Researchers suggest pathway for improving stability of next-generation solar cells
2021-05-14
Scientists have uncovered the exact mechanism that causes new solar cells to break down, and suggest a potential solution.
Solar cells harness energy from the Sun and provide an alternative to non-renewable energy sources like fossil fuels. However, they face challenges from costly manufacturing processes and poor efficiency - the amount of sunlight converted to useable energy.
Perovskites are materials developed for next-generation solar cells. Although perovskites are more flexible cheaper to make than traditional silicon-based solar panels and deliver similar efficiency, perovskites ...
Researchers pinpoint possible way to prevent permanent hearing loss caused by cancer drug
2021-05-14
University of Alberta scientists have identified a receptor in cells that could be key to preventing permanent hearing loss in childhood cancer survivors who are being treated with the drug cisplatin. The researchers believe by inhibiting the receptor, they may be able to eliminate toxic side-effects from the drug that cause the hearing loss.
Cisplatin is an incredibly effective chemotherapeutic when it comes to treating solid tumours in children, contributing to an 80 per cent overall survival rate over five years, according to U of A researcher Amit Bhavsar, an assistant professor in the Department of Medical Microbiology & Immunology. The problem ...
Access to overdose-reversing drugs declined during pandemic, researchers find
2021-05-14
Boston - While overall emergency department visits have decreased during the pandemic, nonfatal opioid overdose visits have more than doubled. However, few patients who overdosed on opioids had received a prescription for naloxone, a medication designed to block the effects of opioids on the brain and rapidly reverse opioid overdose.
In a new study, clinician-researchers at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) analyzed naloxone prescription trends during the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States and compared them to trends in opioid prescriptions and to overall prescriptions. The team's findings, published in the journal JAMA Health Forum, suggest patents with opioid misuse disorders may be experiencing a dangerous decrease in access to the overdose-reversing ...
New research optimizes body's own immune system to fight cancer
2021-05-14
A groundbreaking study led by engineering and medical researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how engineered immune cells used in new cancer therapies can overcome physical barriers to allow a patient's own immune system to fight tumors. The research could improve cancer therapies in the future for millions of people worldwide.
The research is published in Nature Communications, a peer-reviewed, open access, scientific journal published by Nature Research.
Instead of using chemicals or radiation, immunotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that helps the patient's immune system fight cancer. T cells are a type of white ...
Sensors developed at URI can identify threats at the molecular level
2021-05-14
KINGSTON, R.I. - May 14, 2021 - We are frequently reminded of how vulnerable our health and safety are to threats from nature or those who wish to harm us.
New sensors developed by Professor Otto Gregory, of the College of Engineering at the University of Rhode Island, and chemical engineering doctoral student Peter Ricci, are so powerful that they can detect threats at the molecular level, whether it's explosive materials, particles from a potentially deadly virus or illegal drugs entering the country.
"This is potentially life-saving technology," said Gregory. "We have detected ...
Artificial intelligence identifies the tiger mosquito from photos in the Mosquito Alert
2021-05-14
Researchers from Mosquito Alert (who belong to CEAB-CSIC, CREAF and UPF) together with researchers from the University of Budapest have shown that an artificial intelligence algorithm is capable of recognizing the tiger mosquito (Aedes albopictus) in the photos sent by Mosquito Alert users.
The results of the study published in Scientific Reports have been obtained by applying deep learning technology or deep learning, an aspect of artificial intelligence that seeks to emulate the way of learning of humans and that has previously been used in the health field to interpret ...
Few realistic scenarios left to limit global warming to 1.5°C
2021-05-14
Of the over 400 climate scenarios assessed in the 1.5°C report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), only around 50 scenarios avoid significantly overshooting 1.5°C. Of those only around 20 make realistic assumptions on mitigation options, for instance the rate and scale of carbon removal from the atmosphere or extent of tree planting, a new study shows. All 20 scenarios need to pull at least one mitigation lever at "challenging" rather than "reasonable" levels, according to the analysis. Hence the world faces a high degree of risk of overstepping the 1.5°C limit. The realistic window for meeting the 1.5°C target is very rapidly closing.
