Advertising on popular made-for-kids online channels
2021-05-13
What The Study Did: Advertisements on videos on made-for-kids channels on YouTube, as well as the frequency of age-inappropriate ads, were analyzed in this study.
Authors: Jenny S. Radesky, M.D., of the University of Michigan Medical School in Ann Arbor, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.9890)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
Carbon emissions from dams considerably underestimated so far
2021-05-13
Among other things, dams serve as reservoirs for drinking water, agricultural irrigation, or the operation of hydropower plants. Until now, it had been assumed that dams act as net carbon stores. Researchers from the Helmholtz Centre of Environmental Research (UFZ) together with Spanish scientists from the Catalan Institute for Water Research (ICRA) in Girona and the University of Barcelona showed that dams release twice as much carbon as they store. The study has been published in Nature Geosciences.
Whether leaves, branches, or algae - streams transport large amounts of carbon-containing material. If the water is dammed, the material gradually settles and accumulates at the bottom ...
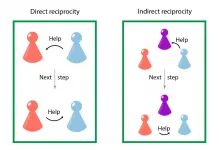
The emergence of cooperation
2021-05-13
Cooperation as a successful strategy has evolved in both nature and human society, but understanding its emergence can be a difficult task. Researchers have to abstract interactions between individuals into mathematical formulas to be able to create a model that can be used for predictions and simulations.
In the field of evolutionary game theory, they often investigate strategies of players in a simple game of giving and receiving benefits. Such strategies tell players how to behave in a given interaction. The scientists' findings counter the narrative that only the strongest and most selfish flourish and survive. Instead, they show how cooperation can be a successful and stable strategy.
Researchers, spearheaded by Laura Schmid ...
COVID-19: Majority of infected children may not show typical symptoms
2021-05-13
The majority of children infected with SARS-CoV-2 may not show typical symptoms such as fever, cough or shortness of breath, according to a study published in Scientific Reports, which examined data on 12,306 children with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 across the United States.
Pakaj Arora and colleagues found that 18.8% of the children included in the study were recorded as having symptoms such as fever, malaise, muscle or joint pain, and disturbances of smell or taste. . 16.5% of children had respiratory symptoms including cough and shortness of breath, 13.9% had gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, 8.1% had dermatological symptoms (rash), and 4.8% had headaches.
5.5% (672) of children included in the study were hospitalized. Of those, 118 (17.6%) and ...
Social media networking doesn't 'level the playing field' for women physicians
2021-05-13
CHICAGO --- For men physicians, the professional perks of networking on social media, like being asked to give a talk, are abundant, a new Northwestern Medicine study reports.
For women physicians, the benefits are far less plentiful, the study found.
What's more, women physicians are more than twice as likely to be sexually harassed on social media than men physicians, according to an earlier study, published in January, of this same group of study participants.
The findings mirror the struggles women physicians face in person when trying to advance their careers, ...
Adolescents and older adults lack attention in social situations
2021-05-13
New research led by the University of Kent has found that adolescents and older adults pay less attention to social cues in real-world interactions than young adults.
The findings published by Nature Human Behaviour show that social attention undergoes age-related change, which has potential implications for how successfully we can interpret social interactions in daily life and throughout the lifespan.
Interpreting the facial expression, tone of voice and gestures of others is a vital element of social interaction that allow us to make rapid inferences about others' mental states, such as their intentions, emotions, desires and beliefs. Successful social interaction prompts perspective-taking and empathy along with other essential ...
Triple-negative breast cancer more deadly for African American women
2021-05-13
Multiple studies have shown that African American women with breast cancer have lower survival rates than white women with the disease. But the association between race or ethnicity and treatment outcomes in triple-negative breast cancer -- an aggressive type of tumor that does not respond to hormonal or other targeted therapies -- has not been well defined.
