The importance of DNA compaction in tissue formation
2021-05-18
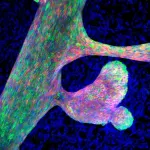
Scientists led by Dr. Salvador Aznar-Benitah, head of the Stem Cells and Cancer laboratory at IRB Barcelona, have described the alterations that occur during mammary gland formation when heterochromatin (the part of DNA that does not actively produce proteins) is poorly regulated. The results, which have been published in the journal Cell Stem Cell, indicate that incorrect DNA packaging makes retrotransposons (a type of transposable element originated in ancestral fragments of viruses integrated into the cell genome) more accessible.
As these fragments are more accessible, they can be "read" and copied ...
White roofs and more green areas would mitigate the effects of heat waves in cities
2021-05-18
The frequency and intensity of heat waves in cities is increasing due to climate change, with a great negative impact on the health and mortality rates of the population. Anthropogenic activities and urban materials affect heat accumulation in cities, and solar radiation stored throughout the day on asphalt and buildings is released slowly during the night, generating significant heat stress. To face this growing problem, cities must establish effective mitigation strategies that allow reducing the temperature during heat waves.
A study carried out by researchers from the Institut de Ciència i Tecnologia Ambientals ...
Time to capitalize on COVID-19 disruptions to lock-in greener behaviors
2021-05-18
As lockdown measures ease this week in the UK, environmental psychologists are urging that before rushing back to business as normal, we take advantage of the shifts observed over the past year to lock-in new, greener behaviours.
Writing in the journal END ...
Peatlands pose complex, poorly understood wildfire risk, researchers warn
2021-05-18
HAMILTON, ON May 18, 2021 -- Five years after the disastrous wildfire in Fort McMurray, Alberta, researchers are warning that the complex role of peatlands, a factor critical to projecting the risk and behaviour of future fires, is missing from the forecasting model.
The Fort McMurray fire burned out of control from May 1 to July 5, 2016, though it continued to smoulder until it was finally declared extinguished Aug. 2, 2017.
Peat deposits - which are prevalent across Canada, especially in Alberta - are complex threats that can complicate and magnify the risk of severe, long-lasting fires and heavy smoke, but they are not yet part of the standard assessment tools that fire managers use.
It's a critical ...
People who have had dengue are twice as likely to develop symptomatic COVID-19
2021-05-18
A study published this May in the journal Clinical Infectious Diseases suggests that people who have had dengue in the past are twice as likely to develop symptoms of COVID-19 if they are infected by the novel coronavirus.
The findings of the study were based on an analysis of blood samples from 1,285 inhabitants of Mâncio Lima, a small town in the state of Acre, part of Brazil’s Amazon region. The principal investigator was Marcelo Urbano Ferreira, a professor at the University of São Paulo’s Biomedical Sciences Institute (ICB-USP) in Brazil. The study was supported by FAPESP.
“Our results show that the populations most exposed to dengue, possibly owing to socio-demographic factors, are precisely ...
How a virtual program may help kids get ready for kindergarten
2021-05-18
COLUMBUS, Ohio - With pandemic lockdowns still in place last summer, The Ohio State University couldn't host its in-person Summer Success Program to help preschoolers from low-income families prepare for kindergarten.
Staff and teachers quickly pivoted to a fully virtual program, but they were worried: Could this really work with 4- and 5-year-olds who had no previous experience with preschool?
A new study suggested it did.
Researchers found that the reimagined Summer Success at Home program was feasible to operate, was popular with teachers and parents, and had at least modest success in helping the children learn ...
Socioeconomic status non-factor in worse COVID-19 for racial, ethnic groups in Twin Cities
2021-05-18
MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (03/18/2021) -- A research team, led by the University of Minnesota Medical School, found that regardless of socioeconomic status, Twin Cities residents of underrepresented racial and ethnic backgrounds endure worse COVID-19 outcomes compared to people who are white.