If all climate mitigation levers are pulled, it may still be possible ...
Researchers develop first-in-class inhibitors against key leukemia protein
2021-05-14
The protein made by the ASH1L gene plays a key role in the development of acute leukemia, along with other diseases. The ASH1L protein, however, has been challenging to target therapeutically.
Now a team of researchers led by Jolanta Grembecka, Ph.D., and Tomasz Cierpicki, Ph.D., from the University of Michigan has developed first-in-class small molecules to inhibit ASH1L's SET domain -- preventing critical molecular interactions in the development and progression of leukemia.
The team's findings, which used fragment-based screening, followed by medicinal chemistry and a structure-based design, appear in Nature Communications.
In mouse models of mixed lineage leukemia, the lead compound, known as AS-99, successfully reduced leukemia progression.
"This ...
Emergence of a new heteronanostructure library
2021-05-14
Organizing functional objects in a complex, sophisticated architecture at the nanoscale can yield hybrid materials that tremendously outperform their solo objects, offering exciting routes towards a spectrum of applications. The development in synthetic chemistry over past decades has enabled a library of hybrid nanostructures, such as core-shell, patchy, dimer, and hierarchical/branched ones.
Nevertheless, the material combinations of these non-van der Waals solids are largely limited by the rule of lattice-matched epitaxy.
A research team led by professor YU Shuhong at the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) has reported a new class of heteronanostructures they ...
The mechanism of action of genes with high mutation frequency in cancer
2021-05-14
After the p53 tumour suppressor gene, the genes most frequently found mutated in cancer are those encoding two proteins of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodelling complex. This complex's function is to "accommodate" the histones that cover the DNA of the chromosomes so that the processes of transcription, DNA repair and replication or chromosome segregation can occur, as appropriate. A group from the University of Seville has demonstrated at CABIMER that the inactivation of BRG1, the factor responsible for the enzymatic activity of the SWI/SNF complexes, leads to high genetic instability, a characteristic common to the vast majority of tumours.
This study's most important contribution is that it deciphers the mechanism by which this occurs. The SWI/SNF complex ...
Yoga and breathing exercises aid children with ADHD to focus
2021-05-14
Yoga and breathing exercises have a positive effect on children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). After special classes, children improve their attention, decrease hyperactivity, they do not get tired longer, they can engage in complex activities longer. This is the conclusion reached by psychologists at Ural Federal University who studied the effect of exercise on functions associated with voluntary regulation and control in 16 children with ADHD aged six to seven years. The results of the study are published in the journal Biological Psychiatry.
"For children with ADHD, as a rule, the part of the brain that is responsible ...
Lockdown led to positive lifestyle changes in older people
2021-05-14
The COVID-19 lockdown was a catalyst for many older people to embrace technology, reconnect with friends and build new relationships with neighbours, according to University of Stirling research.
Understanding the coping mechanisms adopted by some over 60s during the pandemic will play a key role in developing interventions to help tackle loneliness, isolation and wellbeing in the future.
The study, led by the Faculty of Health Sciences and Sport, surveyed 1,429 participants - 84 percent (1,198) of whom were over 60 - and found many had adapted to video conferencing technology to increase ...
Solar wind from the center of the Earth
2021-05-14
High-precision noble gas analyses indicate that solar wind particles from our primordial Sun were encased in the Earth's core over 4.5 billion years ago. Researchers from the Institute of Earth Sciences at Heidelberg University have concluded that the particles made their way into the overlying rock mantle over millions of years. The scientists found solar noble gases in an iron meteorite they studied. Because of their chemical composition, such meteorites are often used as natural models for the Earth's metallic core.
The rare class of iron meteorites ...
