Abortion opposition related to beliefs about fetal pain perception
2021-05-13
A person's stance on abortion is linked to their, often inaccurate, belief about when a fetus can feel pain, a University of Otago study has found.
Lead author Emma Harcourt, PhD candidate in Otago's Centre for Science Communication, says misinformation about abortion and pregnancy is common and potentially harmful.
"The current medical consensus is that it is unlikely that fetal pain perception is possible before the 29th or 30th weeks of pregnancy. However, we found that most people believe that the capacity to feel pain develops much earlier and that this was particularly evident in participants with anti-abortion views," she says.
The study, published in The Australian and New Zealand Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, recruited 374 ...
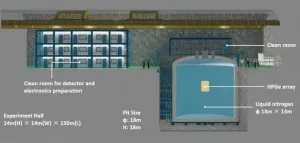
CDEX listens to the sound of cosmology from a laboratory deep underground
2021-05-13
Numerous compelling evidences from astroparticle physics and cosmology indicate that the major matter component in the Universe is dark matter, accounting for about 85% with the remaining 15% is the ordinary matter. Nevertheless, people still know little about the dark matter, including its mass and other properties. Many models predict dark matter particles could couple to ordinary particle at weak interaction level, so it is possible to capture the signal of dark matter particle in the direct detection experiment. The scientific goals of the China ...
Ankle and foot bone evolution gave prehistoric mammals a leg up
2021-05-13
The evolution of ankle and foot bones into different shapes and sizes helped mammals adapt and thrive after the extinction of the dinosaurs, a study suggests.
A surge of evolution following the mass extinction 66 million years ago enabled mammals to diversify and prosper during a period of major global change, researchers say.
Analysis of bones that form part of the ankle and the heel of the foot reveal that mammals during this time - the Paleocene Period - were less primitive than previously thought.
Palaeontologists from the University of Edinburgh made the discovery by comparing the anatomy of Paleocene mammals with species from the earlier Cretaceous ...
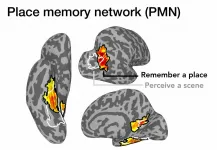
New study reveals where memories of familiar places are stored in the brain
2021-05-13
As we move through the world, what we see is seamlessly integrated with our memory of the broader spatial environment. How does the brain accomplish this feat? A new study from Dartmouth College reveals that three regions of the brain in the posterior cerebral cortex, which the researchers call "place-memory areas," form a link between the brain's perceptual and memory systems. The findings are published in Nature Communications.
"As we navigate our surroundings, information enters the visual cortex and somehow ends up as knowledge of where we are - the question is where this transformation into spatial ...
Ion-selective smart porous membranes
2021-05-13
A research group has developed an ion-selective smart porous membrane that can respond to outer stimuli, potentially paving the way for new applications in molecular separation and sensing applications.
Porous thin films have attracted the attention of scientists because of their potential use in sensors, energy harvesting, and ion/molecular separation.
Nanostructure properties, such as pore size, thickness, and film density, affect molecular selectivity and molecular permeability. Surface properties also have a significant impact on molecular selectivity.
Thus it is important to be able to control both the 3D nanostructures and surface properties of ultrathin porous films.
Previous research shed light on smart porous membranes, which are covered with molecules that can respond ...
Eating more fruit and vegetables linked to less stress - study
2021-05-13
Eating a diet rich in fruit and vegetables is associated with less stress, according to new research from Edith Cowan University (ECU).
The study examined the link between fruit and vegetable intake and stress levels of more than 8,600 Australians aged between 25 and 91 participating in the Australian Diabetes, Obesity and Lifestyle (AusDiab) Study from Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute.
The findings revealed people who ate at least 470 grams of fruit and vegetables daily had 10 per cent lower stress levels than those who consumed less than 230 grams. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends ...
Snakes alive? We're totally fine with them -- just not at our house
2021-05-13
Arizona! The sunsets. The saguaros. The snakes.
All of them are part of life in the sunny Southwest, but keeping cool when the latter is holed up in a golf bag, air compressor or swimming pool pump house is a big ask for a lot of people.
