Herbivory limits vegetation restoration success at sites worldwide, new meta-analysis shows
2023-11-02
Excluding herbivores – or reintroducing their predators – may aid restoration efforts in many locations, suggests a new meta-analysis of more than 600 global studies. According to the analysis, herbivores at restoration sites reduced vegetation abundance by 89%, on average, a larger effect than they had at relatively undisturbed sites. Herbivores also suppressed plant diversity at these locations. Vegetation is a primary foundation of most ecosystems. However, in many, it has been dramatically degraded, contributing to the loss of biodiversity and ...
Southern hemisphere dominates decline in global water availability
2023-11-02
Driven in part by large-scale atmospheric climate modes, the Southern Hemisphere accounts for more than 95% of the recent decline in global water availability, according to a new study. Global land water availability has varied due to climate change and increased human water use. Although this crucial resource underpins livelihoods, socioeconomic development, and ecosystems worldwide, it remains unclear how water availability has changed in recent decades and what is driving these changes at a global scale. Yongqiang Zhang and colleagues combine various data, including streamflow observations of large river basins of ...
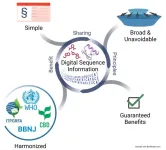
Researchers caution that biodiversity benefit-sharing needs a radically new approach
2023-11-02
At the 2022 COP-15 meeting, signatories of the Convention on Biological Diversity reached a new agreement called the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework, which contained provisions to establish a separate, multilateral benefit-sharing mechanism for the use of “digital sequence information” (DSI), that is, the biological data associated with, or derived from, genetic resources such as nucleotide sequences and epigenetic, protein, and metabolite data.
In a new Policy Forum analysis published ...
Research outlines how sex differences have evolved
2023-11-02
­­­Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 18:00hrs GMT Thursday 2 November 2023
Peer reviewed
Observational study
People and animals
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and Heidelberg University in Germany have shown that sex differences in animals vary dramatically across species, organs and developmental stages, and evolve quickly at the gene level but slowly at the cell type level.
Mammals have different traits depending on sex, like antlers in male deer. These are known as ‘sexually dimorphic’ traits, and include differences which aren’t visible, ...
UCLA researchers develop solid-state thermal transistor for better heat management
2023-11-02
A team of researchers from UCLA has unveiled a first-of-its-kind stable and fully solid-state thermal transistor that uses an electric field to control a semiconductor device’s heat movement.
The group’s study, which will be published in the Nov. 3 issue of Science, details how the device works and its potential applications. With top speed and performance, the transistor could open new frontiers in heat management of computer chips through an atomic-level design and molecular engineering. The advance could also further the understanding of how heat is regulated in the human body.
“The precision control of how heat flows through materials has been a long-held ...
Good news, bad news on dental pain care seen in new study
2023-11-02
Americans who have a tooth pulled or another painful dental procedure in the United States today are far less likely to get opioid painkillers than they were just a few years ago, a new study shows.
That’s good news, since research shows that opioids are not necessary for most dental procedures.
But the COVID-19 pandemic seems to have thrown a wrench into the effort to reduce opioid use in dental care – and not just in the few months after dentists and oral surgeons started providing routine care again after a pause in spring 2020.
The decline in opioid prescriptions filled by dental patients was much faster in the pre-pandemic ...
Researchers identify female sex determining gene in mice
2023-11-02
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 18:00hrs GMT Thursday 2 November 2023
Peer reviewed
Experimental study
Animals
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and the Université Cote d’Azur, together with other labs in France and Switzerland, have identified a gene which is an early determining factor of ovary development in mice.
Typically, mice with XY sex chromosomes develop testes, and mice with XX chromosomes develop ovaries. Whether early gonads become ovaries or testes is due to cells either ...
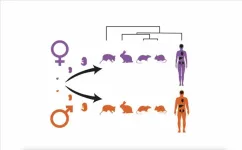
How organs of male and female mammals differ
2023-11-02
The development of sex-specific characteristics is frequently seen in mammals. These characteristics stem from the activation of corresponding genetic programmes that until now have been largely undescribed by the scientific community. An international research team from the Center for Molecular Biology of Heidelberg University and The Francis Crick Institute in London has, for the first time, decoded the programmes that control the sex-specific development of major organs in selected mammals – humans, mice, rats, rabbits, and opossums. By comparing these programmes, the researchers were also able to trace the ...
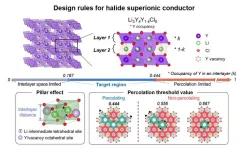
New designs for solid-state electrolytes may soon revolutionize the battery industry
2023-11-02
Researchers led by Professor KANG Kisuk of the Center for Nanoparticle Research within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), have announced a major breakthrough in the field of next-generation solid-state batteries. It is believed that their new findings will enable the creation of batteries based on a novel chloride-based solid electrolyte that exhibits exceptional ionic conductivity.