New perspective on stress pandemics and human resilience from the analysis of COVID-19
2021-05-14
A new analysis of the effects of SARS-CoV-2, the virus causing the current pandemic, on the human body has provided novel insights into the nature of resilience and how we deal with stressful situations. Using COVID-19 as an example, the findings provide a new framework that may be central to managing this disease, minimise the likelihood of ferocious viral outbreaks in the future and deal with other major stresses.
"COVID-19 has been a huge burden on society at all levels. Whilst the prospects are improving in countries with efficient vaccination schemes ...
Maternal stress during pregnancy may shorten lifespans of male lizard offspring
2021-05-14
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Mother fence lizards that experience stress during pregnancy give birth to male offspring with shortened telomeres, or bits of non-coding DNA that cap the ends of chromosomes, according to a Penn State-led study. Shorter telomeres are associated with decreased lifespan in humans; therefore, the team's findings may have implications for human longevity.
"Human men have shorter telomeres than women, which may partly explain why they have shorter lifespans of about seven years," said Tracy Langkilde, professor and Verne M. Willaman dean of the Eberly College of Science. "Our study shows that stress experienced by mothers during gestation could further shorten the telomeres, and therefore the lifespans, of their sons, thereby exacerbating these sex differences." ...
Businesses have a moral duty to explain how algorithms make decisions that affect people
2021-05-14
Increasingly, businesses rely on algorithms that use data provided by users to make decisions that affect people. For example, Amazon, Google, and Facebook use algorithms to tailor what users see, and Uber and Lyft use them to match passengers with drivers and set prices. Do users, customers, employees, and others have a right to know how companies that use algorithms make their decisions? In a new analysis, researchers explore the moral and ethical foundations to such a right. They conclude that the right to such an explanation is a moral right, then address how companies might do so.
The analysis, by researchers at Carnegie Mellon University, appears in Business Ethics Quarterly, a publication of the Society for Business Ethics.
"In most cases, ...
Male hormones regulate stomach inflammation in mice
2021-05-14
Scientists at the National Institutes of Health determined that stomach inflammation is regulated differently in male and female mice after finding that androgens, or male sex hormones, play a critical role in preventing inflammation in the stomach. The finding suggests that physicians could consider treating male patients with stomach inflammation differently than female patients with the same condition. The study was published in Gastroenterology.
Researchers at NIH's National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS) made the discovery after removing adrenal glands from mice of both sexes. Adrenal glands produce glucocorticoids, hormones that have several functions, one of them being suppressing inflammation. With no glucocorticoids, the female mice soon ...
Is the past (and future) there when nobody looks?
2021-05-14
In 1961, the Nobel prize winning theoretical physicist Eugene Wigner proposed what is now known as the Wigner's friend thought experiment as an extension of the notorious Schroedinger's cat experiment. In the latter, a cat is trapped in a box with poison that will be released if a radioactive atom decays. Governed by quantum mechanical laws, the radioactive atom is in a superposition between decaying and not decaying, which also means that the cat is in a superposition between life and death. What does the cat experience when it is in the superposition? ...
Ion transporters in chloroplasts affect the efficacy of photosynthesis
2021-05-14
A study led by LMU plant biologist Hans-Henning Kunz uncovers a new role for ion transporters: they participate in gene regulation in chloroplasts.
In plants, photosynthesis takes place in intracellular 'factories' called chloroplasts. Plant chloroplasts evolved from photosynthetic cyanobacteria, which were engulfed by a non-photosynthetic cell in the course of evolution. As a result of this evolutionary event, chloroplasts possess two envelope membranes, and have retained functional remnants of their original cyanobacterial genomes. Henning Kunz (LMU Biocenter), his group, and their collaborators have now demonstrated that ...