Not as big as you'd think, however.
The first study to analyze snake removals in a social-ecological context was recently published by an Arizona State University conservation biologist working with a local rattlesnake removal company.
"I think one of the surprises was that people don't hate snakes," said researcher Heather Bateman of the College of Integrative Sciences and Arts. "A lot of them responded that the snakes are important to the desert ecosystem and the snake belongs ...
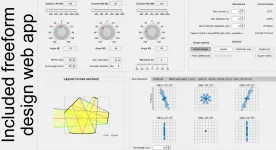
Freeform imaging systems: Fermat's principle unlocks 'first time right' design
2021-05-13
Optical imaging systems have been playing an essential role in scientific discovery and societal progress for several centuries. For more than 150 years scientists and engineers have used aberration theory to describe and quantify the deviation of light rays from ideal focusing in an imaging system. Until recently most of these imaging systems included spherical and aspherical refractive lenses or reflective mirrors or a combination of both. With the introduction of new ultra-precision manufacturing methods, it has become possible to fabricate lenses and mirrors that lack the common translational or ...
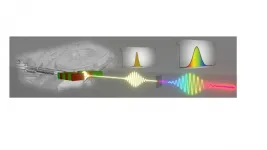
Non-linear optics meets X-rays
2021-05-13
The relevance for radiology applications is probably the most known advantage of X-ray beams (keV energies) with respect to visible radiation (eV energies) and can be traced back to their superior penetration depth. On a more fundamental ground, however, the relevance of this photon energy range relies on the capability of probing inner shell electrons (as they have comparable binding energies) and mapping molecular structures on the atomic-scale (as typical interatomic spacings are comparable to X-ray wavelengths). Building on such capabilities, large efforts have been devoted by the scientific community to develop X-ray sub-picosecond sources able to access matter properties with a time resolution sufficient to access elemental molecular motions. Free electron lasers (FEL), nowadays available ...
Scientists show how to attack the 'fortress' surrounding pancreatic cancer tumors
2021-05-13
UNSW medical researchers have found a way to starve pancreatic cancer cells and 'disable' the cells that block treatment from working effectively. Their findings in mice and human lab models - which have been 10 years in the making and are about to be put to the test in a human clinical trial - are published today in Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
"Pancreatic cancer has seen minimal improvement in survival for the last four decades - and without immediate action, it is predicted to be the world's second biggest ...
Pandemic stigma: Foreigners, doctors wrongly targeted for COVID-19 spread in India
2021-05-13
The Indian public blamed foreigners, minority groups and doctors for the rapid spread of COVID-19 across the country during the first wave, due to misinformation, rumour and long-held discriminatory beliefs, according to an international study led by Monash University.
This resulted in people refusing to get tested for fear of humiliation or public reprisals, which included attacks on Muslims and health care workers.
However, when presented with accurate and reliable information about the virus spread, the Indian public back-pedalled on those negative sentiments and were more likely to get tested and seek medical help, highlighting the importance of health advice from credible sources.
A ...
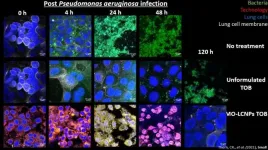
Novel nanotech improves cystic fibrosis antibiotic by 100,000-fold
2021-05-13
World-first nanotechnology developed by the University of South Australia could change the lives of thousands of people living with cystic fibrosis (CF) as groundbreaking research shows it can improve the effectiveness of the CF antibiotic Tobramycin, increasing its efficacy by up to 100,000-fold.
The new technology uses a biomimetic nanostructured material to augment Tobramycin - the antibiotic prescribed to treat chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infections in severe cases of CF - eradicating the infection in as little as two doses.
In Australia, cystic fibrosis (CF) affects one in 2500 babies - or one baby born every four days - causing severe impairments to a person's ...
Study: Obesity slows progress against cancer deaths
2021-05-13
Cancer death rates have fallen dramatically in the United States, but factor in obesity, as researchers did at the University of North Carolina Gillings School of Global Public Health, and the picture changes.