Now, new research from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis shows that non-Hispanic African American women with triple-negative breast cancer also do not fare as well as non-Hispanic white women with this type of breast cancer. The study demonstrates the need for additional research to address disparities in cancer care and understand whether tumor biology or nonbiological reasons such as systemic racism -- ...
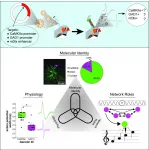
Songbird neurons for advanced cognition mirror the physiology of mammalian counterparts
2021-05-13
University of Massachusetts Amherst neuroscientists examining genetically identified neurons in a songbird's forebrain discovered a remarkable landscape of physiology, auditory coding and network roles that mirrored those in the brains of mammals.
The research, published May 13 in Current Biology, advances insight into the fundamental operation of complex brain circuits. It suggests that ancient cell types in the pallium - the outer regions of the brain that include cortex - most likely retained features over millions of years that are the building blocks for advanced cognition in birds and mammals.
"We as neuroscientists are catching on that birds can do sophisticated things and they have sophisticated circuits to do those things," ...
Antarctic ice sheet retreat could trigger chain reaction
2021-05-13
The Antarctic ice sheet was even more unstable in the past than previously thought, and at times possibly came close to collapse, new research suggests.
The findings raise concerns that, in a warmer climate, exposing the land underneath the ice sheet as it retreats will increase rainfall on Antarctica, and this could trigger processes that accelerate further ice loss.
The research is based on climate modelling and data comparisons for the Middle Miocene (13-17 million years ago) when atmospheric carbon dioxide and global temperatures reached levels similar to those expected by the end of this century.
The study was carried out by ...
New evidence for electron's dual nature found in a quantum spin liquid
2021-05-13
A new discovery led by Princeton University could upend our understanding of how electrons behave under extreme conditions in quantum materials. The finding provides experimental evidence that this familiar building block of matter behaves as if it is made of two particles: one particle that gives the electron its negative charge and another that supplies its magnet-like property, known as spin.
"We think this is the first hard evidence of spin-charge separation," said Nai Phuan Ong, Princeton's Eugene Higgins Professor of Physics and senior author on the paper published this week in the journal Nature Physics.
The experimental results fulfill a prediction made decades ago to explain one of the most mind-bending states ...
Ingredient in common weed killer impairs insect immune systems, study suggests
2021-05-13
The chemical compound glyphosate, the world's most widely used herbicide, can weaken the immune systems of insects, suggests a study from researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. Glyphosate is the active ingredient in Round Up™, a popular U.S. brand of weed killer products.
The researchers investigated the effects of glyphosate on two evolutionarily distant insects, Galleria mellonella, the greater wax moth, and Anopheles gambiae, a mosquito that is an important transmitter of malaria to humans in Africa. They found that ...
Study: Drivers with shift work sleep disorder 3x more likely to be in crash
2021-05-13
People who work nontraditional work hours, such as 11 p.m.-7 p.m., or the "graveyard" shift, are more likely than people with traditional daytime work schedules to develop a chronic medical condition -- shift work sleep disorder -- that disrupts their sleep. According to researchers at the University of Missouri, people who develop this condition are also three times more likely to be involved in a vehicle accident.
"This discovery has many major implications, including the need to identify engineering counter-measures to help prevent these crashes from happening," said Praveen Edara, department chair and professor of civil and environmental ...
Treating the COVID-19 'infodemic' as an epidemic
2021-05-13
Writing in the New England Journal of Medicine, a trio of science communication researchers proposes to treat the Covid-19 misinformation "infodemic" with the same methods used to halt epidemics.
"We believe the intertwining spreads of the virus and of misinformation and disinformation require an approach to counteracting deceptions and misconceptions that parallels epidemiologic models by focusing on three elements: real-time surveillance, accurate diagnosis, and rapid response," the authors write in a Perspective article.
"The word 'communicable' comes from the Latin communicare, ...
