Ultrafast lasers on ultra-tiny chips
2023-11-09
Lasers have become relatively commonplace in everyday life, but they have many uses outside of providing light shows at raves and scanning barcodes on groceries. Lasers are also of great importance in telecommunications and computing as well as biology, chemistry, and physics research.
In those latter applications, lasers that can emit extremely short pulses—those on the order of one-trillionth of a second (one picosecond) or shorter—are especially useful. Using lasers operating on such small timescales, researchers can study physical and chemical ...
Pesticides, herbicides, fungicides detected in New York state beeswax
2023-11-09
An analysis of beeswax in managed honeybee hives in New York found a wide variety of pesticide, herbicide and fungicide residues – exposing current and future generations of bees to long-term toxicity.
The study, published in the Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation, notes that people may be similarly exposed through contaminated honey, pollen and wax in cosmetics. Though the chemicals found in wax are not beneficial to humans, the small amounts in these products are unlikely to ...
Study reveals bacterial protein capable of keeping human cells healthy
2023-11-09
Researchers at the University of São Paulo (USP) in Brazil, partnering with colleagues in Australia, have identified a novel bacterial protein that can keep human cells healthy even when the cells have a heavy bacterial burden. The discovery could lead to new treatments for a wide array of diseases relating to mitochondrial dysfunction, such as cancer and auto-immune disorders. Mitochondria are organelles that supply most of the chemical energy needed to power cells’ biochemical reactions.
An article on the study is published in the journal PNAS. The researchers ...
Endangered thick-billed parrots at risk of losing newly identified, unprotected Sierra Madre forest habitats to logging, deforestation, study shows
2023-11-09
DOWNLOAD PHOTOS AND VIDEO: https://sandiegozoo.box.com/s/x50kzaoukdtyjxsv9mzqgn0fu1m6kddk
A binational team of scientists, using creativity and innovation, adorned dozens of endangered thick-billed parrots with tiny solar-powered satellite transmitters to track and reveal their winter migratory nesting sites in the remote treetops of the Sierra Madre Occidental ranges. Their research reveals new critical habitat, 80% of which has no formal protection.
In a study published this month in the journal Global ...
Atomic dance gives rise to a magnet
2023-11-09
Quantum materials hold the key to a future of lightning-speed, energy-efficient information systems. The problem with tapping their transformative potential is that, in solids, the vast number of atoms often drowns out the exotic quantum properties electrons carry.
Rice University researchers in the lab of quantum materials scientist Hanyu Zhu found that when they move in circles, atoms can also work wonders: When the atomic lattice in a rare-earth crystal becomes animated with a corkscrew-shaped vibration known as a chiral phonon, the crystal is transformed ...
Milky Way-like galaxy found in the early universe
2023-11-09
Using the James Webb Space Telescope, an international team, including astronomer Alexander de la Vega of the University of California, Riverside, has discovered the most distant barred spiral galaxy similar to the Milky Way that has been observed to date.
Until now it was believed that barred spiral galaxies like the Milky Way could not be observed before the universe, estimated to be 13.8 billion years old, reached half of its current age.
The research, published in Nature this week, was led by scientists at the Centro de Astrobiología in Spain.
“This galaxy, named ceers-2112, formed soon after ...
Side-effect avoiding treatment shows early promise against breast cancer in mice
2023-11-09
New experimental evidence suggests that substances known as narrow-spectrum Wnt signaling inhibitors—which could have fewer side effects than other related substances—are capable of suppressing the growth of breast cancer tumors in mice. Aina He of Shanghai Jiaotong University Affiliated Sixth People’s Hospital, China, and colleagues present these findings November 9th in the open access journal PLOS Biology.
While certain subtypes of breast cancer can be targeted with special medications, others can only be treated with standard chemotherapy. For some patients, chemotherapy may lead to the growth of stem cell-like cancer cells that are drug resistant. Previous ...
Bacteria-virus arms race provides rare window into rapid and complex evolution
2023-11-09
As conceived by Charles Darwin in the 1800s, evolution is a slow, gradual process during which species adaptations are inherited incrementally over generations. However, today biologists can see how evolutionary changes unfold on much more accelerated timescales.
Rather than the evocative plants and animals of the Galapagos Islands that Darwin studied in forming his theory of evolution, Postdoctoral Scholar Joshua Borin and Associate Professor Justin Meyer of UC San Diego’s School of Biological Sciences are documenting rapid evolutionary processes in simple laboratory flasks.
Borin ...
Open-science “COVID Moonshot” discovers new antivirals to treat COVID-19
2023-11-09
Although the group’s work has been freely available since its inception in March 2020, the COVID Moonshot Consortium is finally formally reporting their results. The COVID Moonshot – an open-science, crowdsourced, and patent-free drug discovery campaign targeting the SARS-CoV-2 virus – has yielded a wealth of data on the virus’s main protease, including insights that could pave the way for the development of new and better therapeutics. “The lead therapeutics described by [these researchers] may not be ready in time to affect the current pandemic, considering the timelines and challenges of drug approval,” write Brian Shoichet and Charles ...