The study was just published in the Journal of General Internal Medicine and is one of the first papers to discuss which social and cultural factors, including non-English speaking, may or may not contribute to racial and ethnic health disparities related to COVID-19.
"For people of color, even in the highest socioeconomic status, our data shows they still have worse COVID-19 outcomes compared to people who are white," said Nicholas Ingraham, MD, a third-year fellow in the ...
Iran's groundwater depletion is reaching crisis levels, warn Concordia researchers
2021-05-18
More than three quarters of Iran's land is under extreme groundwater overdraft, where the rate of human uptake is higher than the rate of natural recharge. This is according to a new study led by Concordia researchers published in the Nature journal Scientific Reports.
The article was co-authored by Samaneh Ashraf, a former Horizon postdoctoral researcher now at the Université de Montréal, and Ali Nazemi, an assistant professor in the Department of Building, Civil and Environmental Engineering. Amir AghaKouchak of the University of California, ...
How Russia can protect its rights in the Artic
2021-05-18
Climate change-induced ice melting in the Arctic has led to contradictions in the assessment of Russia's rights in the region. As ice cover diminishes, Russia may be losing its influence on the territories that it has historically developed. This is partially due to the changing width of territorial waters by low-water lines. However, there are alternative legally valid ways to establish fair borders, which are described by researchers of the HSE Institute of Ecology in their paper 'Prospects for the evolution of the system of baselines in the Arctic' https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4441/13/8/1082/htm.
Baselines are one of the key factors shaping international maritime law. From these lines the breadth of a territorial sea is measured, over ...
Conn. medication-assisted opioid treatment programs retain patients at higher rates
2021-05-18
Medication-assisted treatment, or MAT, is an important tool in the ongoing fight against opioid use dependence in the United States. Employing certain medications in combination with counseling and behavioral therapy, MAT offers a comprehensive, "whole-patient" approach to addressing opioid use.
According to a new study from researchers at the UConn School of Social Work and the Connecticut Department of Mental Health and Addiction Services, Connecticut's MAT programs have higher-than-average patient retention rates - more people who enter Connecticut's programs stay in the program to completion.
But the study - recently published in the journal Substance Use and Misuse - also found that ...
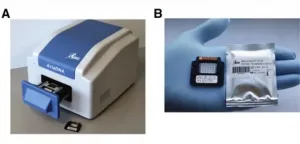
New testing platform for COVID-19 is an efficient and accurate alternative to gold-standard RT-qPCR tests
2021-05-18
Philadelphia, May 18, 2021 - Throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, supply chain shortages of reagents and test kits have limited the rapid expansion of clinical testing needed to contain the virus. Investigators have developed and validated a new microchip real-time technology platform that uses 10-fold less reagents compared to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)-approved tube-based RT-PCR tests, and reports results in as little as 30 minutes. Its accuracy was 100 percent predictive in clinical samples, investigators explain in the Journal of Molecular Diagnostics, published by Elsevier.
"Sensitivity is critical for early detection of COVID-19 ...
New material could create 'neurons' and 'synapses' for new computers
2021-05-18
Classic computers use binary values (0/1) to perform. By contrast, our brain cells can use more values to operate, making them more energy-efficient than computers. This is why scientists are interested in neuromorphic (brain-like) computing. Physicists from the University of Groningen (the Netherlands) have used a complex oxide to create elements comparable to the neurons and synapses in the brain using spins, a magnetic property of electrons. Their results were published on 18 May in the journal Frontiers in Nanotechnology.
Although computers can do straightforward calculations much faster than humans, our brains outperform silicon machines in tasks like object recognition. Furthermore, our brain uses less energy than ...
Diabetes-prevention program supports addition of years to average lifespan
2021-05-18
You can do a lot in four years: go from white to black belt in taekwondo, plant a dwarf apple tree and pick its fruit, see your grandchild off to college and attend her graduation or get your own degree. But the most severe complications of diabetes--from stroke to neuropathy to amputation--can make activities like these difficult or impossible for some people.
