Team creates synthetic enzymes to unravel molecular mysteries
2023-11-09
A University of Texas at Dallas bioengineer has developed synthetic enzymes that can control the behavior of the signaling protein Vg1, which plays a key role in the development of muscle, bone and blood in vertebrate embryos.
The team of researchers is using a new approach, called the Synthetic Processing (SynPro) system, in zebrafish to study how Vg1 is formed. By learning the molecular rules of signal formation in a developing animal, researchers aim to engineer mechanisms — such as giving cells new instructions — that could play a role in treating or preventing disease.
Dr. P.C. Dave P. Dingal, assistant professor of bioengineering in the Erik Jonsson ...
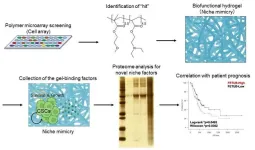
Finding your niche: A synthetic cancer stem cell microenvironment
2023-11-09
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) report the construction of a synthetic polymer biomaterial that successfully recapitulates the pancreatic adenocarcinoma microenvironment and could be used to identify novel treatment targets
Tokyo, Japan – One of the biggest challenges in biomedical research is finding a way to capture the complexity of the human body in laboratory-based techniques, to enable them to be investigated accurately. Now, researchers from Japan report an approach for precisely imitating a key feature of aggressive cancers in the laboratory.
In a study published recently in Inflammation and Regeneration, researchers from Tokyo Medical and ...
Vigorous exercise, rigorous science: What scientists learned from firefighters in training
2023-11-09
The 11 young firefighters went through a rigorous training exercise, carrying up to 40 pounds of gear over hilly terrain during a 45-minute training exercise in the California sun. Gloves, helmets, flashlights, goggles, and more weighted them down as they sprinted through the countryside wearing fire-resistant clothing to show they were ready to serve as wildland firefighters.
When the training was over, they immediately went to the medical tent—not to rest and recover but to give samples of their blood, ...
Study reveals the structure of brain waves associated with memory consolidation
2023-11-09
The reactivation of patterns of neuronal activity based on experience is crucial for learning and memory, but these patterns and the associated brain waves vary widely and are difficult to classify. Such events, dubbed ripples, are characteristic of the hippocampus, a brain region responsible for memory. Until now, the most common way to study ripples was using frequency analysis, but a project led by the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) has proposed a new classification strategy.
Using data science tools, a research group from the Instituto Cajal (IC-CSIC) headed by Liset M. de la Prida has managed to figure out the temporal structure of hippocampal ripples. The scientists ...
Reducing vitamin B5 slows breast cancer growth in mice
2023-11-09
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 16:00hrs GMT Thursday 9 November 2023
Peer reviewed
Experimental study
People and animals
Reducing vitamin B5 slows breast cancer growth in mice
A group of researchers led by the Francis Crick Institute, working with the National Physical Laboratory (NPL) and Imperial College London, have discovered that breast cancer cells expressing a cancer-driving gene heavily rely on vitamin B5 to grow and survive. The researchers are part of Cancer Grand Challenges team Rosetta, funded by Cancer Research UK.
In their research published today in Nature Metabolism, the team studied the metabolic effects of one of the major cancer-driving ...
Smell and taste function 3 years after mild COVID-19
2023-11-09
About The Study: There was a favorable evolution in smell and taste function throughout the observation period of this study, with taste dysfunction showing lower frequency and faster recovery compared with smell dysfunction in this analysis that included 88 cases and 88 controls. Recovery from smell dysfunction continued over the 3-year study period. At the 3-year study endpoint, smell dysfunction was comparable between both groups. Patients with post–COVID-19 condition exhibiting chemosensory alterations should be reassured that a recovery of smell function appears to continue over three years ...
Assessment of changes in cancer treatment during the first year of the pandemic
2023-11-09
About The Study: In this study including 3.5 million patients diagnosed with cancer, a significant deficit was noted in the number of cancer treatments provided in the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic in the U.S. Data indicated that this deficit in the number of cancer treatments provided was associated with decreases in the number of cancer diagnoses, not changes in treatment strategies.
Authors: Leticia M. Nogueira, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the American Cancer Society in Kennesaw, Georgia, is the corresponding author.
To access ...
Social-behavioral findings can be highly replicable, six-year study by four labs suggests
2023-11-09
Roughly two decades ago, a community-wide reckoning emerged concerning the credibility of published literature in the social-behavioral sciences, especially psychology. Several large scale studies attempted to reproduce previously published findings to no avail or to a much lesser magnitude, sending the credibility of the findings — and future studies in social-behavioral sciences — into question.
A handful of top experts in the field, however, set out to ...
