(Press-News.org) Irvine, Calif., Jan. 6, 2021-- In the United States, Black, Latino and low-income communities have historically lacked nearby access to pharmacy services. To provide the first record of these "pharmacy deserts" in Los Angeles County, a University of California, Irvine study identified communities where the nearest pharmacy was at least one mile away.
Unlike previous studies, this one describes pharmacy deserts in terms of social determinants of health - such as owning a vehicle, crime rates and poverty - to determine which communities have the greatest need for pharmacy access. Published in the Journal of Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities, it is the first study to look at pharmacy deserts in the state of California.
"My goal is to bring these concepts together at the intersection of pharmacy practice, public health and social justice to reduce health disparities," said Cheryl Wisseh, a health sciences assistant clinical professor of clinical pharmacy practice at UCI and the study's first author.
The study was conducted in collaboration with researchers at Charles R. Drew University of Medicine and Science in Los Angeles.
They found that some Los Angeles County areas lacking pharmacy access are characterized by denser populations, larger numbers of Latino and Black residents, less vehicle and home ownership, higher crime rates, and greater poverty.
"These social determinants of health compound the negative effects of pharmacy shortage through competing needs," Wisseh said. "For example, some residents living below the poverty line may choose to forgo picking up their medications so that they can pay for food, rent and other necessities."
A pharmacy shortage likely equates to fewer clinical pharmacy services, such as health screenings, vaccines and medication management, Wisseh added.
Since pharmacies are a large distributor of vaccines across the U.S., the COVID-19 pandemic makes access to pharmacists even more pressing.
"As the COVID-19 vaccines start rolling out, pharmacists will be key to the rapid and equitable distribution and administration of doses, just as they have been with COVID-19 testing," said Jan D. Hirsch, founding dean of the UCI's School of Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences.
Wisseh added that the communities within pharmacy deserts are particularly vulnerable to COVID-19.
"The same forces of structural inequity and systemic racism that contribute to the formation of Los Angeles pharmacy deserts contribute to the disproportionate test positivity, incidence and mortality rates of COVID-19 in racial and ethnic minorities," she said.
"Residents in Los Angeles County pharmacy deserts might benefit greatly from equitable, innovative, community-based interventions that increase access to medications, pharmacy services and pharmacists," the researchers wrote in the study. For instance, the county could add pharmacists to local clinics and other primary care settings to provide clinical services. In her own clinical practice, Wisseh works with county-led programs in South Los Angeles to improve pharmacy access for patients.
Wisseh plans to conduct a similar study on a larger scale - perhaps across California - to examine how pharmacy deserts contribute to whether minority communities take medications as prescribed and investigate disparities in available medications within pharmacies.
INFORMATION:
About the University of California, Irvine: Founded in 1965, UCI is the youngest member of the prestigious Association of American Universities. The campus has produced three Nobel laureates and is known for its academic achievement, premier research, innovation and anteater mascot. Led by Chancellor Howard Gillman, UCI has more than 36,000 students and offers 222 degree programs. It's located in one of the world's safest and most economically vibrant communities and is Orange County's second-largest employer, contributing $5 billion annually to the local economy. For more on UCI, visit http://www.uci.edu.
Media access: Radio programs/stations may, for a fee, use an on-campus ISDN line to interview UCI faculty and experts, subject to availability and university approval. For more UCI news, visit news.uci.edu. Additional resources for journalists may be found at communications.uci.edu/for-journalists.
NOTE TO EDITORS: PHOTO AND IMAGE AVAILABLE AT
https://news.uci.edu/2021/01/06/uci-study-first-to-link-disparities-and-pharmacy-deserts-in-california/
Contact:
Nicole Feldman
949-501-9192
nefeldma@uci.edu
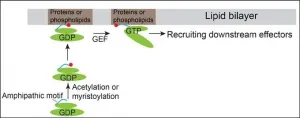
The small GTPases of the ADP-ribosylation factor (Arf) family are key initiators of various physiological processes including secretion, endocytosis, phagocytosis and signal transduction. Arf family proteins function to mediate recruitment of cytosolic effectors to specific subcellular compartments. This process facilitates Arf effectors to perform cargo recognition, lipid modification or other cellular functions. Blocking the activities of Arf family proteins inhibits secretion of important molecules from the cell and also inhibits cellular uptake of nutrients. Defects in Arfs or their regulatory proteins are related to various inherited diseases, including X-linked intellectual disability (XLID), Joubert syndrome, Bardet-Biedl syndrome and cilia dysfunction. Thus, studying molecular ...
