Oncotarget: CABYR-a/b and CABYR-c hold promise as targets for specific immunotherapy
2021-05-17
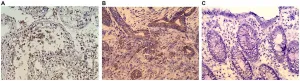
Oncotarget published "The cancer testis antigens CABYR-a/b and CABYR-c are expressed in a subset of colorectal cancers and hold promise as targets for specific immunotherapy" which reported that Calcium-binding tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated protein is expressed in the human germ line but not in adult human tissues, thus, it is considered a cancer testis protein.
The aim of this study is to evaluate the CABYR isoforms: a/b and c mRNA expression in colorectal cancer and to determine if these proteins hold promise as vaccine targets.
CABYR mRNA expression in a set of normal human tissues, including the testis, were determined ...
COVID-19 vaccination: Thrombosis can be prevented by prompt treatment
2021-05-17
A rare syndrome has been observed in people following vaccination against Covid-19. This involves thrombosis at unusual sites in the body, associated with a low thrombocyte (blood platelet) count and a clotting disorder. In medical jargon, this syndrome is referred to as VITT (vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia). Doctors at the Department of Medicine I of MedUni Vienna and Vienna General Hospital (Division of Hematology and Hemastaseology) have now successfully treated an acute instance of this syndrome.
VITT is most probably caused by a defective immune response, whereby thrombocyte-activating antibodies are produced resulting ...
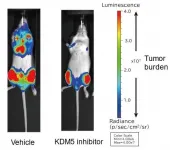
New epigenetic regulatory mechanisms involved in multiple myeloma growth
2021-05-17
An international team of researchers from Japan, the US and the UK has analyzed the function of the histone demethylase KDM5A in multiple myeloma, one of the three major hematological cancers, and clarified the mechanism by which it promotes myeloma cell proliferation. They also developed a novel KDM5 inhibitor and showed that it inhibits cancer cell growth in a myeloma mouse model. The researchers expect that new therapies targeting KDM5A will be developed in the future.
The prognosis for multiple myeloma is improving every year with the introduction of new ...
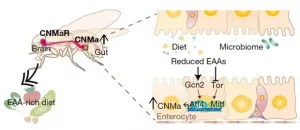
Gut hormone triggers craving for more proteins
2021-05-17
A new study led by KAIST researchers using fruit flies reveals how protein deficiency in the diet triggers cross talk between the gut and brain to induce a desire to eat foods rich in proteins or essential amino acids. This finding reported in the May 5 issue of Nature can lead to a better understanding of malnutrition in humans.
"All organisms require a balanced intake of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats for their well being," explained KAIST neuroscientist and professor Greg Seong-Bae Suh. "Taking in sufficient calories alone won't do the job, as it can still lead to severe forms of malnutrition including kwashiorkor, if the diet does not include enough proteins," he added.
Scientists already knew that inadequate ...
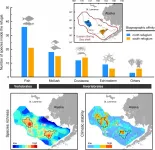
Two biodiversity refugia identified in the Eastern Bering Sea
2021-05-17
Scientists from Hokkaido University have used species survey and climate data to identify two marine biodiversity refugia in the Eastern Bering Sea - regions where species richness, community stability and climate stability are high.
Marine biodiversity, the diversity of life in the seas and oceans, supports ecosystem services of immense societal benefits. However, climate change and human activities have been adversely affecting marine biodiversity for many decades, resulting in population decline, community shifts, and species loss and extinction. Developing effective means to mitigate ...
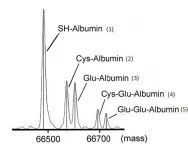
Cysteinylated albumin: A new early diagnostic marker for diabetic kidney disease
2021-05-17
A research group from Kumamoto University, Japan has discovered that cysteinylated albumin (oxidized albumin) in serum can be used as an early diagnostic marker for diabetic kidney disease. Compared with urinary albumin, serum oxidized albumin not only reflects renal pathology at an earlier stage, but can also predict the progression of renal pathology by its degree of elevation. The researchers believe that it can be used as a new diagnostic marker for early diagnosis of diabetic kidney disease.
Diabetic kidney disease is one of three major complications of diabetes. Its prognosis is difficult to improve as it progresses so diagnosing it as early as possible and providing appropriate therapeutic intervention ...
