Making gluten-free, sorghum-based beers easier to brew and enjoy
2023-11-02
Though beer is a popular drink worldwide, it’s usually made from barley, which leaves those with a gluten allergy or intolerance unable to enjoy the frothy beverage. Sorghum, a naturally gluten-free grain, could be an alternative, but complex preparation steps have hampered its widespread adoption by brewers. Now, researchers reporting the molecular basis behind sorghum brewing in ACS’ Journal of Proteome Research have uncovered an enzyme that could improve the future of sorghum-based beers.
Traditionally, beer brewers start with barley grains, which they malt, mash, ...
Jurassic worlds might be easier to spot than modern Earth
2023-11-02
ITHACA, N.Y. –Things may not have ended well for dinosaurs on Earth, but Cornell University astronomers say the “light fingerprint” of the conditions that enabled them to emerge here provide a crucial missing piece in our search for signs of life on planets orbiting alien stars.
Their analysis of the most recent 540 million years of Earth’s evolution, known as the Phanerozoic Eon, finds that telescopes could better detect potential chemical signatures of life in the atmosphere of an Earth-like exoplanet more closely resembling the age the dinosaurs inhabited than the ...
Archaeology: Larger-scale warfare may have occurred in Europe 1,000 years earlier
2023-11-02
A re-analysis of more than 300 sets of 5,000-year-old skeletal remains excavated from a site in Spain suggests that many of the individuals may have been casualties of the earliest period of warfare in Europe, occurring over 1,000 years before the previous earliest known larger-scale conflict in the region. The study, published in Scientific Reports, indicates that both the number of injured individuals and the disproportionately high percentage of males affected suggest that the injuries resulted from a period of conflict, potentially lasting at least months.
Conflict during the European Neolithic period (approximately 9,000 ...
Study warns API restrictions by social media platforms threaten research
2023-11-02
University researchers from the UK, Germany and South Africa warn of a threat to scientific knowledge and the future of research in a paper published in Nature Human Behaviour, outlining the implications of changes to social media Application Programming Interfaces (APIs).
Over the course of 2023, numerous social media platforms including X, TikTok, and Reddit made substantial changes to their APIs – drastically reducing access or increasing charges for access, which the researchers say will in many cases make research harder.
APIs have been routinely tapped by researchers ...
Researchers engineer colloidal quasicrystals using DNA-modified building blocks
2023-11-02
Evanston, IL. --- A team of researchers from the Mirkin Group at Northwestern University’s International Institute for Nanotechnology in collaboration with the University of Michigan and the Center for Cooperative Research in Biomaterials- CIC biomaGUNE, unveils a novel methodology to engineer colloidal quasicrystals using DNA-modified building blocks. Their study will be published in the journal Nature Materials under the title "Colloidal Quasicrystals Engineered with DNA."
Characterized ...
Nanoparticle quasicrystal constructed with DNA
2023-11-02
Images
Nanoengineers have created a quasicrystal—a scientifically intriguing and technologically promising material structure—from nanoparticles using DNA, the molecule that encodes life.
The team, led by researchers at Northwestern University, the University of Michigan and the Center for Cooperative Research in Biomaterials in San Sebastian, Spain, reports the results in Nature Materials.
Unlike ordinary crystals, which are defined by a repeating structure, the patterns in quasicrystals don't repeat. Quasicrystals built from atoms can have exceptional properties—for ...
Damaging thunderstorm winds increasing in central U.S.
2023-11-02
Destructive winds that flow out of thunderstorms in the central United States are becoming more widespread with warming temperatures, according to new research by the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR).
The new study, published this week in Nature Climate Change, shows that the central U.S. experienced a fivefold increase in the geographic area affected by damaging thunderstorm straight line winds in the past 40 years. The research uses a combination of meteorological observations, very high-resolution computer modeling, and analyses of fundamental ...
Climate-induced loss is impeding human rights in the Pacific
2023-11-02
Climate change is impeding the human rights of a large group of people living in the Pacific, a recent report in Nature reveals.
The paper substantiates a submission to the International Court of Justice (ICJ) on the legal responsibility of countries to act on climate change.
Evidence gathered in Vanuatu supports a clarification on loss and damage finance which could activate powerful legal tools to hold polluters accountable.
Research Fellow at the Griffith University Climate Action Beacon, Dr Ross Westoby said the report explores how climate-induced loss and damage in the Pacific is already occurring and outlines ...