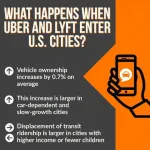
When ridesourcing companies Uber and Lyft show up in urban areas, vehicle registrations per capita increase by 0.7% on average, increasing even more in car-dependent cities. Researchers reporting in the journal iScience on January 6 made this discovery by analyzing data from major US cities between 2011 to 2017, comparing trends in cities where Uber and Lyft entered with those where they didn't. They also found that Uber and Lyft displace transit more in cities with higher income and fewer children.
"I would have expected people to own fewer vehicles once they gain access to this alternative transportation mode," says Jeremy Michalek, a professor of engineering and public policy at Carnegie Mellon University and co-author ...
Researchers have successfully used a DNA-editing technique to extend the lifespan of mice with the genetic variation associated with progeria, a rare genetic disease that causes extreme premature aging in children and can significantly shorten their life expectancy. The study was published in the journal Nature, and was a collaboration between the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), part of the National Institutes of Health; Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT, Boston; and the Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee.?
DNA is made up of four chemical bases -- A, C, G and T. Progeria, which is also known as Hutchinson-Gilford ...
A new class of protein material that interacts with living cells without being absorbed by them can influence cell signaling, a new study shows. The material does this by binding and sequestering cell surface receptors.
The discovery could have far-reaching implications for stem cell research and enable the development of new materials designed to modulate the behavior of living systems.
The research, reported in the January 6 edition of Nature, was led by the Baker lab at the University of Washington School of Medicine and the Derivery lab at the Medical Research Council Laboratory of Molecular Biology in Cambridge, U.K. Their paper is titled, Design of Biologically Active Binary Protein 2D Materials.
Cells ...
The westerlies--or westerly winds--play an important role in weather and climate both locally and on a global scale, by influencing precipitation patterns, impacting ocean circulation and steering tropical cyclones. So, finding a way to assess how they will change as the climate warms is crucial.
Typically, the westerlies blow from west to east across the planet's middle latitudes. But scientists have noticed that over the last several decades, these winds are changing, migrating poleward. Research suggests this is because of climate change. But, scientists have been debating whether the poleward movement of ...
What The Study Did: The findings of this survey study suggest that simply providing maps with COVID-19 case information wasn't necessarily associated with improved public knowledge, risk perception or reported intent to adhere to health guidelines.
Authors: Angela Fagerlin, Ph.D., of the University of Utah in Salt Lake City, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.33538)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional ...
What The Study Did: Changes in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests and fatalities in the Detroit area during the COVID-19 pandemic are compared with year-earlier events for the same period in this observational study.
Authors: Adrienne V. Nickles, M.P.H., of the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services in Lansing, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.32331)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media ...
Writing, driving a screw or throwing darts are only some of the activities that demand a high level of skill. How the brain masters such exquisite movements has now been described in the journal "Nature" by a team of researchers at the University of Basel and the Friedrich Miescher Institute for Biomedical Research. A map of brainstem circuits reveals which neurons control the fine motor skills of the arm and hand.
Picking up a pen and writing our name or reaching for a fork to eat spaghetti with tomato sauce are things we take for granted. However, holding a pen properly or bringing spaghetti to the mouth without making a mess requires precise ...
Chinese scientists from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have found a gene that plays an important role in helping rice adapt to low soil nitrogen.
Nitrogen fertilizer application is a strategic challenge for sustainable agriculture: On the one hand, it plays an indispensable role in increasing crop yields, thus ensuring global food security. On the other hand, it creates a severe threat to ecosystems. For this reason, breeding new crop varieties with high nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) is a high priority for both agricultural production and environmental protection.
Using a diversified rice population derived from different ecogeographical regions, the scientists carefully evaluated how various agronomic traits responded to ...
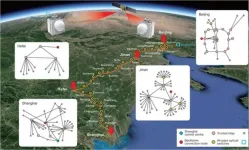
Chinese scientists have established the world's first integrated quantum communication network, combining over 700 optical fibers on the ground with two ground-to-satellite links to achieve quantum key distribution over a total distance of 4,600 kilometers for users across the country. The team, led by Jianwei Pan, Yuao Chen, Chengzhi Peng from the University of Science and Technology of China in Hefei, reported in Nature their latest advances towards the global, practical application of such a network for future communications.
Unlike conventional encryption, quantum communication is considered ...