New, almost non-destructive archaeogenetic sampling method developed
2021-05-05
An Austrian-American research team (University of Vienna, Department Evolutionary Anthropology and Harvard Medical School, Department of Genetics), in collaboration of Hungarian experts from Eötvös Loránd University, has developed a new method that allows the almost non-destructive extraction of genetic material from archaeological human remains. The method allows anthropologists, archaeologists and archaeogeneticists to avoid the risk of serious damage to artefacts of significant scientific and heritage value, which can then be fully examined in future research.
Bioarcheological ...
Depression part of daily life for many Black Canadians
2021-05-05
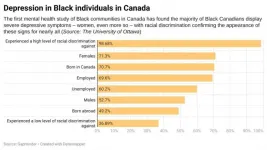
The first mental health study of Black communities in Canada has found the majority of Black Canadians display severe depressive symptoms - women, even more so - with racial discrimination confirming the appearance of these signs for nearly all.
The study, published in Depression and Anxiety, discovered nearly two-thirds (65.87 percent) of surveyed participants reported severe depressive symptoms. Higher rates were found among women; those who are employed; those born in Canada; and nearly all who have been experienced high racial discrimination.
"Rates of depressive symptoms among Black individuals are nearly six times the 12-month prevalence reported for the general population in Canada," says ...
Rapid rovers, speedy sands: fast-tracking terrain interaction modeling
2021-05-05
Granular materials, such as sand and gravel, are an interesting class of materials. They can display solid, liquid, and gas-like properties, depending on the scenario. But things can get complicated in cases of high-speed vehicle locomotion, which cause these materials to enter a "triple-phase" nature, acting like all three fundamental phases of matter at the same time.
As reported in the April 23, 2021 issue of the journal Science Advances, a team of engineers and physicists from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and Georgia Institute ...
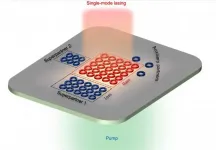
Supersymmetry-inspired microlaser arrays pave way for powering chip-sized optical systems
2021-05-05
The field of photonics aims to transform all manner of electronic devices by storing and transmitting information in the form of light, rather than electricity. Beyond light's raw speed, the way that information can be layered in its various physical properties makes devices like photonic computers and communication systems tantalizing prospects.
Before such devices can go from theory to reality, however, engineers must find ways of making their light sources -- lasers -- smaller, stronger and more stable. Robots and autonomous vehicles that use LiDAR for optical sensing and ranging, manufacturing and material ...
Dark matter detection
2021-05-05
Scientists are certain that dark matter exists. Yet, after more than 50 years of searching, they still have no direct evidence for the mysterious substance.
University of Delaware's Swati Singh is among a small group of researchers across the dark matter community that have begun to wonder if they are looking for the right type of dark matter.
"What if dark matter is much lighter than what traditional particle physics experiments are looking for?" said Singh, an assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering at UD.
Now, Singh, Jack Manley, a UD doctoral student, and collaborators at ...
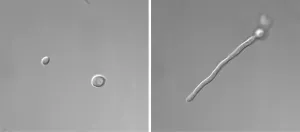
From yeast to hypha: How Candida albicans makes the switch
2021-05-05
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- You might call Candida albicans a shape-shifter: As this fungus grows, it can multiply as single, oval-shaped cells called yeast or propagate in an elongated form called hypha, consisting of thread-like filaments.
This dual nature can help the pathogen survive in the body, where it can cause disease, including dangerous hospital-acquired infections.
But how does this switching ability occur?
New research identifies one factor that may contribute. In a study that will be published on May 5 in the journal mSphere, University at Buffalo biologists Guolei Zhao and Laura Rusche report that a protein called Sir2 may facilitate C. albicans' transition from ovoid yeast ...
New ultrasound technique detects fetal circulation problems in placenta
2021-05-05
WHAT:
A team of researchers funded by the National Institutes of Health has developed a new ultrasound technique to monitor the placenta for impaired fetal blood flow early in pregnancy. The technique, which uses conventional ultrasound equipment, relies on subtle differences in the pulsation of fetal blood through the arteries at the fetal and placental ends of the umbilical cord, potentially enabling physicians to identify placental abnormalities that impair fetal blood flow and, if necessary, deliver the fetus early. Like current ultrasound techniques, the new technique can also detect impaired flow of maternal blood through the placenta.
The study was conducted by John G. Sled, Ph.D., of The Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto, ...
New imaging technique captures how brain moves in stunning detail, holds diagnostic potential
2021-05-05
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) images are usually meant to be static. But now, researchers from Mātai Medical Research Institute (Mātai), Stevens Institute of Technology, Stanford University, the University of Auckland and other institutions, report on an imaging technique that captures the brain in motion in real time, in 3D and in stunning detail, providing a potential diagnostic tool for detecting difficult-to-spot conditions such as obstructive brain disorders and aneurysms - before they become life threatening.
The new technique, called 3D amplified ...
How a Yale scientist and REM star named an ant for a Warhol 'Superstar'
2021-05-05
The ant came in a small vial of ethanol, sealed in a plastic bag, and packed in a small cardboard box. It was addressed to Yale's Douglas B. Booher.
