molecule polyrotaxane to an epoxy resin vitrimer, a type of plastic. Named VPR, the material can hold its form and has strong internal chemical bonds at low temperatures. However, at temperatures above 150 degrees Celsius, those bonds recombine and the material can be reformed into different shapes. Applying heat and a solvent breaks VPR down into its raw components. Submerging it in seawater ...
Brain health in over 50s deteriorated more rapidly during the pandemic
2023-11-02
rain health in over 50s deteriorated more rapidly during the pandemic, even if they didn’t have COVID-19, according to major new research linking the pandemic to sustained cognitive decline.
Researchers looked at results from computerised brain function tests from more than 3,000 participants of the online PROTECT study, who were aged between 50 and 90 and based in the UK. The remote study, led by teams at the University of Exeter and the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN) at King’s ...
Low Emission Zones improve air quality, health, and people’s well-being – new policy brief
2023-11-02
The introduction of London's Low Emission Zone (LEZ) in 2008 and subsequent Ultra-Low Emission Zone (ULEZ) from 2019 has significantly improved air quality, benefiting Londoners’ physical and mental health, according to new analysis from the Department of Economics at the University of Bath.
A new Institute for Policy Research (IPR) policy brief, presenting research from health economists at the University, indicates that the introduction of the LEZ helped to reduce particulate matter (PM10) in Greater London by 13% between 2008-13, compared to pre-LEZ levels (2003-07).
The ULEZ has had an even more substantial impact, ...
An MRI-equipped ambulance: A game-changer for stroke care?
2023-11-02
In the U.S., someone has a stroke every 40 seconds and dies from it every three minutes and 14 seconds, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. When it comes to stroke, experts echo the fact that time is brain. Faster treatment translates to better outcomes, and certain treatments, like the clot-busting drug tPA, have a strict time window for administration.
“The quicker that we can get the patient to treatment, the quicker we can have a good outcome,” said Dustin LeBlanc, M.D., director of Prehospital Medicine and associate chief medical officer for Emergency Management at the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC). ...
Repurposed drug offers new potential for managing type 1 diabetes
2023-11-01
INDIANAPOLIS -- A recent study led by Indiana University School of Medicine in collaboration with the University of Chicago Medicine presents exciting future possibilities for the management of type 1 diabetes and the potential reduction of insulin dependency. The researchers’ findings, published in Cell Reports Medicine, suggest repurposing of the drug α-difluoromethylornithine (DFMO) may open doors to innovative therapies in the future.
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic condition wherein the body's immune system mistakenly ...
UCF hires Director of Development and Operations for Virtual Experience Research Accelerator (VERA)
2023-11-01
UCF Hires Director of Development and Operations for Virtual Experience Research Accelerator (VERA)
ORLANDO, Nov. 1, 2023 – Ali Haskins Lisle, Ph.D., has been named the Director of Development and Operations for the UCF-led Virtual Experience Research Accelerator (VERA).
VERA is a nearly $5 million U.S. National Science Foundation project to develop the first large-scale human-machine system for virtual reality human subjects research, with the goals of affording very large studies, very quickly, with populations that ...
Hebrew prayer book fills gap in Italian earthquake history
2023-11-01
The chance discovery of a note written in a 15th century Hebrew prayer book fills an important gap in the historical Italian earthquake record, offering a brief glimpse of a previously unknown earthquake affecting the Marche region in the central Apennines.
Paolo Galli, who found the note in the Apostolic Vatican Library while looking for contemporaneous accounts of another historic Italian earthquake, writes in Seismological Research Letters that the note “not only helps us partially fill a gap in the seismic history ...
UChicago chemists make breakthrough in drug discovery chemistry
2023-11-01
For years, if you asked the people working to create new pharmaceutical drugs what they wished for, at the top of their lists would be a way to easily replace a carbon atom with a nitrogen atom in a molecule.
But two studies from chemists at the University of Chicago, published in Science and Nature, offer two new methods to address this wish. The findings could make it easier to develop new drugs.
“This is the grand-challenge problem that I started my lab to try to solve,” said Mark Levin, ...
Docetaxel use associated with significant reduction in prostate cancer death in very poor prognostic group
2023-11-01
Men with high-grade prostate cancer and low prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels have a poor prognosis. The question remains as to whether the chemotherapy drug docetaxel, which increases survival in metastatic prostate cancer, can improve the cure rate in these patients.
In a new study, investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, a meta-analysis of five prospective randomized clinical trials (RCTs) found that adding docetaxel to standard-of-care (SOC) treatment was associated with a 70% reduction in death from prostate cancer-specific ...
Pet ownership may contribute to health care barriers for people with HIV
2023-11-01
People living with HIV may face hard choices when balancing their own health needs with caring for a pet, a study led by a University of Florida College of Public Health and Health Professions researcher finds.
For the study, which appears in the journal PLOS ONE, 36% of people with HIV who own pets reported delaying health care, not seeking it or said they expect to do so in the future. Financial and other resource concerns, including not having access to pet sitting or boarding services, are among the leading factors that may contribute to health care barriers among pet owners ...
Test detects co-infection by novel species of parasite in severe cases of visceral leishmaniasis
2023-11-01
In recent years, physicians and scientists in parts of Brazil where visceral leishmaniasis (VL) is endemic have seen rising numbers of cases of co-infection by Leishmania infantum and Crithidia, also a protozoan but hitherto believed to be a mosquito parasite that cannot infect humans or other mammals. Accurate diagnosis is hindered by a lack of simple specific tests (more at: https://agencia.fapesp.br/42072 and https://agencia.fapesp.br/31581).
To accelerate and facilitate detection of the pathogens involved, supporting appropriate decisions regarding treatment, researchers at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar) have developed a PCR test ...
[1] ... [1571]
[1572]
[1573]
[1574]
[1575]
[1576]
[1577]
[1578]
1579
[1580]
[1581]
[1582]
[1583]
[1584]
[1585]
[1586]
[1587]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.