Many do not recognise animal agriculture's link to infectious diseases
2021-05-13
New research led by the University of Kent has found that people fail to recognise the role of factory farming in causing infectious diseases.
The study published by Appetite demonstrates that people blame wild animal trade or lack of government preparation for epidemic outbreaks as opposed to animal agriculture and global meat consumption.
Scientists forewarned about the imminence of global pandemics such as Covid-19, but humankind failed to circumvent its arrival. They had been warning for decades about the risks of intensive farming practices for public health. The scale of production and overcrowded conditions on factory farms make it easy for viruses to migrate and spread. Furthermore, ...
NK cells with bispecific antibody show activity against lymphoma cells
2021-05-13
HOUSTON - Cytokine-activated natural killer (NK) cells derived from donated umbilical cord blood, combined with an investigational bispecific antibody targeting CD16a and CD30 known as AFM13, displayed potent anti-tumor activity against CD30+ lymphoma cells, according to a new preclinical study from researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
The findings were published today in Clinical Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. These results led to the launch of a Phase I clinical trial to evaluate the combination of cord blood-derived NK cells (cbNK cells) with AFM13 as an experimental cell-based immunotherapy in patients with CD30+ lymphoma.
"Developing novel NK cell therapies has been a priority for my ...
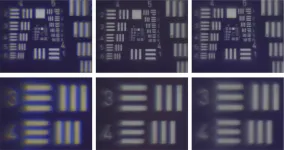
Researchers 3D print complex micro-optics with improved imaging performance
2021-05-13
WASHINGTON -- In a new study, researchers have shown that 3D printing can be used to make highly precise and complex miniature lenses with sizes of just a few microns. The microlenses can be used to correct color distortion during imaging, enabling small and lightweight cameras that can be designed for a variety of applications.
"The ability to 3D print complex micro-optics means that they can be fabricated directly onto many different surfaces such as the CCD or CMOS chips used in digital cameras," said Michael Schmid, a member of the research team from University of Stuttgart in Germany. "The micro-optics can ...
Species losses on isolated Panamanian island show importance of habitat connectivity
2021-05-13
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Free from human disturbance for a century, an inland island in Central America has nevertheless lost more than 25% of its native bird species since its creation as part of the Panama Canal's construction, and scientists say the losses continue.
The Barro Colorado Island extirpations show how forest fragmentation can reduce biodiversity when patches of remnant habitat lack connectivity, according to a study by researchers at Oregon State University.
Even when large remnants of forest are protected, some species still fail to survive because of subtle ...
Scientists identify source of weight gain from antipsychotics
2021-05-13
DALLAS - May 12, 2021 - Scientists with UT Southwestern's Peter O'Donnell Jr. Brain Institute have identified the molecular mechanism that can cause weight gain for those using a common antipsychotic medication. The findings, published in the Journal of Experimental Medicine, suggest new ways to counteract the weight gain, including a drug recently approved to treat genetic obesity, according to the study, which involved collaborations with scientists at UT Dallas and the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology.
"If this effect can be shown in clinical trials, it could give us a way to effectively treat ...
Mixing massive stars
2021-05-13
Astronomers commonly refer to massive stars as the chemical factories of the Universe. They generally end their lives in spectacular supernovae, events that forge many of the elements on the periodic table. How elemental nuclei mix within these enormous stars has a major impact on our understanding of their evolution prior to their explosion. It also represents the largest uncertainty for scientists studying their structure and evolution.
A team of astronomers led by May Gade Pedersen, a postdoctoral scholar at UC Santa Barbara's Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics, have now measured the internal mixing within an ensemble of these stars using observations ...
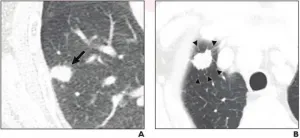
CT promising for sublobar resection in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer
2021-05-13
Leesburg, VA, May 13, 2021--According to an open-access Editor's Choice article in ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), CT features may help identify which patients with stage IA non-small cell lung cancer are optimal candidates for sublobar resection, rather than more extensive surgery.