Finding control in hard-to-predict systems
2021-05-14
Input one, output one; input two, output two; input three; output purple --what kind of system is this? Computer algorithms can exist as non-deterministic systems, in which there are multiple possible outcomes for each input. Even if one output is more likely than another, it doesn't necessarily eliminate the possibility of putting in three and getting purple instead of three. Now, a research team from Iowa State University has developed a way to control such systems with more predictability. The results were published in IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica.
"The supervisory control problem for discrete event systems under control involves ...
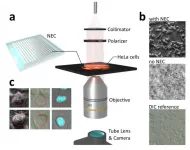
Nanophotonics enhanced coverslip for phase imaging in biology
2021-05-14
The ability to visualize transparent objects such as biological cells is of fundamental importance in biology and medical diagnostics. Conventional approaches to achieve this include phase-contrast microscopy and techniques that rely on chemical staining of biological cells. These techniques, however, rely on expensive and bulky optical components or require changing, and in some cases damaging, the cell by introducing chemical contrast agents. Significant recent advances in nanofabrication technology permit structuring materials on the nanoscale with unprecedented ...
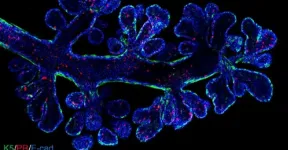
New cellular atlas maps out healthy and cancerous breast tissue
2021-05-14
Australian researchers have documented the diversity of cells in the human breast, explaining the relationship between healthy breast cells and breast cancer cells.
The research, which relied on expertise spanning from breast cancer biology through to bioinformatics, measured gene expression in single cells taken from healthy women and cancerous breast tissue, including tissue carrying a faulty BRCA1 gene. This enabled the researchers to create an 'RNA atlas' that details the different cells found in these tissues.
The atlas, which was described in EMBO Journal, ...
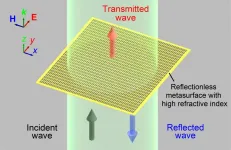
Using micro-sized cut metal wires, Japanese team forges path to new uses for terahertz waves
2021-05-14
Japanese researchers successfully tested reflectionless, highly refractive index metasurface that may eventually be used in practical applications to send, receive, and manipulate light and radio waves in the terahertz waveband (THz). THz is measured in millionths of a meter, known as micrometers. The metasurface, an artificial two-dimensional flat material, was made of micro-sized cut metal wires of silver paste ink placed on both the front and back of a polyimide film. The team, led by Takehito Suzuki, Associate Professor at the Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology (TUAT) Institute of Engineering, published their findings on April 29, 2021 in Optics Express.
Such flat metasurfaces ...
Virtual reality warps your sense of time
2021-05-14
Psychology researchers at UC Santa Cruz have found that playing games in virtual reality creates an effect called "time compression," where time goes by faster than you think. Grayson Mullen, who was a cognitive science undergraduate at the time, worked with Psychology Professor Nicolas Davidenko to design an experiment that tested how virtual reality's effects on a game player's sense of time differ from those of conventional monitors. The results are now published in the journal Timing & Time Perception.
Mullen designed a maze game that could be played in both virtual reality and conventional formats, then the research team recruited 41 UC Santa Cruz undergraduate ...
Study of hip fracture patient characteristics and outcomes pre- and post-COVID-19 outbreak
2021-05-14
The COVID-19 pandemic has been shown to have caused a significant strain on the healthcare system and resources in the United States. However, data regarding the impact of the virus on hip fractures, primarily seen in elderly patients, is lacking.
Researchers at Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) sought to compare characteristics and outcomes of hip fracture patients admitted during the COVID-19 outbreak to patients admitted before the outbreak. They also examined characteristics and outcomes of hip fracture patients with and without the virus. Their findings were presented at the 2021 Spring American Society of Regional Anesthesia and ...
[1] ... [2334]
[2335]
[2336]
[2337]
[2338]
[2339]
[2340]
[2341]
2342
[2343]
[2344]
[2345]
[2346]
[2347]
[2348]
[2349]
[2350]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.