German entomologist Phillip Hoenle had discovered the ant, which he noted had some peculiar features, in a rain forest in Ecuador. Now he wanted Booher, a research associate in the Yale Center for Biodiversity and Global Change and the Department of Ecology & Evolutionary Biology, to confirm whether this trap ant was truly a new species. If so, Hoenle and Booher would have the honor of naming it.
Booher had imagined ...
Crohn's disease patients have specific IgG antibodies to human bacterial flagellins
2021-05-05
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. - Last year, Charles O. Elson, M.D., demonstrated a potential preventive treatment for Crohn's disease, a form of inflammatory bowel disease. He used a mouse model that included immune-reactive T cells from patients with Crohn's disease in a flagellin peptide-specific immunotherapy. This study provided proof-of-principle that a flagellin-directed immunotherapy might provide similar benefits in patients.
Now University of Alabama at Birmingham researchers have moved a step closer to possible clinical testing of this treatment, say Elson and co-first authors Katie Alexander, Ph.D., ...
Cardiovascular disease could be diagnosed earlier with new glowing probe
2021-05-05
Researchers have created a probe that glows when it detects an enzyme associated with issues that can lead to blood clots and strokes.
The team of researchers, from the Department of Chemistry and the National Lung and Heart Institute at Imperial College London, demonstrated that their probe quickly and accurately detects the enzyme in modified E. Coli cells.
They are now expanding this proof-of-concept study, published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society and funded by the British Heart Foundation (BHF), with the hope of creating rapid tests for cardiovascular problems and a new way to track long-term conditions.
The build-up of plaque in the arteries - known as atherosclerosis - can lead to coronary artery ...
Research confirms trawl ban substantially increases the abundance of marine organisms
2021-05-05
Biodiversity is of crucial importance to the marine ecosystem. The prohibition of trawling activities in the Hong Kong marine environment for two and a half years has significantly improved biodiversity, an inter-university study led by City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has found. Research results showed that the trawl ban could restore and conserve biodiversity in tropical coastal waters.
The research team was led by Professor Kenneth Leung Mei-yee, CityU's Director of the State Key Laboratory of Marine Pollution (SKLMP) and Chair Professor in the Department ...
Magnetic material invented by Irish scientists breaks super-fast switching record
2021-05-05
Researchers at CRANN (The Centre for Research on Adaptive Nanostructures and Nanodevices), and the School of Physics at Trinity College Dublin, today announced that a magnetic material developed at the Centre demonstrates the fastest magnetic switching ever recorded.
The team used femtosecond laser systems in the Photonics Research Laboratory at CRANN to switch and then re-switch the magnetic orientation of their material in trillionths of a second, six times faster than the previous record, and a hundred times faster than the clock speed of a personal computer.
This discovery demonstrates the potential of the material for a new generation of energy efficient ultra-fast computers and data storage systems.
The researchers ...
The oldest human burial in Africa
2021-05-05
Despite being home to the earliest signs of modern human behaviour, early evidence of burials in Africa are scarce and often ambiguous. Therefore, little is known about the origin and development of mortuary practices in the continent of our species' birth. A child buried at the mouth of the Panga ya Saidi cave site 78,000 years ago is changing that, revealing how Middle Stone Age populations interacted with the dead.
Panga ya Saidi has been an important site for human origins research since excavations began in 2010 as part of a long-term partnership between archaeologists from the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human ...
New modeling of Antarctic ice shows unstoppable sea level rise if Paris targets overshot
2021-05-05
AMHERST, Mass. - The world is currently on track to exceed three degrees Celsius of global warming, and new research led by the University of Massachusetts Amherst's Rob DeConto, co-director of the School of Earth & Sustainability, shows that such a scenario would drastically accelerate the pace of sea-level rise by 2100. If the rate of global warming continues on its current trajectory, we will reach a tipping point by 2060, past which these consequences would be "irreversible on multi-century timescales."
The new paper, published today in Nature, models the impact of several different warming scenarios on the Antarctic Ice Sheet, including the Paris Agreement target of two degrees Celsius of warming, an aspirational 1.5 degree scenario, ...
Artificial intelligence system may improve diagnosis of complicated metastatic cancers
2021-05-05
In 1 to 2 percent of cancer cases, the primary site of tumor origin cannot be determined. Because many modern cancer therapeutics target primary tumors, the prognosis for a cancer of unknown primary (CUP) is poor, with a median overall survival of 2.7-to-16 months. In order to receive a more specific diagnosis, patients often must undergo extensive diagnostic workups that can include additional laboratory tests, biopsies and endoscopy procedures, which delay treatment. To improve diagnosis for patients with complex metastatic cancers, especially those in low-resource settings, researchers from the Mahmood Lab at the Brigham and Women's Hospital developed an artificial intelligence (AI) system that uses routinely acquired histology slides to accurately find the origins of metastatic ...