187 new genetic variants linked to prostate cancer found in largest, most diverse study of its kind
2023-11-09
A globe-spanning scientific team has compiled the most comprehensive list of genetic variants associated with prostate cancer risk — 451 in all — through a whole-genome analysis that ranks as the largest and most diverse investigation into prostate cancer genetics yet. The research, led by the USC Center for Genetic Epidemiology, the Keck School of Medicine of USC and USC Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center, and in the United Kingdom by The Institute of Cancer Research, London, included major increases in representation ...
The autism-linked gene SYNGAP1 could impact early stages of human brain development, USC study reveals
2023-11-09
The gene SYNGAP1, the variants of which are top risk factors for Autism Apectrum Disorder (ASD), has previously unappreciated effects on the developing brain, according to a new study published in Nature Neuroscience. The study shows how disease-causing variants of SYNGAP1, thought primarily to affect synapses between mature neurons, could disrupt early development in a key region of the brain known as the cortex.
“Our findings reframe our understanding ...
Almost half of people who use drugs in rural areas were recently incarcerated
2023-11-09
New research finds that almost half of people who use illicit drugs in rural areas have been recently incarcerated.
Results from a survey of almost 3,000 people in eight rural areas nationwide who report using illicit drugs published today in the journal JAMA Network Open. The study found that 42% had been incarcerated, either in prison or local jails, in the preceding six months.
The study was conducted by researchers at Oregon Health & Science University and institutions across 10 states.
The findings suggest a prime ...
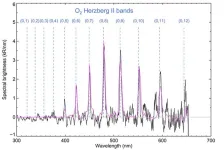
Glow in the visible range detected for the first time in the Martian night
2023-11-09
An international team led by scientists from the University of Liège has observed, for the first time in the visible range, a glow on the night side of the planet Mars. These new observations provide a better understanding of the dynamics of the upper atmosphere of the Red Planet and its variations throughout the year.
A scientific team led by researchers from the Laboratory for Planetary and Atmospheric Physics (LPAP) at the University of Liège (BE) has just observed, for the first time, lights in the night sky over Mars using the UVIS-NOMAD instrument on ...
UChicago's Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering advances lithium-metal batteries, paving the way for safer, more powerful devices
2023-11-09
The boom in phones, laptops and other personal devices over the last few decades has been made possible by the lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery, but as climate change demands more powerful batteries for electric vehicles and grid-scale renewable storage, lithium-ion technology might not be enough.
Lithium-metal batteries (LMBs) have theoretical capacities an order of magnitude greater than lithium-ion, but a more literal boom has stymied research for decades.
“A compounding challenge that further doomed the first wave of LMB commercialization in the late 1980s was their propensity to ...
Sylvester research shows how interactions between tumor genes and microenvironment influence treatment response in multiple myeloma
2023-11-09
MIAMI, FLORIDA (EMBARGOED UNTIL NOV. 9, 2023, AT 11 A.M. ET) – A multicenter study led by researchers at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine shows how interactions between tumor cells and immune components of the microenvironment can impact treatment responses and outcomes in patients newly diagnosed with multiple myeloma who undergo combination treatments that include targeted immunotherapy.
New drugs developed over the past two decades have dramatically improved survival rates, with “deep” and sustained treatment ...
Scientists caution against a reliance on mechanical devices to clear water bodies of plastic
2023-11-09
An international group of scientists has cautioned against reliance on mechanical cleanup devices as a means of addressing the plastic pollution crisis.
The researchers – comprising a number of the world’s foremost experts in plastic pollution – say they appreciate the clear and pressing need to tackle the millions of tonnes of waste that have already accumulated in the ocean and waterways.
However, they caution that plastic removal technologies used so far have shown varied efficiency in the amount of waste material they are able to collect, many have not been tested at all.
In fact, some have been shown to harm quantities of marine organisms – including ...
UTSA’s Jessica Eise wins funding to advance climate science advocacy research
2023-11-09
(San Antonio, November 9, 2023) — The National Science Foundation (NSF) has awarded Jessica Eise, an assistant professor of social and environmental challenges in the University of Texas at San Antonio Department of Communication, $425,000 for her project to explore how to create enduring change in environmental public behavior to support actions that will effectively address climate change and its impacts on society.
Despite four decades of climate change communication, the world has yet to see adequate public action and policymaker support to substantively address the challenge. Eise’s findings will empower ...
Women produce skin temperature data that are just as predictable as men
2023-11-09
Women produce physiological data that is just as predictable as men, at least when it comes to skin temperature. This might seem like common sense, but variations in body signals due to menstrual cycles, such as temperature, were used as an excuse to keep women out of clinical studies for decades.
The data for the finding was gathered from a wearable device to continuously monitor the skin temperature of 600 people, half female and half male, over six months.