High-intensity intermittent training improves spatial memory in rats
2021-05-17
Tsukuba, Japan--Researchers at the University of Tsukuba found that, despite only covering about one-third of the distance in HIIT compared with that covered in endurance training, similar improvements in exercise capacity and brain function were observed for both forms of exercise.
"We investigated how rats' muscles and brains--specifically, the region of the brain involved in spatial learning called the hippocampus--adapted to these types of exercise, and how the rats consequently learned and remembered navigating mazes," explains Professor Hideaki Soya, the principal investigator.
In the experiment, rats were assigned to 1 of 3 groups--resting, endurance running, or alternating intervals ...
Cypriot grapes perform well in heat and on taste
2021-05-17
Researchers at the University of Adelaide have found several grape varieties native to Cyprus, which tolerate drought conditions better than some international varieties popular in Australia, contain chemical compounds responsible for flavours preferred by Australian consumers.
The study published in OENO One follows earlier research with Cypriot grape varieties Maratheftiko and Xynisteri in particular, which showed they are well adapted to a hot climate and continue to perform well as the climate becomes hotter.
Lead author and PhD student Alexander Copper, from the University of ...
New combination immunotherapy plus ART expand innate cells critical to controlling HIV
2021-05-17
ATLANTA - Yerkes National Primate Research Center researchers in collaboration with Institut Pasteur have determined a combination immunotherapy of Interleukin-21 (IL-21) and interferon alpha (IFN?) when added to antiviral therapy (ART) is effective in generating highly functional natural killer (NK) cells that can help control and reduce simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) in animal models. This finding, published online today in Nature Communications, is key for developing additional treatment options to control HIV/AIDS, which impacts 38 million people worldwide.
ART is the current leading treatment for HIV/AIDS. It is capable of reducing the virus to undetectable levels, but is ...
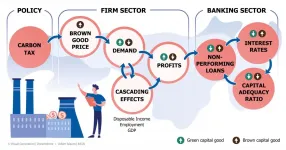
Climate policies, transition risk, and financial stability
2021-05-17
The way in which banks react to climate risks and uncertainty could impact financial stability as well as the world's transition to a low-carbon economy. A new study by researchers from IIASA and the Vienna University of Economics and Business explored the role that banks' expectations about climate-related risks will play in fostering or hindering an orderly low-carbon transition.
According to the study published in a special issue on climate risks and financial stability of the Journal of Financial Stability, banks and their expectations about climate-related risks - and especially ...
Skoltech researchers developed an enriched method for increasing the capacity of next-generation metal-ion battery cathode materials
2021-05-17
Scientists at Skoltech Center for Energy Science and Technology have developed an enriched and scalable approach for increasing the capacity of a broad range of metal-ion battery cathode materials. These findings, published in Journal of Materials Chemistry A, can be useful for developing a new generation of advanced rechargeable energy storage devices.
Creation of modern lithium-ion batteries became possible owing to several scientific breakthroughs. One of them, made by a Nobel laureate John B. Goodenough, was the development of cathode materials that contain reversibly extractable lithium ions. Implementation ...
"Heat not burn" product compared with cigarettes and e-cigarettes
2021-05-17
Devices that deliver nicotine without smoke inhalation have potential to help smokers who cannot or do not want to stop using nicotine to reduce dramatically the risk of smoking-related disease and death.
However, for smokers to switch to these alternatives, the products need to provide what smokers expect from cigarettes.
The newest study from Queen Mary University of London evaluates safety and effects of these products and has focused on the most popular "heat not burn" product, IQOS.
The researchers compared nicotine delivery and user ratings of IQOS with those of cigarettes, Juul (the US version of a 'pod' based e-cigarette with high nicotine content), and refillable e-cigarettes.
IQOS delivered less nicotine than cigarettes. ...
Errors in large-scale and convective tropical precipitation simulations using current global models may impact climate feedback
2021-05-17
Heavy precipitation can cause large economic, ecological, and human life losses. Both its frequency and intensity have increased due to climate change influences. Therefore, it is becoming increasingly critical to accurately model and predict heavy precipitation events. However, current global climate models (GCMs) struggle to correctly model tropical precipitation, particularly heavy rainfall. Atmospheric scientists are working to identify and minimize model biases that arise when attempting to model large-scale and convective precipitation.
