Youths with diverse gender identities bullied up to three times more than peers
2021-05-12
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Young people with diverse gender identities may be bullied and victimized up to three times more often than peers who identify as male or female, a new study of more than 4,464 adolescents in Illinois found.
The students were part of a statewide survey of eighth- through 12th-grade youths in Illinois schools.
"Transgender youths reported the highest rates of all forms of peer victimization, which were double to nearly triple those of males and up to 2.6 times higher than those of females," said social work professor Rachel Garthe of the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, who led the research.
"Slightly ...
Brain research gets a boost from mosquitos
2021-05-12
Can a protein found in a mosquito lead to a better understanding of the workings of our own brains? Prof. Ofer Yizhar and his team in the Weizmann Institute of Science's Neurobiology Department took a light-sensitive protein derived from mosquitos and used it to devise an improved method for investigating the messages that are passed from neuron to neuron in the brains of mice. This method, reported today in Neuron, could potentially help scientists solve age-old cerebral mysteries that could pave the way for new and improved therapies to treat neurological and psychiatric conditions.
Yizhar and his lab team develop so-called optogenetic methods - research techniques that allow them to "reverse engineer" the activity of specific brain circuits ...
Fighting food insecurity by building better beans
2021-05-12
EAST LANSING, Mich. - As climate change threatens global food security, researchers at Michigan State University are building better beans crucial to human nutrition by tapping into the genetics of the more heat-resistant tepary bean.
The tepary bean (Phaseolus acutifolius A. Gray) is a sister of the common bean which includes kidney, pinto and navy beans. "The common bean is the number one source of protein and nutrients for many people living in Central America and Africa," said Robin Buell, a professor of plant biology in MSU's College of Natural Science and former director of the Plant Resilience Institute.
Her research on bean genetics was published May 11 in Nature Communications.
"Mother nature has already made plants that are adapted to different climates," ...
Building molecules like Tinkertoys? A breakthrough study may pave the way
2021-05-12
Molecules are the building blocks for our modern world, from phones to cars to Doritos. But coming up with new ones is still an incredibly costly and time-consuming process. A group of University of Chicago chemists wants to find a better way.
"If you look at a diagram of a molecule, it seems like you should be able to just snap them together like Tinkertoys, but you can't," said Asst. Prof. Mark Levin. "We'd like to change that."
Their new discovery, published May 12 in Nature, represents a first step towards that transformation: a way to easily cut nitrogen atoms from molecules.
Despite decades of experiments, chemistry remains an art in many ways because molecules are built in a long, iterative process: attaching ...
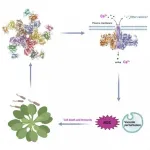
Scientists uncover how resistance proteins protect plants from pathogens
2021-05-12
In plants, disease resistance proteins serve as major immune receptors that sense pathogens and pests and trigger robust defense responses. Scientists previously found that one such disease resistance protein, ZAR1, is transformed into a highly ordered protein complex called a resistosome upon detection of invading pathogens, providing the first clue as to how plant disease resistance proteins work. Precisely how a resistosome activates plant defenses, however, has been unclear.
A joint team led by Profs. ZHOU Jianmin, CHEN Yuhang and HE Kangmin at the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Prof. CHAI Jijie at Tsinghua University recently employed state-of-the-art electrophysiology and single-molecule imaging to investigate the molecular ...
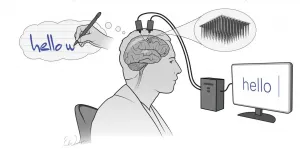
Brain computer interface turns mental handwriting into text on screen
2021-05-12
Scientists are exploring a number of ways for people with disabilities to communicate with their thoughts. The newest and fastest turns back to a vintage means for expressing oneself: handwriting.
For the first time, researchers have deciphered the brain activity associated with trying to write letters by hand. Working with a participant with paralysis who has sensors implanted in his brain, the team used an algorithm to identify letters as he attempted to write them. Then, the system displayed the text on a screen - in real time.
The innovation could, with further development, let people with paralysis rapidly ...
Brain-computer interface creates text by decoding brain signals associated with handwriting
2021-05-12
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- Researchers with the BrainGate collaboration have, for the first time, used an implanted sensor to record the brain signals associated with handwriting, and used those signals to create text on a computer in real time.
In a study published in the journal Nature, a clinical trial participant with cervical spinal cord injury used the system to "type" words on a computer at a rate of 90 characters per minute, more than double the previous record for typing with a brain-computer interface. This was done by the participant merely thinking about the hand motions involved in creating written letters.
The research team is hopeful that such a system could one day help to restore ...
Study reveals structure of key receptors involved in memory and learning
2021-05-12
Scientists have for the first time revealed the structure surrounding important receptors in the brain's hippocampus, the seat of memory and learning.
The study, carried out at Oregon Health & Science University, published today in the journal Nature.
The new study focuses on the organization and function of glutamate receptors, a type of neurotransmitter receptor involved in sensing signals between nerve cells in the hippocampus region of the brain. The study reveals the molecular structure of three major complexes of glutamate receptors in the hippocampus.
