Lockdown led to positive lifestyle changes in older people
2021-05-14
The COVID-19 lockdown was a catalyst for many older people to embrace technology, reconnect with friends and build new relationships with neighbours, according to University of Stirling research.
Understanding the coping mechanisms adopted by some over 60s during the pandemic will play a key role in developing interventions to help tackle loneliness, isolation and wellbeing in the future.
The study, led by the Faculty of Health Sciences and Sport, surveyed 1,429 participants - 84 percent (1,198) of whom were over 60 - and found many had adapted to video conferencing technology to increase ...
Solar wind from the center of the Earth
2021-05-14
High-precision noble gas analyses indicate that solar wind particles from our primordial Sun were encased in the Earth's core over 4.5 billion years ago. Researchers from the Institute of Earth Sciences at Heidelberg University have concluded that the particles made their way into the overlying rock mantle over millions of years. The scientists found solar noble gases in an iron meteorite they studied. Because of their chemical composition, such meteorites are often used as natural models for the Earth's metallic core.
The rare class of iron meteorites ...
New perspective on stress pandemics and human resilience from the analysis of COVID-19
2021-05-14
A new analysis of the effects of SARS-CoV-2, the virus causing the current pandemic, on the human body has provided novel insights into the nature of resilience and how we deal with stressful situations. Using COVID-19 as an example, the findings provide a new framework that may be central to managing this disease, minimise the likelihood of ferocious viral outbreaks in the future and deal with other major stresses.
"COVID-19 has been a huge burden on society at all levels. Whilst the prospects are improving in countries with efficient vaccination schemes ...
Maternal stress during pregnancy may shorten lifespans of male lizard offspring
2021-05-14
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Mother fence lizards that experience stress during pregnancy give birth to male offspring with shortened telomeres, or bits of non-coding DNA that cap the ends of chromosomes, according to a Penn State-led study. Shorter telomeres are associated with decreased lifespan in humans; therefore, the team's findings may have implications for human longevity.
"Human men have shorter telomeres than women, which may partly explain why they have shorter lifespans of about seven years," said Tracy Langkilde, professor and Verne M. Willaman dean of the Eberly College of Science. "Our study shows that stress experienced by mothers during gestation could further shorten the telomeres, and therefore the lifespans, of their sons, thereby exacerbating these sex differences." ...
Businesses have a moral duty to explain how algorithms make decisions that affect people
2021-05-14
Increasingly, businesses rely on algorithms that use data provided by users to make decisions that affect people. For example, Amazon, Google, and Facebook use algorithms to tailor what users see, and Uber and Lyft use them to match passengers with drivers and set prices. Do users, customers, employees, and others have a right to know how companies that use algorithms make their decisions? In a new analysis, researchers explore the moral and ethical foundations to such a right. They conclude that the right to such an explanation is a moral right, then address how companies might do so.
The analysis, by researchers at Carnegie Mellon University, appears in Business Ethics Quarterly, a publication of the Society for Business Ethics.
"In most cases, ...
Male hormones regulate stomach inflammation in mice
2021-05-14
Scientists at the National Institutes of Health determined that stomach inflammation is regulated differently in male and female mice after finding that androgens, or male sex hormones, play a critical role in preventing inflammation in the stomach. The finding suggests that physicians could consider treating male patients with stomach inflammation differently than female patients with the same condition. The study was published in Gastroenterology.
Researchers at NIH's National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS) made the discovery after removing adrenal glands from mice of both sexes. Adrenal glands produce glucocorticoids, hormones that have several functions, one of them being suppressing inflammation. With no glucocorticoids, the female mice soon ...
Is the past (and future) there when nobody looks?
2021-05-14
In 1961, the Nobel prize winning theoretical physicist Eugene Wigner proposed what is now known as the Wigner's friend thought experiment as an extension of the notorious Schroedinger's cat experiment. In the latter, a cat is trapped in a box with poison that will be released if a radioactive atom decays. Governed by quantum mechanical laws, the radioactive atom is in a superposition between decaying and not decaying, which also means that the cat is in a superposition between life and death. What does the cat experience when it is in the superposition? ...
Ion transporters in chloroplasts affect the efficacy of photosynthesis
2021-05-14
A study led by LMU plant biologist Hans-Henning Kunz uncovers a new role for ion transporters: they participate in gene regulation in chloroplasts.
In plants, photosynthesis takes place in intracellular 'factories' called chloroplasts. Plant chloroplasts evolved from photosynthetic cyanobacteria, which were engulfed by a non-photosynthetic cell in the course of evolution. As a result of this evolutionary event, chloroplasts possess two envelope membranes, and have retained functional remnants of their original cyanobacterial genomes. Henning Kunz (LMU Biocenter), his group, and their collaborators have now demonstrated that ...
Finding control in hard-to-predict systems
2021-05-14
Input one, output one; input two, output two; input three; output purple --what kind of system is this? Computer algorithms can exist as non-deterministic systems, in which there are multiple possible outcomes for each input. Even if one output is more likely than another, it doesn't necessarily eliminate the possibility of putting in three and getting purple instead of three. Now, a research team from Iowa State University has developed a way to control such systems with more predictability. The results were published in IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica.