Shrinking a mode-locked laser to the size of an optical chip
2023-11-09
Setting out to improve a technology that usually requires bulky, bench-top equipment, Quishi Guo and colleagues have shrunk a mode-locked laser (MLL) to the size of an optical chip with an integrated nanophotonic platform. The results show promise for developing ultrafast nanophotonic systems for a wide range of applications. Mode-locked lasers (MLLs) can produce coherent ultrashort pulses of light at extremely fast speeds – on the order of picoseconds and femtoseconds. These devices have enabled numerous technologies in photonics, including extreme nonlinear optics, two-photon microscopy, ...
Wildfire risk to US homes is rising, especially in western grasslands and shrublands
2023-11-09
Drawing on 30 years of data, researchers show that the number of homes within wildfire perimeters in the U.S. has doubled since the 1990s. This increasing risk is driven by both an increase in wildfires and the expansion of new homes into wildfire-prone areas, especially in the wildland-urban interface. Wildfire risks to homes are increasing, particularly in the wildland-urban interface (WUI), where houses and wildland vegetation are in close proximity. Over the last 12 years, more than 55,000 homes in the U.S. have been lost to wildfires due to rapid increases ...
Introducing: Ceramic- and glass-based passive radiative cooling materials resistance to harsh environments
2023-11-09
Two studies highlight new glass- and ceramic-based passive radiative cooling materials. Unlike passive radiative cooling approaches that rely on polymers, these hard materials are more durable and versatile, making them more attractive for a wide range of outdoor passive cooling applications, including those that could help reduce the need for air conditioning. The energy demand for cooling continues to rise, particularly in regions rapidly warming due to climate change. To make matters worse, the growing carbon footprint of cooling systems further contributes to global warming, exacerbating the need for cooling solutions. Passive radiative cooling (PRC) materials, which ...
Researchers identify previously unknown step in cholesterol absorption in the gut
2023-11-09
UCLA researchers have described a previously unknown step in the complex process by which dietary cholesterol is processed in the intestines before being released into the bloodstream – potentially revealing a new pathway to target in cholesterol treatment.
Although an existing drug and statins impact part of the process, an experimental drug being studied in UCLA research labs appears to specifically target the newfound pathway, possibly adding a new approach to the cholesterol management toolbox.
“Our results show that certain proteins in the Aster family play a critical role in moving cholesterol through the absorption and uptake process,” said ...
Desert birds lay larger eggs when they have more helpers
2023-11-09
Desert birds lay larger eggs when they have more helpers to feed their chicks, new research shows.
White-browed sparrow weavers live in family groups in which only a dominant pair breeds and their grown-up offspring, particularly females, help to feed nestlings.
The study, by researchers at the University of Exeter, found that mothers increased the size of their eggs when they had more female helpers on hand.
The number of male helpers did not affect egg size, probably because male helpers feed chicks at substantially lower rates than female helpers.
“We don’t yet fully understand why helped mothers are laying heavier ...
Ethical, environmental and political concerns about climate change affect reproductive choices
2023-11-09
People are beginning to reconsider their reproductive decisions due to complex concerns about climate change, with many choosing to forego childbearing, or reduce the number of children they have as a result, finds a new study by UCL researchers.
The research, published in PLOS Climate, is the first systematic review to explore how and why climate change-related concerns may be impacting reproductive decision-making.
The team examined 13 studies, involving 10,788 participants, which were conducted between 2012 and 2022, primarily in Global North countries ...
Photonics team develops high-performance ultrafast lasers that fit on a fingertip
2023-11-09
Lasers are essential tools for observing, detecting, and measuring things in the natural world that we can’t see with the naked eye. But the ability to perform these tasks is often restricted by the need to use expensive and large instruments.
In a newly published cover-story paper in the journal Science, researcher Qiushi Guo demonstrates a novel approach for creating high-performance ultrafast lasers on nanophotonic chips. His work centers on miniaturizing mode-lock lasers — a unique laser that emits a train of ultrashort, coherent light pulses in femtosecond intervals, which is an astonishing quadrillionth ...
Scientists flag conflicts of interest ahead of UN plastic and chemical talks
2023-11-09
An international group of 35 scientists is calling out conflicts of interest plaguing global plastic treaty negotiations and that have interfered with timely action on other health and environmental issues. They urge the implementation of strict guidelines to prevent the same problems from affecting the UN’s upcoming Science Policy Panel on chemicals. Their concerns and recommendations are outlined in a featured paper in the journal Environmental Science & Technology.
“From Big Tobacco to Big Oil, powerful industries use the same playbook to manufacture doubt and sow misinformation,” said co-author Bethanie ...