The findings may be immediately useful in drug development for conditions such as epilepsy, said senior author Eric Gouaux, Ph.D., senior scientist in the OHSU Vollum Institute, ...
Stanford scientists' software turns 'mental handwriting' into on-screen words, sentences
2021-05-12
Stanford scientists' software turns 'mental handwriting' into on-screen words, sentences
Call it "mindwriting."
The combination of mental effort and state-of-the-art technology have allowed a man with immobilized limbs to communicate by text at speeds rivaling those achieved by his able-bodied peers texting on a smartphone.
Stanford University investigators have coupled artificial-intelligence software with a device, called a brain-computer interface, implanted in the brain of a man with full-body paralysis. The software was able to decode information from the BCI to quickly convert the man's thoughts about handwriting into text on a computer screen.
The man was able to write ...
Drug overdose deaths before, after shelter-in-place orders during COVID-19 pandemic in San Francisco
2021-05-12
What The Study Did: Researchers describe overdose deaths in San Francisco before and after the initial COVID-19 shelter-in-place order to try to make clear whether characteristics of fatal overdoses changed during this time in an effort to guide future prevention efforts.
Authors: Luke N. Rodda, Ph.D., of the Office of the Chief Medical Examiner for the city and county of San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10452)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, ...
Perinatal outcomes during COVID-19 pandemic in Ontario, Canada
2021-05-12
What The Study Did: Rates of preterm birth and stillbirth in Ontario, Canada, during the first six months of the COVID-19 pandemic are evaluated in this study.
Authors: Andrea N. Simpson, M.D., M.Sc., of St Michael's Hospital, Unity Health Toronto, in Toronto, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10104)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this news release.
Embed this ...
Violence-related medical treatment among US children, adolescents
2021-05-12
What The Study Did: This survey study estimated the number of children and adolescents in the United States who have received medical care as a result of assault, abuse or exposure to violence.
Authors: David Finkelhor, Ph.D., of the University of New Hampshire in Durham, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.9250)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and ...
Sunburn injuries in Australia, New Zealand
2021-05-12
What The Study Did: Researchers used registry data to examine the number, characteristics and outcomes of patients with sunburns severe enough to warrant admission to specialist burn services in Australia and New Zealand.
Authors: Lincoln M. Tracy, Ph.D., of Monash University in Melbourne, Australia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.1110)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, ...
Delayed localized hypersensitivity reactions to Moderna COVID-19 vaccine
2021-05-12
What The Study Did: Delayed localized injection-site reactions to the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine for 16 patients are described in this report.
Authors: Alicia J. Little, M.D., Ph.D., of the Yale University School of Medicine in New Haven, Connecticut, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.1214)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict ...
Mitochondrial enzyme found to block cell death pathway points to new cancer treatment strategy
2021-05-12
HOUSTON - The mitochondrial enzyme dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) plays an important and previously unknown role in blocking a form of cell death called ferroptosis, according to a new study published today in Nature by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. Preclinical findings suggest that targeting DHODH can restore ferroptosis-driven cell death, pointing to new therapeutic strategies that may be used to induce ferroptosis and inhibit tumor growth.
"By understanding ferroptosis and how cells defend against it, we can develop therapeutic strategies to block those defense mechanisms and trigger cell death," said senior author Boyi Gan, Ph.D., associate professor of Experimental ...
Researchers reveal the internal signals cells use to maintain energy
2021-05-12
LA JOLLA, CALIF. - May 12, 2021 - Scientists at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute have taken a deep dive into a previously overlooked family of proteins and discovered that they are essential to maintaining the energy that cells need to grow and survive. The proteins, known as lipid kinases, produce messengers that help balance cellular metabolism and promote overall health. The findings, published in Developmental Cell, provide further support to pursue lipid kinases as promising therapeutic targets for diseases that demand excess energy, such as cancer.
"Cancer cells are hungry--they grow faster than most cell types and need energy to support their aggressive attempts to metastasize," says Brooke Emerling, Ph.D., assistant professor in the ...
Online CBT effective for social anxiety disorder in young people
2021-05-12
Social anxiety disorder can cause considerable suffering in children and adolescents and, for many with the disorder, access to effective treatment is limited. Researchers at Centre for Psychiatry Research at Karolinska Institutet and Region Stockholm in Sweden have now shown that internet-delivered cognitive behavioural therapy is an efficacious and cost-effective treatment option. The study is published in the journal JAMA Psychiatry.
Social anxiety disorder (SAD, previously known as social phobia) has a typical onset during childhood and is characterised by an intense and persistent fear of being scrutinised and negatively evaluated in social or performance situations.
The fear typically leads to avoidance of such anxiety triggering situations or are endured under great ...