A pressing concern with current commercial batteries their reliance on liquid electrolytes, which leads to flammability ...
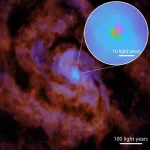
Black holes are messy eaters
2023-11-02
New observations down to light-year scale of the gas flows around a supermassive black hole have successfully detected dense gas inflows and shown that only a small portion (about 3 percent) of the gas flowing towards the black hole is eaten by the black hole. The remainder is ejected and recycled back into the host galaxy.
Not all of the matter which falls towards a black hole is absorbed, some of it is ejected as outflows. But the ratio of the matter that the black hole “eats,” and the amount “dropped” ...
New strategy attacks treatment-resistant lymphomas
2023-11-02
A surprising mechanism that makes some cancers treatment-resistant has been discovered by Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian investigators. The mechanism, which involves the shuttling of messenger RNAs (mRNAs) from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, ultimately facilitates DNA repair in cancer cells. These cancer cells can thereby thwart treatments aimed at damaging their DNA.
In a project encompassing both fundamental research and clinical studies they demonstrated that a combination of approved chemotherapies, ...
At least 14% of Americans have had long COVID
2023-11-02
One in seven people in the US reported having had long Covid by the end of 2022, suggests a large-scale investigation of long Covid and symptom prevalence by academics at UCL and Dartmouth.
Having had long Covid is associated with anxiety and low mood, as well as an increased likelihood of continued physical mobility problems and challenges with memory, concentration or understanding, according to the findings published in PLOS ONE.
The risk of anxiety and low mood appeared to be lower for those who have been vaccinated, ...
Mount Sinai researchers receive $7 million to improve outcomes for high-risk blood cancer patients from the Multiple Myeloma Research Foundation
2023-11-02
New York, NY (November 2nd, 2023) — The Mount Sinai Health System has received a $7 million grant from the Multiple Myeloma Research Foundation for a three-year project that aims to fast-track novel translational concepts to improve outcomes for people with high risk myeloma, the second most common blood cancer in the United States.
This grant award will facilitate a multidisciplinary research project that will analyze a large, diverse cohort of patient samples from all over the United States at the genomic and immune level and apply novel functional genomics technology to understand the critical events that drive ...
Pascal Lee awarded the 2023 Carl Sagan Prize for Science Popularization
2023-11-02
November 2, 2023, Mountain View, CA -- The SETI Institute is delighted to announce that Dr. Pascal Lee will be honored with the 2023 Carl Sagan Prize for Science Popularization presented by Wonderfest. The prestigious Sagan Prize recognizes and encourages individuals who “have contributed wonderfully to the public understanding and appreciation of science.” Previous recipients from the SETI Institute include SETI Institute co-founder and SETI pioneer Jill Tarter, senior astronomer Seth Shostak and trustee Andrew Fraknoi.
“I am truly delighted and humbled by this award,” says Pascal Lee, “all the more because Carl Sagan was, and remains, ...
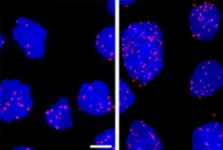
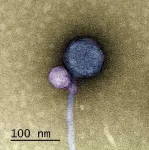
UMBC team makes first-ever observation of a virus attaching to another virus
2023-11-02
No one had ever seen one virus latching onto another virus, until anomalous sequencing results sent a UMBC team down a rabbit hole leading to a first-of-its-kind discovery.
It’s known that some viruses, called satellites, depend not only on their host organism to complete their life cycle, but also on another virus, known as a “helper,” explains Ivan Erill, professor of biological sciences. The satellite virus needs the helper either to build its capsid, a protective shell that encloses the virus’s genetic material, or to help it replicate ...
Research connecting gut bacteria and oxytocin provides a new mechanism for microbiome-promoted health benefits
2023-11-02
The gut microbiome, a community of trillions of microbes living in the human intestines, has an increasing reputation for affecting not only gut health but also the health of organs distant from the gut. For most microbes in the intestine, the details of how they can affect other organs remain unclear, but for gut resident bacteria L. reuteri the pieces of the puzzle are beginning to fall into place.
“L. reuteri is one of such bacteria that can affect more than one organ in the body,” said co-corresponding author Dr. Sara Di Rienzi, ...
How “blue” and “green” appeared in a language that didn’t have words for them
2023-11-02
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- The human eye can perceive about 1 million colors, but languages have far fewer words to describe those colors. So-called basic color terms, single color words used frequently by speakers of a given language, are often employed to gauge how languages differ in their handling of color. Languages spoken in industrialized nations such as the United States, for example, tend to have about a dozen basic color terms, while languages spoken by more isolated populations often have fewer.
