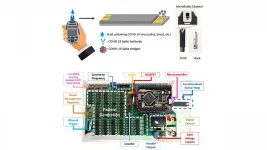
COVID-19 testing method gives results within one second
2021-05-18
WASHINGTON, May 18, 2021 -- The COVID-19 pandemic made it clear technological innovations were urgently needed to detect, treat, and prevent the SARS-CoV-2 virus. A year and a half into this epidemic, waves of successive outbreaks and the dire need for new medical solutions -- especially testing -- continue to exist.
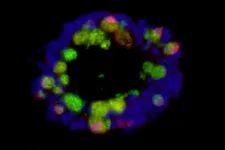
In the Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B, researchers from the University of Florida and Taiwan's National Chiao Tung University report a rapid and sensitive testing method for COVID-19 biomarkers.
The researchers, who previously demonstrated ...
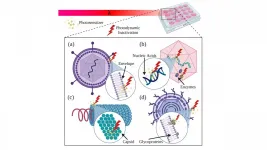
Adding antibodies to enhance photodynamic therapy for viral and bacterial disease
2021-05-18
WASHINGTON, May 18, 2021 -- The COVID-19 pandemic has reinforced the pressing need to mitigate a fast-developing virus as well as antibiotic-resistant bacteria that are growing at alarming rates worldwide.
Photodynamic therapy (PDT), or using light to inactivate viruses, bacteria, and other microbes, has garnered promising results in recent decades for treating respiratory tract infections, such as pneumonia, and some types of cancer.
In Applied Physics Reviews, by AIP Publishing, researchers at Texas A&M University and the University of São Paulo in Brazil ...
Disabled researcher calls for better support for faculty
2021-05-18
Academic institutions need to do much more to support faculty members with disabilities and to create an environment in which they can thrive, argues a commentary published May 18 in the journal Trends in Neurosciences. The paper was written by Justin Yerbury, a cell and molecular neurobiologist who has amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and his wife, Rachel Yerbury, a research psychologist.
"We want people to understand how tough life is for people with a disability," says Justin Yerbury (@jjyerbury), a professor at the University of Wollongong in Australia. "When you add academia on top of ...
Hepatitis C screening doubles when tests ordered ahead of time
2021-05-18
Twice as many eligible patients got screened for hepatitis C when it was already ordered for them compared to those who had to request it, according to a new study by researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Additionally, the patients in the study - whose average age was 63 - completed their screenings much more often when they were contacted via mail as opposed to electronic messaging. The study was published today in BMJ.
"We think that sending the lab order with outreach was so successful because it ...
Discovery increases likelihood of growing food despite drought
2021-05-18
University of California scientists have discovered genetic data that will help food crops like tomatoes and rice survive longer, more intense periods of drought on our warming planet.
Over the course of the last decade, the research team sought to create a molecular atlas of crop roots, where plants first detect the effects of drought and other environmental threats. In so doing, they uncovered genes that scientists can use to protect the plants from these stresses.
Their work, published today in the journal Cell, achieved a high degree of understanding of the root functions because it combined genetic data from different cells of tomato roots grown both indoors and outside.
"Frequently, ...
USPSTF lowers recommended ages for colorectal cancer screening
2021-05-18
Bottom Line: The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends that adults ages 45 to 75 be screened for colorectal cancer, lowering the age for screening that was previously 50 to 75. The USPSTF also recommends that clinicians selectively offer screening to adults 76 to 85 years of age. Colorectal cancer is the third leading cause of cancer death for both men and women in the United States. In 2016, 26% of eligible adults had never been screened and nearly one-third were not up to date with screening in 2018. The USPSTF routinely makes recommendations about the effectiveness of preventive care services and this statement replaces its 2016 recommendation.
To access the embargoed study: ...
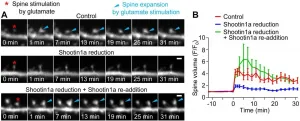
Shootin1a - The missing link underlying learning and memory
2021-05-18
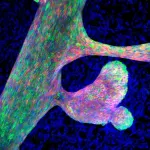
Ikoma, Japan - In neurons, changes in the size of dendritic spines - small cellular protrusions involved in synaptic transmission - are thought to be a key mechanism underlying learning and memory. However, the specific way in which these structural changes occur remains unknown. In a study published in Cell Reports, researchers from Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST) have revealed that the binding of cell adhesion molecules with actin, via an important linker protein in the structural backbone of synapses, is vital for this process of structural plasticity.