Bartering light for light: scientists discover new system to control the chaotic behavior of light
2023-11-02
NEW YORK, November 2, 2023 — Harnessing and controlling light is vital for the development of technology, including energy harvesting, computation, communications, and biomedical sensing. Yet, in real-world scenarios, complexity in light's behavior poses challenges for its efficient control. Physicist Andrea Alù likens the behavior of light in chaotic systems to the initial break shot in a game of billiards.
“In billiards, tiny variations in the way you launch the cue ball will lead to different patterns of the balls bouncing around the table,” said Alù, Einstein ...
Study links changes in global water cycle to higher temperatures
2023-11-02
It’s a multi-billion dollar question: What will happen to water as temperatures continue to rise? There will be winners and losers with any change that redistributes where, when and how much water is available for humans to drink and use.
To find answers and make informed predictions, scientists look to the past. Reconstructions of past climate change using geologic data have helped to show the far-reaching influence of human activity on temperatures since the Industrial Age. But assembling hydroclimate records for the same timeframe has proved to be much harder.
A study from the Past Global Changes (PAGES) Iso2k project team, ...
Metabolite tells cells whether to repair DNA
2023-11-02
Metabolites called nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA and can impact cancer’s sensitivity or resistance to chemotherapy and radiation in brain cancer.
Findings from researchers at the University of Michigan Health Rogel Cancer Center, published in Cancer Discovery, show how a specific nucleotide metabolite, called GTP, controls responses to radiation and chemotherapy in an unexpected way.
“We learned that if you increase a cell’s GTP levels, it makes it really resistant to ...
American Thyroid Association® names Trevor E. Angell, MD new Editor-in-Chief of Clinical Thyroidology®
2023-11-02
The American Thyroid Association® (ATA®) is pleased to announce that Trevor E. Angell, MD has been selected as the new Editor-in-Chief of the ATA monthly journal Clinical Thyroidology®. Dr. Angell’s term as Editor-in-Chief will begin in January 2024.
Clinical Thyroidology is one of the ATA’s official journals and is published in partnership with Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. This highly valued abstract and commentary publication provides a comprehensive look at clinical thyroid literature. Experts ...
Hollings researchers uncover new targets for breast cancers resistant to standard therapies
2023-11-02
Researchers at MUSC Hollings Cancer Center believe that some drugs already approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration or currently in clinical trials could be repurposed for certain breast cancer patients whose cancer has become resistant to standard therapies.
Ozgur Sahin, Ph.D., a professor and SmartState Endowed Chair in the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, led the research, which was published Nov. 2 in Nature Communications.
The research, funded by an American Cancer Society Research Scholar Grant, started as an investigation into cancer resistance to the drug tamoxifen but expanded as the research questions led down new ...
Start-up dedicated to developing new antibiotics
2023-11-02
It all began with basic research: While conducting laboratory experiments, a team at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) came across an active agent against multidrug-resistant bacteria with a fundamental difference to antibiotics developed to date. The researchers have since established a start-up to develop a new drug based on this agent. The entrepreneurs have now been nominated for Science Breakthrough of the Year in the Science Start-Up category at the international Falling Walls summit.
Rising numbers of bacteria are developing ...
Two million European households could abandon the electrical grid by 2050
2023-11-02
Researchers report that 53% of European freestanding homes could have supplied all their own energy needs in 2020 using only local rooftop solar radiation, and this technical feasibility could increase to 75% in 2050. Publishing November 2 in the journal Joule, the study shows that there is no economic advantage for individual households to be fully self-sufficient under current or future conditions, though in some cases the costs are on par with remaining on-grid. The researchers estimate that self-sufficiency will be economically feasible for 5% (two million) of Europe’s 41 million freestanding single-family homes in 2050, ...
One sleepless night can rapidly reverse depression for several days
2023-11-02
All-nighters can cause giddy and slap-happy feelings
This effect is caused by increased dopamine release in distributed brain regions
This dopamine signal also enhances plasticity in the neuronal connections, causing a potent antidepressant effect that lasts for days
Study suggests that prefrontal cortex and its dopamine inputs are key for rapid plasticity and antidepressant effects after brief sleep loss
EVANSTON, Ill. — Most people who have pulled an all-nighter are all too familiar with that “tired and wired” ...
Circuit-specific gene therapy brings new hope for treatment of Parkinson’s disease
2023-11-02
Researchers from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and their collaborators have developed a gene therapy strategy to selectively manipulate Parkinson's disease-affected circuitry and attenuate the core motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease in rodent and nonhuman primate animals.
The study was published in Cell on Nov. 2.