Catastrophic sea-level rise from Antarctic melting possible with severe global warming
2021-05-05
The Antarctic ice sheet is much less likely to become unstable and cause dramatic sea-level rise in upcoming centuries if the world follows policies that keep global warming below a key END ...
How mitochondria make the cut
2021-05-05
Mitochondria either split in half to multiply within the cell, or cut off their ends to get rid of damaged material. That's the take-away message from EPFL biophysicists in their latest research investigating mitochondrial fission. It's a major departure from the classical textbook explanation of the life cycle of this well-known organelle, the powerhouse of the cell. The results are published today in Nature.
"Until this study, it was poorly understood how mitochondria decide where and when to divide," says EPFL biophysicist Suliana Manley and senior author of the study.
The big question : regulating mitochondrial fission
Mitochondrial fission is important for the proliferation of mitochondria, which is fundamental for cellular growth. As a cell gets bigger, ...
Africa's oldest human burial site uncovered
2021-05-05
The discovery of the earliest human burial site yet found in Africa, by an international team including several CNRS researchers1, has just been announced in the journal Nature. At Panga ya Saidi, in Kenya, north of Mombasa, the body of a three-year-old, dubbed Mtoto (Swahili for 'child') by the researchers, was deposited and buried in an excavated pit approximately 78,000 years ago. Through analysis of sediments and the arrangement of the bones, the research team showed that the body had been protected by being wrapped in a shroud made of perishable material, and that the head had likely rested on an object also of perishable material. Though there are no signs of offerings or ochre, both common at more recent burial ...
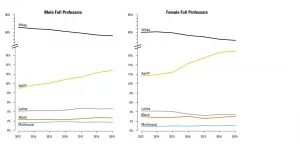
Black and Latinx surgeons continue to hit glass ceiling in America
2021-05-05
Among the upper echelons of academic surgery, Black and Latinx representation has remained flat over the past six years, according to a study published today in JAMA Surgery by researchers at Virginia Commonwealth University Massey Cancer Center and University of Florida Health.
The study tracked trends across more than 15,000 faculty in surgery departments across the U.S. between 2013-2019. Although the data revealed modest diversity gains among early-career faculty during this period, especially for Black and Latina women, the percentage of full professors and department chairs identifying as Black or Latinx continued to hover in the single digits. ...
Biologists discover a trigger for cell extrusion
2021-05-05
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- For all animals, eliminating some cells is a necessary part of embryonic development. Living cells are also naturally sloughed off in mature tissues; for example, the lining of the intestine turns over every few days.
One way that organisms get rid of unneeded cells is through a process called extrusion, which allows cells to be squeezed out of a layer of tissue without disrupting the layer of cells left behind. MIT biologists have now discovered that this process is triggered when cells are unable to replicate their DNA during cell division.
The researchers discovered this mechanism in the worm C. elegans, and they showed that ...
Medicaid enrollment during COVID-19 pandemic
2021-05-05
What The Study Did: This study analyzed changes in Medicaid enrollment for all 50 states and the District of Columbia during the first nine months of last year during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Authors: Peggah Khorrami, M.P.H., of the Harvard T.H.Chan School of Public Health in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.9463)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other ...
Stem cells create early human embryo structure in advance for fertility research
2021-05-05
Exeter scientists have discovered a simple, efficient way to recreate the early structure of the human embryo from stem cells in the laboratory. The new approach unlocks news ways of studying human fertility and reproduction.
Stem cells have the ability to turn into different types of cell. Now, in research published in Cell Stem Cell and funded by the Medical Research Council, scientists at the University of Exeter's Living Systems Institute, working with colleagues from the University of Cambridge, have developed a method to organise lab-grown stem cells into an accurate model of the first stage of human embryo development.
The ability to create artificial ...
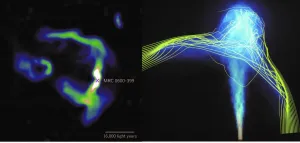
A new window to see hidden side of magnetized universe
2021-05-05
New observations and simulations show that jets of high-energy particles emitted from the central massive black hole in the brightest galaxy in galaxy clusters can be used to map the structure of invisible inter-cluster magnetic fields. These findings provide astronomers with a new tool for investigating previously unexplored aspects of clusters of galaxies.
As clusters of galaxies grow through collisions with surrounding matter, they create bow shocks and wakes in their dilute plasma. The plasma motion induced by these activities can drape intra-cluster magnetic ...
Fast changing smells can teach mice about space
2021-05-05
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and UCL (University College London) have found that mice can sense extremely fast and subtle changes in the structure of odours and use this to guide their behaviour. The findings, published in Nature today (Wednesday), alter the current view on how odours are detected and processed in the mammalian brain.
Odour plumes, like the steam off a hot cup of coffee, are complex and often turbulent structures, and can convey meaningful information about an animal's surroundings, like the movements of a predator or the location of food sources. But it has previously been assumed that mammalian brains can't fully process these temporal ...
[1] ... [2344]
[2345]
[2346]
[2347]
[2348]
[2349]
[2350]
[2351]
2352
[2353]
[2354]
[2355]
[2356]
[2357]
[2358]
[2359]
[2360]
... [8813]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.