Researchers use arcuate organoids to study development and disease of the hypothalamus
2021-05-10
PHILADELPHIA-- Human brain organoids are remarkable platforms for modeling features of human brain development and diseases. Building on methods to generate organoids to model different brain regions such as the cortex and the midbrain, researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania have generated the first organoids of the arcuate nucleus (ARC), an essential structure in the hypothalamus that sends signals of hunger and feeling full. This part of the hypothalamus exhibits a tremendous amount of cell diversity, and is far more complex than previously modeled parts of the brain.
In a paper ...
New mapping technique reveals epigenetic drivers of cancers
2021-05-10
Scientists have made major advances in understanding and developing treatments for many cancers by identifying genetic mutations that drive the disease. Now a team led by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine, NewYork-Presbyterian and the New York Genome Center (NYGC) has developed a machine learning technique for detecting other modifications to DNA that have a similar effect.
The study, published May 10 in Cancer Discovery, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research, focuses on a type of chemical modification to DNA, called methylation, that typically silences nearby genes. The new technique can analyze the thousands of DNA methylation changes detected in tumor cells and infer which ones are likely ...
Single-cell map of early stage lung cancer and normal lung sheds light on tumor development, new therapeutic targets
2021-05-10
HOUSTON - Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have developed a first-of-its-kind spatial atlas of early-stage lung cancer and surrounding normal lung tissue at single-cell resolution, providing a valuable resource for studying tumor development and identifying new therapeutic targets. The study was published today in Cancer Discovery, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
The findings reveal a heterogeneous lung cancer ecosystem, with extensive interactions between cancer cells and the surrounding microenvironment that regulate early cancer development. ...
Time running out to save coral reefs
2021-05-10
New research on the growth rates of coral reefs shows there is still a window of opportunity to save the world's coral reefs--but time is running out.
The international study was initiated at the ARC Centre of Excellence for Coral Reef Studies (Coral CoE), which is headquartered at James Cook University (JCU).
Co-author Professor Morgan Pratchett from Coral CoE at JCU said the results show that unless carbon dioxide emissions are drastically reduced the growth of coral reefs will be stunted.
"The threat posed by climate change to coral reefs is already very apparent based on recurrent episodes of mass coral bleaching," Prof Pratchett said. "But changing environmental conditions will have other far-reaching consequences."
Co-author Professor Ryan Lowe, from Coral CoE at The University ...
Turns out developing a taste for carbs wasn't a bad thing
2021-05-10
A new study looking at the evolutionary history of the human oral microbiome shows that Neanderthals and ancient humans adapted to eating starch-rich foods as far back as 100,000 years ago, which is much earlier than previously thought.
The findings suggest such foods became important in the human diet well before the introduction of farming and even before the evolution of modern humans. And while these early humans probably didn't realize it, the benefits of bringing the foods into their diet likely helped pave the way for the expansion of the human brain because of the glucose in starch, which is the brain's main fuel source.
"We think we're seeing evidence of a really ...
Flying at up to Mach 16 could become reality with UCF's developing propulsion system
2021-05-10
ORLANDO, May 10, 2021 -University of Central Florida researchers are building on their technology that could pave the way for hypersonic flight, such as travel from New York to Los Angeles in under 30 minutes.
In their latest research published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the researchers discovered a way to stabilize the detonation needed for hypersonic propulsion by creating a special hypersonic reaction chamber for jet engines.
"There is an intensifying international effort to develop robust propulsion systems for hypersonic and supersonic flight that would allow flight through our atmosphere at very high speeds and also allow efficient entry and exit from planetary atmospheres," ...
Geoscientists find that shallow wastewater injection drives deep earthquakes in Texas
2021-05-10
In a newly published paper, Virginia Tech geoscientists have found that shallow wastewater injection -- not deep wastewater injections -- can drive widespread deep earthquake activity in unconventional oil and gas production fields.
Brine is a toxic wastewater byproduct of oil and gas production. Well drillers dispose of large quantities of brine by injecting it into subsurface formations, where its injection can cause earthquakes, according to Guang Zhai, a postdoctoral research scientist in the Department of Geosciences, part of the Virginia Tech College of Science, and a ...
Grand Challenge research harnesses AI to fight breast cancer
2021-05-10
Breast cancer has recently overtaken lung cancer to become the most common cancer globally, END ...
New theory may revolutionize treatment of endometriosis
2021-05-10
Endometriosis, a disease found in up to 10 per cent of women, has been enigmatic since it was first described. A new theory developed by researchers at Simon Fraser University suggests a previously overlooked hormone -- testosterone -- has a critical role in its development. The research could have direct impacts on diagnosis and treatment of the disease, signaling hope for women with endometriosis worldwide.
The disease is caused by endometrial tissue growing outside of the uterus, usually in the pelvic area, where it contributes to pain, inflammation, and infertility. But why some women get it, and others do not, has remained unclear.