The team found that there were more differences between any ...
Vanderbilt and Duke awarded Moore Foundation grant to improve oversight of AI technology in health care systems
2023-11-09
Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC) and Duke University School of Medicine have been awarded a $1.25 million grant from the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation for the project “Measuring Artificial Intelligence (AI) Maturity in Healthcare Organizations.”
Working with the Coalition for Health AI (CHAI) and the University of Iowa, a team of experts will leverage the grant to develop a maturity model framework. The project leads are Peter Embí, MD, MS, and Laurie Novak, ...
Doctoral degrees without borders
2023-11-09
Doctoral students at nine New York City area graduate engineering programs will soon be able to take courses at each other’s institutions without any additional tuition, as part of a new multi-school agreement announced today.
The Inter-University Engineering Doctoral Consortium (IUEDC), led by NYU Tandon School of Engineering, encourages Ph.D. students to complement their primary program by taking courses of interest offered at different schools, providing access to specialty instruction and expertise that may not be available at their home universities. Students should be ...
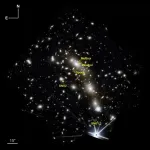
Scientists find 14 new transient objects in space by peering through the 'Christmas Tree Galaxy Cluster'
2023-11-09
An international team of scientists, led by University of Missouri’s Haojing Yan, used NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) to discover 14 new transient objects during their time-lapse study of galaxy cluster MACS0416 — located about 4.3 billion light years from Earth — which they’ve dubbed as the “Christmas Tree Galaxy Cluster.”
“Transients are objects in space, like individual stars, that appear to suddenly brighten by orders of magnitudes and then fade away,” said Yan, an associate professor in the Department ...
2023 AAAS Kavli Science Journalism Award winners named
2023-11-09
Stories about troubling aspects of science’s past as well as some hopeful signs for its future are among the winners of the 2023 AAAS Kavli Science Journalism Awards.
Presenter Adam Rutherford and producer Ilan Goodman won a Gold Award in the Audio category for a BBC series on the eugenics movement and its continuing repercussions in the modern age. Ashley Smart of Undark magazine won the Gold Award in the Science Reporting In-Depth category for a piece on the lingering impact of scientific racism, including the appropriation of legitimate genetics research for extremist ends.
On a more ...
Regenstrief experts will address national, global challenges at AMIA symposium
2023-11-09
INDIANAPOLIS -- Regenstrief Institute informaticians and other data experts will share their research insights and innovations from November 11-15 at the 2023 American Medical Informatics Association (AMIA) Annual Symposium in New Orleans, Louisiana.
Two Regenstrief researchers also were part of the leadership team that organized and helped set the agenda for the conference, “Transforming Healthcare and Biomedicine for a Sustainable Future.”
AMIA’s Annual Symposium is the premier medical informatics event, presenting leading-edge scientific research and a wide array of scientific sessions. The symposium presents work from across the spectrum of the informatics ...
Early life exposure to broccoli sprouts protects against colitis in inflammatory bowel disease
2023-11-09
Washington, D.C.—High fiber diets, like those that include broccoli sprouts or other cruciferous vegetables, may reduce disease symptoms and improve quality of life in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), according to a study conducted in mice. The study was published in mSystems, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
In the study, the investigators used a popular interleukin-10-knockout (IL-10-KO) mouse model of Crohn’s to investigate the interactions between mice and their immune systems, as well as the broccoli ...
The Paul G. Allen Frontiers Group announces Allen Discovery Center for Neuroimmune Interactions at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
2023-11-09
SEATTLE, W.A.—November 9, 2023—The Paul G. Allen Frontiers Group, a division of the Allen Institute, today announced the launch of the Allen Discovery Center (ADC) for Neuroimmune Interactions at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. The research team will comprehensively define and map the interactions between the nervous system and the immune system that take place distant from the brain, such as at the skin, lung, and gut surfaces, and analyze how these interactions relay a variety of sensations back to the brain and regulate organ physiology and tissue immune responses.
"Understanding ...
Lei Shi elected as a member of the STM Board
2023-11-09
On 16 October 2023, the newly elected STM Board Members were announced at the Annual General Meeting. Lei Shi, the Deputy Editor-in-Chief of Tsinghua University Press (TUP), and the Director of both the Journal Publishing Center and Academic Publishing Center of TUP has been elected to the designated seat representing non-Europe/US based companies. He became the first Chinese representative on the STM Board.
STM is the world’s leading association of scholarly publishers, who is committed to advance trusted research for ...
[1] ... [1567]
[1568]
[1569]
[1570]
[1571]
[1572]
[1573]
[1574]
1575
[1576]
[1577]
[1578]
[1579]
[1580]
[1581]
[1582]
[1583]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.