First-ever crowd-sourced small molecule discovery and a potent SARS-CoV-2 antiviral lead compound announced by COVID Moonshot Consortium
2023-11-09
The work of the COVID Moonshot Consortium is being published in the prestigious journal Science on 10 November, revealing their discovery of a potent SARS-CoV-2 antiviral lead compound. It also reflects on the success of its open science approach in launching a patent-free antiviral discovery program to rapidly develop a differentiated lead in response to a pandemic emergency. Open science discovery of potent noncovalent SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors ) DOI 10.1126/science.abo7201.
The COVID Moonshot initiative ...
Cornell chemists image basic blocks of synthetic polymers
2023-11-09
ITHACA, N.Y. -- Synthetic polymers are everywhere in our society – from nylon and polyester clothing to Teflon cookware and epoxy glue. At the molecular level, these polymers’ molecules are made of long chains of monomer building blocks, the complexity of which increases functionality in many such materials.
In particular, copolymers, which consist of different types of monomers in the same chain, allow for fine-tuning of the material’s properties, said Peng Chen, the Peter J.W. Debye Professor of Chemistry in the College of Arts and Sciences (A&S). The monomer sequence plays a critical role in a material’s properties, but scientists until ...
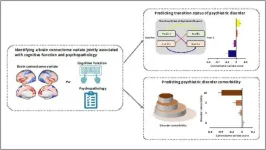
Brain imaging identifies biomarkers of mental illness
2023-11-09
Philadelphia, November 9, 2023 – Research and treatment of psychiatric disorders are stymied by a lack of biomarkers – objective biological or physiological markers that can help diagnose, track, predict, and treat diseases. In a new study, researchers use a very large dataset to identify predictive brain imaging-based biomarkers of mental illness in adolescents. The work appears in Biological Psychiatry, published by Elsevier.
Traditionally, psychiatric disorders such as depression have been diagnosed based on symptoms according to subjective assessments. The identification of biomarkers to aid in diagnosis and treatment selection would greatly advance treatments.
In ...
Cary Institute partners on $3M USDA-funded study on COVID-19 variants that could emerge from wildlife
2023-11-09
Many wild animals can carry COVID-19, including those that live among us, such as deer mice, red foxes, white-tailed deer, and more. These species may act as reservoirs, offering new opportunities for the virus to mutate and spill back into people. The omicron variant, for example, is thought to have emerged from mice.
With $3 million in federal grant funding, a new five-year research project will bring together virology, disease ecology, and artificial intelligence to better understand how SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19) behaves ...
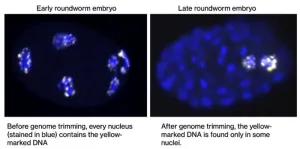
The enigma of embryonic development: How certain animals trim their genomes
2023-11-09
New research is underway to decipher a fascinating biological puzzle—how some animals can naturally discard more than half of their genetic information during embryonic development.
This radical natural phenomenon has captivated scientists for over 130 years, presenting a tantalizing question in the field of developmental biology and genetics.
Equipped with the latest in genetic engineering tools, the team at The University of Warwick is working to dissect the mechanisms behind this selective genomic editing. By uncovering the processes that allow some nematode worms to abandon up to ...
New URI lab developing adaptive technology, secures National Science Foundation grant
2023-11-09
New URI lab developing adaptive technology, secures National Science Foundation grant
Reza Abiri and Yalda Shahriari receive National Science Foundation award totaling $460,000 for work to improve stroke patient rehabilitation
Passing by Reza Abiri’s office at the University of Rhode Island, one might suspect him of nursing a serious coffee habit. A colorful collection of various mugs and cups dot his office, and though he is friendly enough to likely welcome any visitors stopping by to chat, the cups serve a larger purpose.
Abiri and Yalda Shahriari, professors in ...
MD Anderson announces Institute for Data Science in Oncology to advance mission to end cancer
2023-11-09
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center today announced the launch of its Institute for Data Science in Oncology (IDSO), which integrates the most advanced computational and data science approaches with the institution’s extensive scientific and clinical expertise to significantly improve patient’s lives by transforming cancer care and research.
Bringing top data scientists from a variety of fields together with clinicians and cancer scientists, the institute builds on MD Anderson’s culture of collaboration and connectivity to tackle the field’s most pressing needs in new and innovative ways. IDSO’s efforts have been catalyzed by philanthropic ...
Researchers decipher the mechanism by which the MAF protein promotes breast cancer metastasis
2023-11-09
The MAF protein interacts with the estrogen receptor, alters its function, and promotes the spread of cancer.
The KDM1A enzyme plays a fundamental role in the epigenetic remodelling that facilitates the function of pro-metastatic genes.
The work carried out in Dr. Roger Gomis Lab at IRB Barcelona has been published in the journal Nature Cell Biology.
Barcelona, 9 November 2023 – Breast cancer is the most common form of cancer among women, with more than 2 million new cases diagnosed each year. In cases where the tumour remains localised in the breast, survival rates are remarkably high, ...
[1] ... [1566]
[1567]
[1568]
[1569]
[1570]
[1571]
[1572]
[1573]
1574
[1575]
[1576]
[1577]
[1578]
[1579]
[1580]
[1581]
[1582]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.