In a study published May 10 in JAMA Network Open, researchers showed that obesity-related cancer deaths are improving, but at a slowing pace.
Based on mortality data for 50 million people, deaths from cancers not associated with obesity -- that's lung cancer and skin cancer, among others - are declining at a rate almost three times faster than cancers linked to obesity, such as stomach, colorectal, uterine, thyroid and postmenopausal breast cancer.
"These are cancers where we could see even larger mortality improvements with creative and practical tools to combat ...
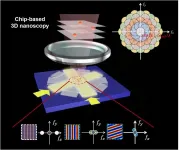
Can the diffraction limit overcome in the linear imaging system?
2021-05-13
Compared with the superresolution microscopy that bases on squeezing the point spread function in the spatial domain, the superresolution microscopy that broadens the detection range in the spatial frequency domain through the spatial-frequency-shift (SFS) effect shows intriguing advantages including large field of view, high speed, and good modularity, owing to its wide-field picture acquisition process and universal implementation without using special fluorophores labeling.
To enable spatial-frequency-shift microscopy with a superresolution at the subwavelength scale, it is essential to use the near-field evanescent wave with a larger wave vector than the far-field propagation wave for illumination, which can be built on the integrated photonics, paving the way for compact ...
A new polarized fluorescent probe for revealing architectural dynamics of living cells
2021-05-13
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU), collaborating with scientists from the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) and RIKEN, develop a novel technique for live-cell fluorescent imaging which leads them to discover a new actin structure in starfish early embryos.
Tokyo, Japan - Monitoring alignments of the building blocks of cells is important to understand how the cells are built. By collaborating with imaging scientists at the MBL, researchers from Japan have developed a new probe which they call POLArIS, allowing real-time imaging of molecular orientations in live cells.
A fluorophore emits polarized light as it glows. The orientation of polarized fluorescence ...
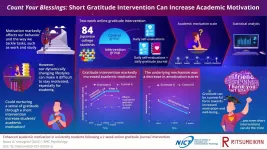
Count your blessings: Short gratitude intervention can increase academic motivation
2021-05-13
It is difficult for us to succeed in whatever we set out to do if we lack motivation. We usually need it as a driving force to achieve both short- and long-term goals, from household chores to getting a degree. However, because of the ongoing pandemic, our lifestyles have been subjected to drastic and dynamic changes, and many work- and study-related activities are now carried out online exclusively. This, among other complex factors, have made it difficult for some people to stay focused and motivated, and psychology researchers are trying to find effective and widely applicable solutions to address such problems.
In a END ...
Dental procedures during pandemic are no riskier than a drink of water
2021-05-13
COLUMBUS, Ohio - A new study's findings dispel the misconception that patients and providers are at high risk of catching COVID-19 at the dentist's office.
SARS-CoV-2 spreads mainly through respiratory droplets, and dental procedures are known to produce an abundance of aerosols - leading to fears that flying saliva during a cleaning or a restorative procedure could make the dentist's chair a high-transmission location.
Ohio State University researchers set out to determine whether saliva is the main source of the spray, collecting samples from personnel, equipment and other surfaces reached by aerosols during a range ...
Health effects of prenatal exposure to 1994 genocide against the Tutsi in Rwanda
2021-05-13
Twenty-seven years ago, more than 1 million Rwandans were killed during the genocide against the Tutsi in Rwanda from April 7 to July 4, 1994. It is estimated that 100,000 to 250,000 women were raped during the 100-day genocide, and that 10,000 children were born as a result. A new study finds that Rwandans who were conceived by mothers who survived the 1994 genocide against the Tutsi have poorer adult health outcomes than those who were conceived by Rwandan mothers living outside the country at that time. In addition, those who were conceived through genocidal rape have poorer adult health ...
Obesity during adolescence linked to increased risk of stroke as an adult
2021-05-13
DALLAS, May 13, 2021 -- Higher body mass index (BMI) in adolescence is associated with a significantly higher risk of first ischemic stroke in adults under age 50 regardless of whether they had Type 2 diabetes, according to new research published today in Stroke, a journal of the American Stroke Association, a division of the American Heart Association.