This retrospective study included 904 patients (453 men, 451 women; mean age, 62 years) who underwent lobectomy (n=574) or sublobar resection (n=330) for stage IA non-small cell lung cancer. Two thoracic radiologists independently evaluated findings on preoperative chest CT, later resolving any discrepancies. Recurrences were identified via medical record review.
"In patients with stage IA non-small cell lung cancer, pathologic ...
COVID-19 mRNA vaccines are immunogenic in pregnant and lactating women
2021-05-13
Boston - Pregnant women with symptomatic COVID-19 have a higher risk of intensive care unit admissions, mechanical ventilation and death compared to non-pregnant reproductive age women. Increases in preterm birth and still birth have also been observed in pregnancies complicated by the viral infection. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommended that people who are pregnant may choose to be vaccinated at their own discretion with their healthcare provider. However, pregnant and lactating women were not included in Phase 3 vaccine efficacy trials; thus, data on vaccine safety and immunogenicity in this population is limited.
In a new study from Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC), ...
High genomic diversity is good news for California condor
2021-05-13
Despite having been driven nearly to extinction, the California condor has a high degree of genetic diversity that bodes well for its long-term survival, according to a new analysis by University of California researchers.
Nearly 40 years ago, the state's wild condor population was down to a perilous 22. That led to inbreeding that could have jeopardized the population's health and narrowed the bird's genetic diversity, which can reduce its ability to adapt to changing environmental conditions.
In comparing the complete genomes of two California condors with those of an Andean condor and a turkey vulture, UC San Francisco and UC Berkeley scientists did find genetic evidence of inbreeding over the past few centuries, but, overall, a ...
Evolutionary biologists discover mechanism that enables lizards to breathe underwater
2021-05-13
TORONTO, ON - A team of evolutionary biologists from the University of Toronto has shown that Anolis lizards, or anoles, are able to breathe underwater with the aid of a bubble clinging to their snouts.
Anoles are a diverse group of lizards found throughout the tropical Americas. Some anoles are stream specialists, and these semi-aquatic species frequently dive underwater to avoid predators, where they can remain submerged for as long as 18 minutes.
"We found that semi-aquatic anoles exhale air into a bubble that clings to their skin," says Chris Boccia, a recent Master of Science graduate from the Faculty of Arts & Science's Department of Ecology ...
Urban traffic noise causes song learning deficits in birds
2021-05-13
Traffic noise leads to inaccuracies and delays in the development of song learning in young birds. They also suffer from a suppressed immune system, which is an indicator of chronic stress. A new study by researchers of the Max Planck Institute for Ornithology and colleagues shows that young zebra finches, just like children, are particularly vulnerable to the effects of noise because of its potential to interfere with learning at a critical developmental stage.
Traffic noise is a pervasive pollutant that adversely affects the health and well-being ...
Study finds mechanism leading to herceptin resistance and Rx approach to reverse it
2021-05-13
New Orleans, LA - Research conducted by an international team of scientists discovered a mechanism that leads to Herceptin resistance, representing a significant clinical obstacle to successfully treating HER2-positive breast cancer. They also identified a new approach to potentially overcome it. The work is published online in Nature Communications, available here.
"This work attempts to understand why some HER2-positive breast cancer patients do not benefit from treatment with Herceptin, which is a generally effective HER2-targeted therapy," explains Bolin Liu, MD, Professor of Genetics at LSU Health New Orleans' School of Medicine and Stanley S. Scott Cancer Center.
The researchers found increased signaling by IGF2/IRS1 (genes involved in ...
[1] ... [2315]
[2316]
[2317]
[2318]
[2319]
[2320]
[2321]
[2322]
2323
[2324]
[2325]
[2326]
[2327]
[2328]
[2329]
[2330]
[2331]
... [8812]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.