"The supervisory control problem for discrete event systems under control involves ...
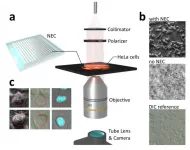
Nanophotonics enhanced coverslip for phase imaging in biology
2021-05-14
The ability to visualize transparent objects such as biological cells is of fundamental importance in biology and medical diagnostics. Conventional approaches to achieve this include phase-contrast microscopy and techniques that rely on chemical staining of biological cells. These techniques, however, rely on expensive and bulky optical components or require changing, and in some cases damaging, the cell by introducing chemical contrast agents. Significant recent advances in nanofabrication technology permit structuring materials on the nanoscale with unprecedented ...
New cellular atlas maps out healthy and cancerous breast tissue
2021-05-14
Australian researchers have documented the diversity of cells in the human breast, explaining the relationship between healthy breast cells and breast cancer cells.
The research, which relied on expertise spanning from breast cancer biology through to bioinformatics, measured gene expression in single cells taken from healthy women and cancerous breast tissue, including tissue carrying a faulty BRCA1 gene. This enabled the researchers to create an 'RNA atlas' that details the different cells found in these tissues.
The atlas, which was described in EMBO Journal, ...
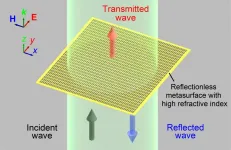
Using micro-sized cut metal wires, Japanese team forges path to new uses for terahertz waves
2021-05-14
Japanese researchers successfully tested reflectionless, highly refractive index metasurface that may eventually be used in practical applications to send, receive, and manipulate light and radio waves in the terahertz waveband (THz). THz is measured in millionths of a meter, known as micrometers. The metasurface, an artificial two-dimensional flat material, was made of micro-sized cut metal wires of silver paste ink placed on both the front and back of a polyimide film. The team, led by Takehito Suzuki, Associate Professor at the Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology (TUAT) Institute of Engineering, published their findings on April 29, 2021 in Optics Express.
Such flat metasurfaces ...
Virtual reality warps your sense of time
2021-05-14
Psychology researchers at UC Santa Cruz have found that playing games in virtual reality creates an effect called "time compression," where time goes by faster than you think. Grayson Mullen, who was a cognitive science undergraduate at the time, worked with Psychology Professor Nicolas Davidenko to design an experiment that tested how virtual reality's effects on a game player's sense of time differ from those of conventional monitors. The results are now published in the journal Timing & Time Perception.
Mullen designed a maze game that could be played in both virtual reality and conventional formats, then the research team recruited 41 UC Santa Cruz undergraduate ...
Study of hip fracture patient characteristics and outcomes pre- and post-COVID-19 outbreak
2021-05-14
The COVID-19 pandemic has been shown to have caused a significant strain on the healthcare system and resources in the United States. However, data regarding the impact of the virus on hip fractures, primarily seen in elderly patients, is lacking.
Researchers at Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) sought to compare characteristics and outcomes of hip fracture patients admitted during the COVID-19 outbreak to patients admitted before the outbreak. They also examined characteristics and outcomes of hip fracture patients with and without the virus. Their findings were presented at the 2021 Spring American Society of Regional Anesthesia and ...
Interim study suggests oral TXA is equally effective in preventing blood loss in joint replacement
2021-05-14
Interim results of a study conducted by researchers at Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) suggest that oral tranexamic acid (TXA) is non-inferior to intravenous (IV) TXA in preventing blood loss in total knee and total hip replacement surgery. These findings were presented at the 2021 Spring American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine (ASRA) Annual Meeting.1
Previously available information suggests that oral, IV and topical TXA are all effective at reducing blood loss and drastically reducing blood transfusion rates during and after surgery, but research with direct comparisons for each method is limited.
"TXA in orthopedic surgery has become the standard ...
The eyes offer a window into Alzheimer's disease
2021-05-14
While it has been said that the eyes are a window to the soul, a new study shows they could be a means for understanding diseases of the brain. According to new research by scientists at the UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences, retinal scans can detect key changes in blood vessels that may provide an early sign of Alzheimer's, while offering important insights into how one of the most common Alzheimer's risk genes contributes to the disease.
"The most prevalent genetic risk for Alzheimer's disease is a variant of the APOE gene, known as APOE4," said lead author Fanny Elahi, MD, PhD. "We still don't fully understand how this variant increases risk of brain degeneration, we just know that it does, and that this risk is modified by sex, race, and lifestyle. "Our ...
Which animals will survive climate change?
2021-05-14
Climate change is exacerbating problems like habitat loss and temperatures swings that have already pushed many animal species to the brink. But can scientists predict which animals will be able to adapt and survive? Using genome sequencing, researchers from McGill University show that some fish, like the threespine stickleback, can adapt very rapidly to extreme seasonal changes. Their findings could help scientists forecast the evolutionary future of these populations.
A popular subject of study among evolutionary ecologists, stickleback are known for their different shapes, sizes, and behaviours - they can even live in both seawater and freshwater, and under a wide range of temperatures. But what ...