While rates of adolescent obesity and stroke among adults under the age of 50 years continue to rise around the world, the precise link between the two conditions is still not fully understood.
"Adults who survive stroke earlier in life face poor functional outcomes, which can lead to unemployment, depression and anxiety," said study co-author Gilad Twig, M.D., M.P.H., Ph.D., an ...
Largest-ever study of artificial insemination in sharks--and the occasional 'virgin birth'
2021-05-13
It's a tough time to be a shark. Pollution, industrialized fishing, and climate change threaten marine life, and the populations of many top ocean predators have declined in recent years. In addition to studying sharks in the wild, scientists working to save sharks rely on ones living in zoos and aquariums so that they can help build breeding programs and learn more about the conditions sharks need to thrive. One important way the scientists do that is by playing matchmakers to the sharks, pairing up individuals in ways that increase genetic diversity. In a new study in Scientific Reports, scientists undertook the largest-ever effort to artificially inseminate sharks.Their work resulted in 97 new baby sharks, ...
Orangutan finding highlights need to protect habitat
2021-05-13
Wild orangutans are known for their ability to survive food shortages, but scientists have made a surprising finding that highlights the need to protect the habitat of these critically endangered primates, which face rapid habitat destruction and threats linked to climate change.
Scientists found that the muscle mass of orangutans on the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia was significantly lower when less fruit was available. That's remarkable because orangutans are thought to be especially good at storing and using fat for energy, according a Rutgers-led study in the journal Scientific Reports.
The findings highlight ...
Life may have become cellular by using unusual molecules
2021-05-13
All modern life is composed of cells, from single-celled bacteria to more complex organisms such as humans, which may contain billions or even trillions of cells, but how life came to be cellular remains uncertain. New research led by specially appointed assistant professor Tony Z. Jia at the Earth-Life Science Institute (ELSI) at Tokyo Institute of Technology, along with colleagues from around the world (Japan, Malaysia, France, Czech Republic, India and the USA), shows that simple chemical compounds known as hydroxy acids, which were likely common on primitive Earth, spontaneously link together ...
Scientists find molecular patterns that may help identify extraterrestrial life
2021-05-13
Scientists have begun the search for extraterrestrial life in the Solar System in earnest, but such life may be subtly or profoundly different from Earth-life, and methods based on detecting particular molecules as biosignatures may not apply to life with a different evolutionary history. A new study by a joint Japan/US-based team, led by researchers at the Earth-Life Science Institute (ELSI) at the Tokyo Institute of Technology, has developed a machine learning technique which assesses complex organic mixtures using mass spectrometry to reliably classify them as biological or abiological.
In season 1, episode 29 ("Operation: Annihilate!") of Star Trek, which aired in 1966, the human-Vulcan hybrid character ...
Congestion pricing could shrink car size
2021-05-13
PULLMAN, Wash. - Rush hour will likely return when pandemic lockdowns lift, but a new study suggests that congestion pricing--policies that charge tolls for driving during peak hours--could not only cure traffic jams but also convince motorists it is safe to buy smaller, more efficient cars.
Researchers from Washington State University and the Brookings Institution studied a sample of nearly 300 households in the Seattle area over a six-year period, finding that the more congested their commutes, the more likely they would buy bigger cars which they perceive as safer and more ...
Study finds that obesity drug semaglutide supresses appetite, food cravings and energy intake
2021-05-13
New research presented at this year's European Congress on Obesity (held online, 10-13 May) shows that the obesity drug semaglutide reduces appetite, food cravings and energy intake in people given a meal where they could eat as much as they liked. The study is by Dr Dorthe Skovgaard, Novo Nordisk A/S (the manufacturer of the drug), Søborg, Denmark, and colleagues.
Semaglutide, in the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogue drug class, is currently available at the dose of 1.0 mg injected once weekly for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and is under development for chronic weight management at the dose ...
[1] ... [2340]
[2341]
[2342]
[2343]
[2344]
[2345]
[2346]
[2347]
2348
[2349]
[2350]
[2351]
[2352]
[2353]
[2354]
[2355]
[2356]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.