Parkinson's disease, characterized by the loss of midbrain dopaminergic neurons, is one of the most common neurodegenerative diseases in the elderly population, affecting more than 6 million people worldwide.
Dopamine ...
Higher risk of breast cancer in women with false positive mammography result
2023-11-02
Women who receive a false positive mammography result are more likely to develop breast cancer over the subsequent 20 years, report researchers from Karolinska Institutet in a study published in JAMA Oncology. The risk is highest for women aged between 60 and 75 and who have low breast density.
In global terms, breast cancer is the most common form of cancer among women, and screening is an important tool for catching women with a tumour at the earliest possible stage. In Sweden, all women between ...
PTSD symptoms and cardiovascular and brain health in women
2023-11-02
About The Study: In this study of 274 midlife women, greater posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms were associated with higher carotid atherosclerosis and, among women who were APOEɛ4 carriers, greater brain small vessel disease and poorer cognitive performance. These findings point to the adverse implications of PTSD symptoms for cardiovascular and neurocognitive health among women in midlife, particularly for women who are APOEɛ4 carriers.
Authors: Rebecca C. Thurston, Ph.D., of the University of Pittsburgh, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed ...
Breast cancer incidence after a false-positive mammography result
2023-11-02
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that the risk of developing breast cancer after a false-positive mammography result differs by individual characteristics and follow-up. These findings can be used to develop individualized risk-based breast cancer screening after a false-positive result.
Authors: Xinhe Mao, M.Sc., of the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2023.4519)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
Practicing mindfulness can help people make heart-healthy eating choices
2023-11-02
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Practicing mindfulness focused on healthy eating can be good for the heart, a new study shows, because it improves self-awareness and helps people stick to a heart-healthy diet.
When people who had elevated blood pressure participated in an eight-week mindfulness-based blood pressure reduction program for the study, they significantly improved their scores on measures of self-awareness and adherence to a heart-healthy diet compared to a control group. The results were published in JAMA Network Open.
“Participants ...
Infirmary Health partners with Ochsner Accountable Care Network to improve health outcomes for seniors across the Gulf Coast
2023-11-02
NEW ORLEANS, LA- Ochsner Health, the leading healthcare system in the Gulf South, and Infirmary Health, Alabama's largest private non-profit healthcare provider, are proud to announce a landmark partnership with Ochsner Accountable Care Network, a top-performing accountable care organization (ACO) in both clinical performance and healthcare savings for the Medicare population. The partnership aims to improve health outcomes for seniors across the Gulf Coast region.
Infirmary Health's hospitals and acute care facilities are recognized as national leaders in innovative and compassionate care for ...
Imaging advance poised to provide new insights into reproduction and infertility
2023-11-02
WASHINGTON — Researchers have developed a new optical coherence tomography (OCT) approach that can directly image coordination of tiny hair-like structures known as motile cilia in their natural environment. The ability to observe cilia dynamics in living organisms gives researchers a powerful new tool to investigate how these structures move cells and substances through the female reproductive system, as well as other functions of cilia throughout the body.
“Our new method has the potential to answer the longstanding question about cilia's ...
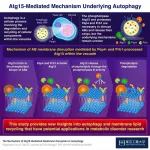
New study sheds light on the molecular mechanisms underlying lipid recycling within cells
2023-11-02
Recycling is just as essential in cells as in our more familiar macroscopic world. Cells continuously generate waste products and accumulate damaged components while performing regular functions. Various recycling mechanisms have evolved to ensure efficient use of these resources and help maintain homeostasis, with autophagy being one of the most well-preserved among countless animal, plant, and fungal lineages.
In the main form of autophagy, materials floating in the cell are transported to specialized organelles, such as lysosomes or vacuoles, within small capsule-like structures called ...
Researchers identify the mutations that drive resistance to PI3K inhibitors in breast cancer that can be overcome by next generation agents
2023-11-02
Mutations in the PIK3CA gene that lead to elevated production of the PI3Ka protein are among the most frequent alterations found in cancer, including in approximately 40% of hormone receptor–positive breast cancers.
Alpelisib, the first drug targeting PI3Ka, was approved for use in the United States four years ago, but cancers with mutated PIK3CA eventually develop resistance to the medication.
A team led by investigators at the Mass General Cancer Center, a member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, recently identified that resistance in some cases can be caused by secondary mutations in the PIK3CA gene itself. This leads ...
[1] ... [1578]
[1579]
[1580]
[1581]
[1582]
[1583]
[1584]
[1585]
1586
[1587]
[1588]
[1589]
[1590]
[1591]
[1592]
[1593]
[1594]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.