"Unrealistic ...
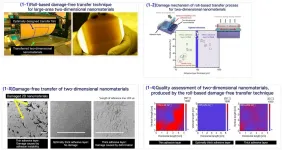
Fast, affordable solution proposed for transparent displaysand semiconductors
2021-05-17
The Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (KIMM) under the Ministry of Science and ICT developed a roll-based damage-free transfer technique that allows two-dimensional (2D) nanomaterials to be transferred into wafer scale without damage. The proposed technique has a variety of applications from transparent displays and semiconductors to displays for self-driving cars, and is expected to accelerate the commercialization of 2D nanomaterial-based high-performance devices.
Dr. Kwang-Seop Kim, principal researcher of the Department of Nano-Mechanics at KIMM, succeeded in developing a technique ...
Scientists find new way of predicting COVID-19 vaccine efficacy
2021-05-17
(SYDNEY, Monday 17th May 2021) The early immune response in a person who has been vaccinated for COVID-19 can predict the level of protection they will have to the virus over time, according to analysis from Australian mathematicians, clinicians, and scientists, and published today in Nature Medicine.
The researchers from UNSW's Kirby Institute, the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity, and the University of Sydney have identified an 'immune correlate' of vaccine protection. This has the potential to dramatically cut development times for new vaccines, by measuring neutralising antibody levels as a 'proxy' for immune protection from COVID-19.
"Neutralising antibodies are tiny Y-shaped proteins produced by our body in response to infection or vaccination. They ...
Greenland becoming darker, warmer as its snow ages and changes shape
2021-05-17
A weather pattern that pushes snowfall away from parts of Greenland's ice sheet is causing the continent to become darker and warmer, according to Dartmouth research published in Geophysical Research Letters.
The reduction in the amount of fresh, light-colored snow exposes older, darker snow on the surface of the ice sheet. The resulting decrease in reflectivity, known as albedo, causes the ice to absorb more heat, also likely contributing to faster melting.
"As snow ages, even over hours to a few days, you get this reduction in reflectivity, and that's why the fresh snow is so important," said Erich Osterberg, associate professor of earth sciences at Dartmouth and the principal investigator of the study.
According to the ...
Scientists explain why climate models can't reproduce the early-2000s global warming slowdown
2021-05-17
A new study led by Dr. Wei and Dr. Qiao from the First Institute of Oceanography, Ministry of Natural Resources provides an evaluation of the performance of the newly released CMIP6 models in simulating the global warming slowdown observed in the early 2000s. This study reveals that the key in simulating and predicting near-term temperate change is to correctly separate and simulate the two distinct signals, i.e., the human-induced long-term warming trend and natural variabilities, especially those at interannual, interdecadal and multidecadal scales. This work was online published in SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences on April 15th, 2021.
After the unprecedented warming over the last quarter of the 20th century, the global surface temperature growth slowed unexpectedly during ...
Anisotropic zoning in the upper crust of the Tianshan Tectonic Belt
2021-05-17
The collision between the Indian and Eurasian plates resulted in the formation of the Tianshan Tectonic Belt; however, the formation mechanism of Tianshan and the construction of a dynamic model explaining it remain to be achieved and an integrated understanding has not been reached. A new study adopted shear-wave splitting system to collect and analyze shear-wave splitting parameters of 33 stations in the Tianshan area, it provides new evidence for potentially enhance the understanding the dynamic mechanism of the Tianshan tectonic belt.
The research paper is titled:"Anisotropic zoning in the upper crust of the Tianshan Tectonic Belt, Published in Science China Earth Sciences Issue 4, 2021, Corresponding author ...
The perfect blend: Optimizing gas mixtures for hydrogen storage in clathrate hydrates
2021-05-17
In our ongoing quest to transform into a more eco-friendly society, hydrogen (H2) is heralded as the clean fuel of tomorrow. Because H2 can be produced from water (H2O) without generating carbon emissions, developing H2-compatible technologies has become a top priority. However, the road ahead is bumpy, and many technical limitations must be ironed out. "Hydrogen is the smallest molecule in nature, and finding feasible ways to store it is a critical issue to realize a hydrogen economy," states Associate Professor Youngjune Park from the Gwangju Institute of Science ...