The new research is based on recent findings that women with endometriosis developed, as fetuses in their mother's womb, under conditions of relatively ...
Does driving wear you out? You might be experiencing 'accelerousal'
2021-05-10
Admit it: Daily commutes - those stops, the starts, all that stress - gets on your last nerve.
Or is that just me?
It might be, according to a new study from the University of Houston's Computational Physiology Lab. UH Professor Ioannis Pavlidis and his team of researchers took a look at why some drivers can stay cool behind the wheel while others keep getting more irked.
"We call the phenomenon 'accelerousal.' Arousal being a psychology term that describes stress. Accelarousal is what we identify as stress provoked by acceleration events, even small ones," said Pavlidis, ...
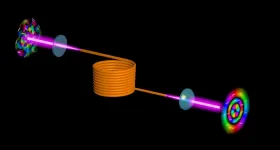
'Flipping' optical wavefront eliminates distortions in multimode fibers
2021-05-10
The use of multimode optical fibers to boost the information capacity of the Internet is severely hampered by distortions that occur during the transmission of images because of a phenomenon called modal crosstalk.
However, University of Rochester researchers at the Institute of Optics have devised a novel technique, described in a paper in Nature Communications, to "flip" the optical wavefront of an image for both polarizations simultaneously, so that it can be transmitted through a multimode fiber without distortion. Researchers at the University of South Florida and at the University of Southern California collaborated ...
Stanford researchers map how people in cities get a health boost from nature
2021-05-10
Your local city park may be improving your health, according to a new paper led by Stanford University researchers. The research, published in END ...
Even when they include them, gifted programs aren't serving Black or low-income kids
2021-05-10
After years of criticism for their lack of diversity, programs for high achievers may not be adequately serving their Black and low-income students, a new study shows.
"The potential benefits aren't equally distributed," said lead author and University of Florida College of Education professor Christopher Redding, Ph.D., who evaluated data from gifted programs in elementary schools nationwide. "The conversation up to this point has been about access, with less emphasis on how students perform once in gifted programs."
While academic achievement gains for students overall were modest -- going from ...
Top educational apps for children might not be as beneficial as promised
2021-05-10
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Log on to any app store, and parents will find hundreds of options for children that claim to be educational. But new research suggests these apps might not be as beneficial to children as they seem.
A new study analyzed some of the most downloaded educational apps for kids using a set of four criteria designed to evaluate whether an app provides a high-quality educational experience for children. The researchers found that most of the apps scored low, with free apps scoring even lower than their paid counterparts on some criteria.
Jennifer Zosh, associate professor of human development ...
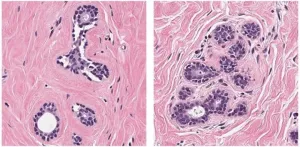
CDK inhibitors may improve immune therapy effectiveness for recurrent breast cancer
2021-05-10
Recurrent, metastatic breast cancer resists treatment and is usually fatal.
These tumors often have low numbers of immune cells in them, which renders immune therapies less effective for the disease.
This preclinical study suggests that drugs called CDK4 and CDK6 inhibitors may make immune-cell therapies an effective option for treating recurrent ER-positive metastatic breast cancer.
COLUMBUS, Ohio - A class of drugs that inhibits breast cancer progression when used with hormonal therapy might also boost the effectiveness of immune therapy in cases of recurrent, metastatic breast cancer, according to a new study led by researchers at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center - Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital ...
The next generation of hunters could look different
2021-05-10
A new survey led by researchers from North Carolina State University found that the future of hunting in the United States might look different than it has in the past.
In The Journal of Wildlife Management, researchers reported findings from a nationwide survey of college students' interest and participation in hunting. They found current, active hunters were more likely to be white, male and from rural areas, and to have family members who hunted. But they also found a group of potential hunters - with no hunting experience but an interest in trying it - who were more diverse in terms of gender, ...
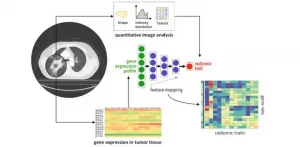
Integrating medical imaging and cancer biology with deep neural networks
2021-05-10
Despite our remarkable advances in medicine and healthcare, the cure to cancer continues to elude us. On the bright side, we have made considerable progress in detecting several cancers in earlier stages, allowing doctors to provide treatments that increase long-term survival. The credit for this is due to "integrated diagnosis," an approach to patient care that combines molecular information and medical imaging data to diagnose the cancer type and, eventually, predict treatment outcomes.
There are, however, several intricacies involved. The correlation of molecular patterns, such as gene expression and mutation, with image features (e.g., how a tumor appears in a CT scan), is ...
Timing is everything in new implant tech
2021-05-10
HOUSTON - (May 10, 2021) - Implants that require a steady source of power but don't need wires are an idea whose time has come.