In a new study, West Virginia University School of Public Health researchers found that taking part in a year-long diabetes-prevention program supports the addition of 4.4 quality-adjusted life-years to participants' average lifespan.
"Fatalism can play a major role in community health--like, 'Oh, yeah, my family has diabetes. I'm going to get it eventually,'" said Adam Baus, a research assistant professor ...
Scientists map gene changes underlying brain and cognitive decline in aging
2021-05-18
Alzheimer's disease shares some key similarities with healthy aging, according to a new mathematical model described today in eLife.
The model provides unique insights into the multiscale biological alterations in the elderly and neurodegenerative brain, with important implications for identifying future treatment targets for Alzheimer's disease.
Researchers developed their mathematical model using a range of biological data - from 'microscopic' information using gene activity to 'macroscopic' information about the brain's burden of toxic proteins (tau and amyloid), its neuronal function, cerebrovascular flow, metabolism and tissue structure from molecular PET and MRI scans.
"In both aging and disease research, most studies ...
Environmental concerns propel research into marine biofuels
2021-05-18
A global effort to reduce sulfur and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from ships has researchers from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) and other Department of Energy facilities investigating the potential use of marine biofuels.
"Biofuels turned out to be very good options because they have zero or very, very low sulfur compared to fossil fuels," said Eric Tan, a senior research engineer at NREL and lead author of a new article published in the journal Environmental Science and Technology.
His co-authors of "Biofuel Options for Marine Applications: Techno-Economic and Life-Cycle Analyses" are Ling Tao, also from NREL, along with scientists with Argonne National Laboratory, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, ...
Experts call for better design of early drug trials for Alzheimer's and related dementias
2021-05-18
NEW YORK, NY (May 18, 2021) - An expert panel convened by the Alzheimer's Drug Discovery Foundation (ADDF) and The Association for Frontotemporal Degeneration (AFTD) provides guidance on best practices for the design of early drug trials for Alzheimer's disease, frontotemporal degeneration (FTD), and other neurodegenerative dementias. Their guidance was published in the May 18, 2021 issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology ("Value-Generating Exploratory Trials in Neurodegenerative Dementias").
These efficiencies in clinical trials can help to achieve proof of concept more rapidly and at lower costs. The estimated cost of developing ...
BU study: Racial disparities in COVID-19 mortality wider than reported
2021-05-18
More than a year into the pandemic, the disproportionate burden of COVID-19 among racial and ethnic minorities in the US has been well documented. But a new study by Boston University School of Public Health (BUSPH) reveals that previous research has underestimated the true extent of racial disparities in COVID-19 deaths--as well as the extent to which structural racism contributes to these deaths.
Published in the Journal of Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities, the paper is the first to quantify the state-level differences in racial disparities in COVID-19 mortality among Black and White populations, using directly ...
Tulane researchers develop test that can detect childhood tuberculosis a year ahead
2021-05-18
Researchers at Tulane University School of Medicine have developed a highly sensitive blood test that can find traces of the bacteria that causes tuberculosis (TB) in infants a year before they develop the deadly disease, according to a study published in BMC Medicine.
Using only a small blood sample, the test detects a protein secreted by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which causes TB infection. It can screen for all forms of TB and rapidly evaluate a patient's response to treatment, said lead study author Tony Hu, PhD, Weatherhead Presidential Chair in Biotechnology Innovation at Tulane University.
"This is a breakthrough for infants with tuberculosis because ...
Combining immunotherapies against cancer
2021-05-18
A new cancer vaccine could boost the positive effects of existing immunotherapy drugs, improving the success rate of treatments from 20% to 75% of cases, according to a new study by immunologists from the University of Konstanz. The vaccine, which incorporates a new immunostimulant that is safe for use in humans, was shown to partially eliminate tumours in mice. However, the study further demonstrated that combining the vaccine with an immune checkpoint inhibitor -- an established immunotherapy drug with a 20% success rate overall for patients -- can vastly ...