Low- and high-dose aspirin achieve similar protection, safety for those with heart disease
2021-05-17
WASHINGTON, DC--People with cardiovascular disease (CVD) taking aspirin to lower their chances of suffering a heart attack or stroke experienced similar health benefits, including reduced death and hospitalization for heart attack and stroke, whether they took a high or low dose of aspirin, according to a study presented today at ACC.21, the American College of Cardiology's 70th Annual Scientific Session and published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
CVD--and atherosclerosis, in particular, which is a narrowing and hardening of the arteries--is a leading cause of death for men, women, and most racial and ethnic groups in the United States, with estimated direct costs of END ...
Early biomarker warning of heart disease for diabetic patients
2021-05-17
New research has shown that people with type 1 diabetes may have features of premature heart disease induced by the condition often before they even get their diagnosis.
Early markers for this heart disease could be used to ensure patients get targeted therapies as soon as they are diagnosed with type 1 diabetes to slow down or even halt cardiovascular problems.
The findings, published in Stem Cell Research and Therapy, show that tiny pieces of genetic material, called miR-424-5p, increased in early stages of heart disease - these could be targeted to help reduce inflammation in order to compensate for elevated risk.
Early heart disease
Dr Jolanta Weaver, from Newcastle University's Faculty of Medical Sciences, UK, ...
Shrinking planets could explain mystery of universe's missing worlds
2021-05-17
There's been a breakthrough in the case of the missing planets.
While planet-hunting missions have discovered thousands of worlds orbiting distant stars, there's a severe scarcity of exoplanets that measure between 1.5 and two times Earth's radius. That's the middle ground between rocky super-Earths and larger, gas-shrouded planets called mini-Neptunes. Since discovering this 'radius gap' in 2017, scientists have been sleuthing out why there are so few midsize heavenly bodies.
The new clue arose from a fresh way of looking at the data. A team of researchers led by the Flatiron Institute's Trevor David investigated whether the radius gap changes as planets age. They divvied up exoplanets into two groups -- young and old -- and reassessed the gap. The ...
Apixaban not superior to standard care after TAVR
2021-05-17
The blood thinner apixaban was not superior to standard of care following transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), according to findings from a new trial called ATLANTIS presented at the American College of Cardiology's 70th Annual Scientific Session. Researchers found that while apixaban reduced the formation of blood clots (thrombosis) around the implanted valve with no increased bleeding risk, a subset of patients taking apixaban who did not have an indication for anticoagulation apart from the TAVR procedure showed a tendency toward a higher rate of non-cardiovascular death--a ...
Left atrial appendage occlusion associated with low rate of stroke
2021-05-17
Transcatheter left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) with a WATCHMAN device was associated with a low rate of stroke at one year even among older patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) who faced a high risk for stroke or bleeding based on their previous health history, according to new data presented at the American College of Cardiology's 70th Annual Scientific Session.
The WATCHMAN device, which blocks a small portion of the heart to help reduce the risk of a dangerous clot forming, was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2015. The device is used to reduce the risk of stroke in patients with AFib, a heart rhythm disorder, that is not caused by problems with the heart valve. ...
Left atrial appendage occlusion reduces stroke after heart surgery
2021-05-17
Patients with an elevated risk of stroke due to heart rhythm problems, or atrial fibrillation (AFib), were much less likely to suffer a stroke after undergoing heart surgery if doctors concurrently performed an additional procedure, called left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO), according to the results of a trial presented at the American College of Cardiology's 70th Annual Scientific Session.
AFib increases a person's risk of stroke or systemic embolism, which are life-threatening conditions caused by blood clots blocking an artery. It has been hypothesized that the blood clots that cause these conditions often originate in the left atrial appendage, a small sac on the upper left chamber of the heart. LAAO is a procedure to ...
[1] ... [2326]
[2327]
[2328]
[2329]
[2330]
[2331]
[2332]
[2333]
2334
[2335]
[2336]
[2337]
[2338]
[2339]
[2340]
[2341]
[2342]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.