Now, for therapies that require multiple, coordinated stimulation implants, their timing has come as well.
Rice University engineers who developed implants for electrical stimulation in patients with spinal cord injuries have advanced their technique to power and program multisite biostimulators from a single transmitter.
A peer-reviewed paper about the advance by electrical and computer engineer Kaiyuan Yang and his colleagues at Rice's Brown School of Engineering won the best paper award at the IEEE's Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, held virtually in the last ...
Informed tourists make whale watching wafer for whales
2021-05-10
According to the International Whaling Commission, whale-watching tourism generates more than $2.5 billion a year. After the COVID-19 pandemic, this relatively safe outdoor activity is expected to rebound. Two new studies funded by a collaborative initiative between the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute (STRI) in Panama and Arizona State University (ASU) show how science can contribute to whale watching practices that ensure the conservation and safety of whales and dolphins.
"The Smithsonian's role is to provide scientific advice to policy makers as they pioneer management strategies to promote whale conservation," said STRI marine biologist, Hector Guzmán, whose previous work led the International Maritime Organization to establish shipping corridors ...
For twins, gesture and speech go hand-in-hand in language development
2021-05-10
ATLANTA--Gestures--such as pointing or waving--go hand in hand with a child's first words, and twins lag behind single children in producing and using those gestures, two studies from Georgia State University psychology researchers show.
Twins produce fewer gestures and gesture to fewer objects than other children, said principal researcher Seyda Ozcaliskan, an associate professor in the Department of Psychology. Language use also lags for twins, and language--but not gesture--is also affected by sex, with girls performing better than boys, Ozcaliskan said.
"The implications are fascinating," said Ozcaliskan. ...
UM scientist joins team partnering with UN's initiative to map ungulate migrations
2021-05-10
MISSOULA - University of Montana Professor Mark Hebblewhite has joined an international team of 92 scientists and conservationists to create the first-ever global atlas of ungulate (hoofed mammal) migrations.
Working in partnership with the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals, a U.N. treaty, the Global Initiative on Ungulate Migration (GIUM) launches May 7 with the publication of a commentary in Science titled " END ...
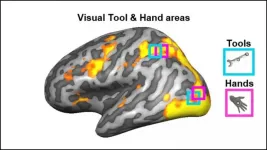
Brain regions involved in vision also encode how to hold tools
2021-05-10
Visual brain areas involved in processing hands also encode information about the correct way to hold tools, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
Each part of the brain's visual system activates in response to a certain type of item -- whether it's faces, tools, objects, or hands. Scientists assumed the brain segregates visual information in this way to optimize motor actions with tools. Yet most studies investigating the brain mechanisms for tool grasping used images of tools or hands, and no actual hand movements were performed.
Knights et al. used fMRI to measure the brain activity of participants as they grasped 3D-printed kitchen tools (spoon, knife, and pizza cutter) and similar-sized non-tools. ...
UEA team reads minds to understand human tool use
2021-05-10
Researchers at the University of East Anglia have made an astonishing discovery about how our brains control our hands.
They used MRI data to study which parts of the brain are used when we handle tools, such as a knives.
They read out the signal from certain brain regions and tried to distinguish when participants handled tools appropriately for use.
Humans have used tools for millions of years, but this research is the first to show that actions such grasping a knife by its handle for cutting are represented by brain areas that also represent images of human hands, our primary 'tool' for interacting with the world.
The research ...
'Unmaking' a move: Correcting motion blur in single-photon images
2021-05-10
Imaging technology has come a long way since the beginning of photography in the mid-19th century. Now, many state-of-the-art cameras for demanding applications rely on mechanisms that are considerably different from those in consumer-oriented devices. One of these cameras employs what is known as "single-photon imaging," which can produce vastly superior results in dark conditions and fast dynamic scenes. But how does single-photon imaging differ from conventional imaging?
When taking a picture with a regular CMOS camera, like the ones on smartphones, ...
Monash study may help boost peptide design
2021-05-10
Peptides " short strings of amino acids" play a vital role in health and industry with a huge range of medical uses including in antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer drugs. They are also used in the cosmetics industry and for enhancing athletic performance. Altering the structure of natural peptides to produce improved compounds is therefore of great interest to scientists and industry. But how the machineries that produce these peptides work still isn't clearly understood.
Associate Professor Max Cryle from Monash University's Biomedicine Discovery Institute (BDI) has revealed a key aspect of peptide machinery in a paper published in Nature Communications today that provides a key to the "Holy Grail" of re-engineering peptides..
The findings will advance his lab's work into ...
[1] ... [2331]
[2332]
[2333]
[2334]
[2335]
[2336]
[2337]
[2338]
2339
[2340]
[2341]
[2342]
[2343]
[2344]
[2345]
[2346]
[2347]
... [8814]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.