New screening method could lead to microbe-based replacements for chemical pesticides
2021-05-14
Plants have evolved unique immunity mechanisms that they can activate upon detecting the presence of a pathogen. Interestingly, the presence of some nonpathogenic microorganisms can also prompt a plant to activate its systemic immunity mechanisms, and some studies have shown that pretreating agricultural crops with such "immunity-activating" nonpathogenic microorganisms can leave the crops better prepared to fight off infections from pathogenic microorganisms. In effect, this means that immunity-activating nonpathogenic microorganisms can function like vaccines for plants, providing a low-risk stimulus for the plant's immune system that prepares it for dealing with genuine threats. These are exciting findings for crop scientists because they suggest the ...
Researchers observe new complexity of traveling brain waves in memory circuits
2021-05-14
Researchers at UC San Francisco have observed a new feature of neural activity in the hippocampus - the brain's memory hub - that may explain how this vital brain region combines a diverse range of inputs into a multi-layered memories that can later be recalled.
Using a special "micro-grid" recording device developed by colleagues at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), the UCSF researchers were able to measure hippocampus activity in study participants undergoing surgery to treat severe epilepsy. They discovered that brain waves travel back and forth across this structure, integrating messages ...
The chemistry of magnesium turned on its head
2021-05-14
The international scientific community agrees that the latest findings of an FAU research team will revolutionise the entire chemistry of magnesium. The research team have discovered magnesium, which usually has a double positive charge in chemical compounds, in the elemental zero-oxidation state. They have published their ground-breaking findings in the journal Nature.
In the periodic table of elements, magnesium (Mg) is a metal with low electronegativity, which means it does not easily attract electrons but easily loses both the electrons in its outer shell during chemical reactions. It therefore only exists in nature as a compound ...
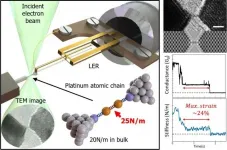
Hanging by a thread: Imaging and probing chains of single atoms
2021-05-14
Ishikawa, Japan - Today, many well-studied materials in various fields, such as electronics and catalysis, are close to reaching their practical limits. To further improve upon modern technology and outperform state-of-the-art devices, researchers looking for new functional materials have to push the boundaries and explore more extreme cases. A clear example of this is the study of low-dimensional materials, such as monoatomic layers (2D materials) and monoatomic chains (1D materials).
It has been proved time and time again that low-dimensional materials exhibit exotic properties that are absent in their 3D bulk counterparts. For example, monoatomic chains of metals like gold ...
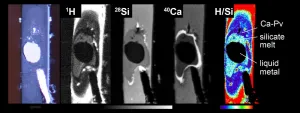
Where on Earth is all the water?
2021-05-14
High-temperature and high-pressure experiments involving a diamond anvil and chemicals to simulate the core of the young Earth demonstrate for the first time that hydrogen can bond strongly with iron in extreme conditions. This explains the presence of significant amounts of hydrogen in the Earth's core that arrived as water from bombardments billions of years ago.
Given the extreme depths, temperatures and pressures involved, we are not physically able to probe very far into the earth directly. So, in order to peer deep inside the Earth, researchers use techniques involving seismic data to ascertain things like composition and density of subterranean material. Something that has stood out for as long as these kinds of measurements have been taking place is that the core is primarily ...
Ecology-inspired mathematical models to understand social networks
2021-05-14
The ease with which anyone can create online content for free, especially on social media, has led to superabundance of information being one of the defining characteristics of today's communication systems. This situation has resulted in increasingly intense competition for attention, which has become a scarce good. The researchers from the Complex Systems group (CoSIN3) at the UOC's Internet Interdisciplinary Institute (IN3) María José Palazzi and Albert Solé --professor at the Faculty of Computer Science, Multimedia and Telecommunications?--, led by Javier Borge, have participated in the design of ...
Less wastage during production of marble slabs in the Roman imperial period than today
2021-05-14
When it comes to ancient Roman imperial architecture, most people usually have a mental image of white marble statues, columns, or slabs. While it is true that many buildings and squares at that time were decorated with marble, it was frequently not white but colored marble that was employed, such as the green-veined Cipollino Verde, which was extracted on the Greek island of Euboea. Because marble was very expensive, it was often placed in thin slabs as a cladding over other, cheaper stones. "To date, however, no actual remains of marble workshops from the Roman imperial era have been found, so little is known about marble processing during this period," said Professor Cees Passchier ...
Charting the expansion history of the universe with supernovae
2021-05-14
An international research team analyzed a database of more than 1000 supernova explosions and found that models for the expansion of the Universe best match the data when a new time dependent variation is introduced. If proven correct with future, higher-quality data from the Subaru Telescope and other observatories, these results could indicate still unknown physics working on the cosmic scale.
Edwin Hubble's observations over 90 years ago showing the expansion of the Universe remain a cornerstone of modern astrophysics. But when you get into the details ...
[1] ... [2311]
[2312]
[2313]
[2314]
[2315]
[2316]
[2317]
[2318]
2319
[2320]
[2321]
[2322]
[2323]
[2324]
[2325]
[2326]
[2327]
... [8812]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.