Global food security: Climate change adaptation requires new cultivars
2021-05-18
Climate change induced yield reductions can be compensated by cultivar adaptation and global production can even be increased.
Global agriculture both is one of the major drivers of climate change and strongly affected by it. Rising temperatures are among the main reasons for yield reductions. Therefore, the agricultural sector is faced with the major challenge of adapting to climate change in order to ensure food security in the future. According to a new study carried out by international researchers, the use of locally adapted cultivars can significantly contribute to achieve this goal. The study ...
New research will allow convenient investigation of human innate immune response to viral infections
2021-05-18
(Boston)--Researchers from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) report the formation of human cells containing a green fluorescent protein or GFP (one of the most important proteins in biology and fluorescence imaging) genetically fused with two interferon stimulated genes (ISGs), namely Viperin and ISG15. This new creation makes these cells highly valuable reagents for reporting innate immune responses to viral infections, including those caused by coronaviruses.
These engineered cells, which turn green when treated with interferon, are highly novel because this is the first time a reporter gene (a gene ...
Nanofiber filter captures almost 100% of coronavirus aerosols
2021-05-18
A filter made from polymer nanothreads blew three kinds of commercial masks out of the water by capturing 99.9% of coronavirus aerosols in an experiment.
"Our work is the first study to use coronavirus aerosols for evaluating filtration efficiency of face masks and air filters," said corresponding author Yun Shen, a UC Riverside assistant professor of chemical and environmental engineering. "Previous studies have used surrogates of saline solution, polystyrene beads, and bacteriophages -- a group of viruses that infect bacteria."
The study, led by engineers at UC Riverside and The George Washington University, compared ...
New peanut has a wild past and domesticated present
2021-05-18
The wild relatives of modern peanut plants have the ability to withstand disease in ways that peanut plants can't. The genetic diversity of these wild relatives means that they can shrug off the diseases that kill farmers' peanut crops, but they also produce tiny nuts that are difficult to harvest because they burrow deep in the soil.
Consider it a genetic trade-off: During its evolution, the modern peanut lost its genetic diversity and much of the ability to fight off fungus and viruses, but gained qualities that make peanut so affordable, sustainable and tasty that people all over the world grow and eat them.
Modern peanut plants were created 5,000 to ...
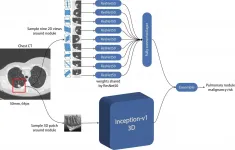
AI predicts lung cancer risk
2021-05-18
OAK BROOK, Ill. - An artificial intelligence (AI) program accurately predicts the risk that lung nodules detected on screening CT will become cancerous, according to a study published in the journal Radiology.
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death worldwide, with an estimated 1.8 million deaths in 2020, according to the World Health Organization. Low-dose chest CT is used to screen people at a high risk of lung cancer, such as longtime smokers. It has been shown to significantly reduce lung cancer mortality, primarily by helping to detect cancers at an early stage when they are easier to treat successfully.
While lung cancer typically shows up as pulmonary nodules on CT images, most nodules are benign ...
Towards a universal flu vaccine for Indigenous populations
2021-05-18
Researchers have identified specific influenza targets that could be used to better protect Indigenous people from experiencing severe influenza disease through a universal, T cell-based vaccine.
In a collaboration with Monash Biomedicine Discovery Institute, Menzies School of Health Research and CQUniversity, Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity (Doherty Institute) researchers took a deep-dive look into how the immune system can protect Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people from severe influenza disease.
"We know that some populations are at high risk from severe influenza, and these include Indigenous people ...
[1] ... [2323]
[2324]
[2325]
[2326]
[2327]
[2328]
[2329]
[2330]
2331
[2332]
[2333]
[2334]
[2335]
[2336]
[2337]
[2338]
[2339]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.