However, the way that a language ...
Plant populations in Cologne are adapted to their urban environments
2023-11-02
A research team from the Universities of Cologne and Potsdam and the Max Planck Institute for Plant Breeding Research has found that the regional lines of the thale cress (Arabidopsis thaliana), a small ruderal plant which populates the streets of Cologne, vary greatly in typical life cycle characteristics, such as the regulation of flowering and germination. This allows them to adapt their reproduction to local environmental conditions such as temperature and human disturbances. The researchers from Collaborative Research Center / Transregio 341 “Plant Ecological Genetics” found that environmental ...
Making gluten-free, sorghum-based beers easier to brew and enjoy
2023-11-02
Though beer is a popular drink worldwide, it’s usually made from barley, which leaves those with a gluten allergy or intolerance unable to enjoy the frothy beverage. Sorghum, a naturally gluten-free grain, could be an alternative, but complex preparation steps have hampered its widespread adoption by brewers. Now, researchers reporting the molecular basis behind sorghum brewing in ACS’ Journal of Proteome Research have uncovered an enzyme that could improve the future of sorghum-based beers.
Traditionally, beer brewers start with barley grains, which they malt, mash, ...
Jurassic worlds might be easier to spot than modern Earth
2023-11-02
ITHACA, N.Y. –Things may not have ended well for dinosaurs on Earth, but Cornell University astronomers say the “light fingerprint” of the conditions that enabled them to emerge here provide a crucial missing piece in our search for signs of life on planets orbiting alien stars.
Their analysis of the most recent 540 million years of Earth’s evolution, known as the Phanerozoic Eon, finds that telescopes could better detect potential chemical signatures of life in the atmosphere of an Earth-like exoplanet more closely resembling the age the dinosaurs inhabited than the ...
Archaeology: Larger-scale warfare may have occurred in Europe 1,000 years earlier
2023-11-02
A re-analysis of more than 300 sets of 5,000-year-old skeletal remains excavated from a site in Spain suggests that many of the individuals may have been casualties of the earliest period of warfare in Europe, occurring over 1,000 years before the previous earliest known larger-scale conflict in the region. The study, published in Scientific Reports, indicates that both the number of injured individuals and the disproportionately high percentage of males affected suggest that the injuries resulted from a period of conflict, potentially lasting at least months.
Conflict during the European Neolithic period (approximately 9,000 ...
Study warns API restrictions by social media platforms threaten research
2023-11-02
University researchers from the UK, Germany and South Africa warn of a threat to scientific knowledge and the future of research in a paper published in Nature Human Behaviour, outlining the implications of changes to social media Application Programming Interfaces (APIs).
Over the course of 2023, numerous social media platforms including X, TikTok, and Reddit made substantial changes to their APIs – drastically reducing access or increasing charges for access, which the researchers say will in many cases make research harder.
APIs have been routinely tapped by researchers ...
Researchers engineer colloidal quasicrystals using DNA-modified building blocks
2023-11-02
Evanston, IL. --- A team of researchers from the Mirkin Group at Northwestern University’s International Institute for Nanotechnology in collaboration with the University of Michigan and the Center for Cooperative Research in Biomaterials- CIC biomaGUNE, unveils a novel methodology to engineer colloidal quasicrystals using DNA-modified building blocks. Their study will be published in the journal Nature Materials under the title "Colloidal Quasicrystals Engineered with DNA."
Characterized ...
Nanoparticle quasicrystal constructed with DNA
2023-11-02
Images
Nanoengineers have created a quasicrystal—a scientifically intriguing and technologically promising material structure—from nanoparticles using DNA, the molecule that encodes life.
The team, led by researchers at Northwestern University, the University of Michigan and the Center for Cooperative Research in Biomaterials in San Sebastian, Spain, reports the results in Nature Materials.
Unlike ordinary crystals, which are defined by a repeating structure, the patterns in quasicrystals don't repeat. Quasicrystals built from atoms can have exceptional properties—for ...
Damaging thunderstorm winds increasing in central U.S.
2023-11-02
Destructive winds that flow out of thunderstorms in the central United States are becoming more widespread with warming temperatures, according to new research by the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR).
The new study, published this week in Nature Climate Change, shows that the central U.S. experienced a fivefold increase in the geographic area affected by damaging thunderstorm straight line winds in the past 40 years. The research uses a combination of meteorological observations, very high-resolution computer modeling, and analyses of fundamental ...
[1] ... [1581]
[1582]
[1583]
[1584]
[1585]
[1586]
[1587]
[1588]
1589
[1590]
[1591]
[1592]
[1593]
[1594]
[1595]
[1596]
[1597]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.