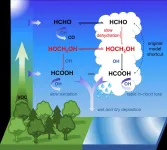
Mechanism deciphered: How organic acids are formed in the atmosphere
2021-05-12
The acidity of the atmosphere is increasingly determined by carbon dioxide and organic acids such as formic acid. The second of these contribute to the formation of aerosol particles as a precursor of raindrops and therefore impact the growth of clouds and pH of rainwater. In previous atmospheric chemistry models of acid formation, formic acid tended to play a small role. The chemical processes behind its formation were not well understood. An international team of researchers under the aegis of Forschungszentrum Jülich has now succeeded in filling this gap and deciphering the dominant ...
A long-lasting, stable solid-state lithium battery
2021-05-12
Long-lasting, quick-charging batteries are essential to the expansion of the electric vehicle market, but today's lithium-ion batteries fall short of what's needed -- they're too heavy, too expensive and take too long to charge.
For decades, researchers have tried to harness the potential of solid-state, lithium-metal batteries, which hold substantially more energy in the same volume and charge in a fraction of the time compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries.
"A lithium-metal battery is considered the holy grail for battery chemistry because of its high capacity and energy density," said Xin Li, Associate Professor ...
Composing thoughts: Mental handwriting produces brain activity turned into text
2021-05-12
Scientists have developed a brain-computer interface (BCI) designed to restore the ability to communicate in people with spinal cord injuries and neurological disorders such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). This system has the potential to work more quickly than previous BCIs, and it does so by tapping into one of the oldest means of communications we have--handwriting.
The study, published in Nature, was funded by the National Institutes of Health's Brain Research Through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies® (BRAIN) Initiative as well as the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) and the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD), both part of the NIH.
Researchers focused on the part of the brain ...
Study finds six degrees celsius cooling on land during the last Ice Age
2021-05-12
Woods Hole, Mass. (May 12, 2021) -- Low-to-mid latitude land surfaces at low elevation cooled on average by 5.8 ± 0.6 degrees C during the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), based on an analysis of noble gases dissolved in groundwater, according to a new study published in Nature.
Temperature estimates in the study are substantially lower than indicated by some notable marine and low-elevation terrestrial studies that have relied on various proxies to reconstruct past temperatures during the LGM, a period about 20,000 years ago that represents the most recent extended period ...
Research team investigates causes of tuberous sclerosis
2021-05-12
Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC) affects between one and two of every 10,000 new-born babies. This genetic disease leads to the formation of benign tumours which can massively impair the proper functioning of vital organs such as the kidneys, the liver and the brain. The disease affects different patients to varying degrees and is triggered by mutations in one of two genes, the TSC1 or TSC2 gene. An interdisciplinary team of researchers led by biochemists Prof. Daniel Kümmel and Dr. Andrea Oeckinghaus from the University of Münster (Germany) examined the "tumour suppressor protein TSC1" and, for the first time, gained insights into its hitherto unclear functions. The team identified a new mechanism, in a central cellular process, which regulates ...
Prehistoric horses, bison shared diet
2021-05-12
University of Cincinnati researchers studied the teeth of prehistoric horses and bison in the Arctic to learn more about their diets compared to modern species.
What they found suggests the Arctic 40,000 years ago maintained a broader diversity of plants that, in turn, supported both more -- and more diverse -- big animals.
The Arctic today is spartan compared to the wildlife-rich landscape during the ice ages of the Pleistocene epoch between 12,000 and 2.6 million years ago when wild horses, mammoths, bison and other big animals roamed the steppes and grasslands of what is now northern Canada, northern Europe, Alaska and Siberia. Short-faced bears, ground sloths and even cave lions called the 49th State home.
The Arctic supported greater populations ...
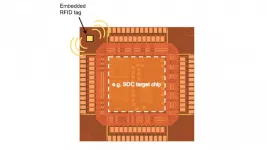
Smaller chips open door to new RFID applications
2021-05-12
Researchers at North Carolina State University have made what is believed to be the smallest state-of-the-art RFID chip, which should drive down the cost of RFID tags. In addition, the chip's design makes it possible to embed RFID tags into high value chips, such as computer chips, boosting supply chain security for high-end technologies.
"As far as we can tell, it's the world's smallest Gen2-compatible RFID chip," says Paul Franzon, corresponding author of a paper on the work and Cirrus Logic Distinguished Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering at NC State.
Gen2 RFID chips are state of the art and are already in widespread use. One of the things that sets ...
Organic meat less likely to be contaminated with multidrug-resistant bacteria, study suggests
2021-05-12
Meat that is certified organic by the U.S. Department of Agriculture is less likely to be contaminated with bacteria that can sicken people, including dangerous, multidrug-resistant organisms, compared to conventionally produced meat, according to a study from researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
The findings highlight the risk for consumers to contract foodborne illness--contaminated animal products and produce sicken tens of millions of people in the U.S. each year--and the prevalence of multidrug-resistant organisms that, when they lead to illness, can complicate treatment.
The researchers found that, compared to conventionally processed meats, organic-certified meats were 56 percent less likely to be contaminated with ...
[1] ... [2319]
[2320]
[2321]
[2322]
[2323]
[2324]
[2325]
[2326]
2327
[2328]
[2329]
[2330]
[2331]
[2332]
[2333]
[2334]
[2335]
... [8812]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.