Actin proteins make up an important part of a cell's structure, or cytoskeleton, and allow for dynamic changes in this structure by forming ...
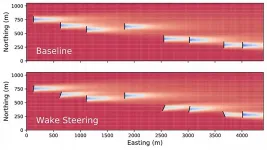
Wake steering potentially boosts energy production at US wind plants
2021-05-18
WASHINGTON, May 18, 2021 -- Wake steering is a strategy employed at wind power plants involving misaligning upstream turbines with the wind direction to deflect wakes away from downstream turbines, which consequently increases the net production of wind power at a plant.
In Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, by AIP Publishing, researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) illustrate how wake steering can increase energy production for a large sampling of commercial land-based U.S. wind power plants.
While some plants showed less potential for wake steering due to unfavorable meteorological conditions or turbine layout, several wind power plants were ideal candidates ...
Community factors associated with telemedicine use during COVID-19 pandemic
2021-05-18
What The Study Did: Telemedicine use grew rapidly during the COVID-19 pandemic but there was geographic variation in its use so researchers in this study examined the association of county-level telemedicine use with community factors among people with commercial or Medicare Advantage insurance.
Authors: Ateev Mehrotra, M.D., M.P.H., of Harvard Medical School in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10330)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and ...
Racial, ethnic disparities in glaucoma clinical trials
2021-05-18
What The Study Did: Demographic information from 105 randomized clinical trials for primary open-angle glaucoma was combined to compare the rate of participation between individuals from racial/ethnic minority groups with white individuals.
Authors: Deepkumar G. Patel, D.D.S., M.P.H., of New York Ophthalmology Associates in Manhattan, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.8348)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this news release.
Embed ...
$8.1 billion in damages from Hurricane Sandy directly linked to human-caused climate change
2021-05-18
Research to be published tomorrow in the journal Nature Communications is the first study to quantify the costs of storm damage caused by sea level rise driven specifically by human-induced climate change. Researchers from Stevens Institute of Technology, Climate Central, Rutgers University and other institutions found this self-inflicted damage to be $8.1 billion of Hurricane Sandy's damage and an additional 71,000 people and 36,000 homes exposed to Sandy's flooding.
Hurricane Sandy struck the northeast U.S. coast in 2012, causing widespread destruction estimated at ...
'45 is the new 50' as age for colorectal cancer screening is lowered
2021-05-18
BOSTON - Prompted by a recent alarming rise in cases of colorectal cancer in people younger than 50, an independent expert panel has recommended that individuals of average risk for the disease begin screening exams at 45 years of age instead of the traditional 50.
The guideline changes by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF), published in the current issue of JAMA, updates its 2016 recommendations and aligns them with those of the American Cancer Society, which lowered the age for initiation of screening to 45 years in 2018.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most preventable malignancies, owing to its long natural history of progression and the availability ...
Western diet found to impair function of immune cells in the gut
2021-05-18
CLEVELAND - According to new study results, a team of researchers led by Cleveland Clinic's Thaddeus Stappenbeck, M.D., Ph.D., have found that a diet high in fat and sugar is associated with impaired intestinal immune cell function in mice. The findings, published in Cell Host & Microbe, provide novel insights into pathways linking obesity and disease-driving gut inflammation, and have implications for developing targets to treat inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) in patients.
Using data from more than 900 patients, the researchers found that elevated body mass index is associated with abnormal Paneth cells among patients with Crohn's disease and non-IBD patients.
Paneth cells are a type of anti-inflammatory immune cell found in ...
Western diet may increase risk of gut inflammation, infection
2021-05-18
Eating a Western diet impairs the immune system in the gut in ways that could increase risk of infection and inflammatory bowel disease, according to a study from researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and Cleveland Clinic.
The study, in mice and people, showed that a diet high in sugar and fat causes damage to Paneth cells, immune cells in the gut that help keep inflammation in check. When Paneth cells aren't functioning properly, the gut immune system is excessively prone to inflammation, putting people at risk of inflammatory bowel disease and undermining effective control of disease-causing microbes. The findings, published May 18 in Cell Host & Microbe, open up new approaches to regulating gut immunity by restoring normal Paneth cell function.
"Inflammatory ...
The importance of DNA compaction in tissue formation
2021-05-18
Scientists led by Dr. Salvador Aznar-Benitah, head of the Stem Cells and Cancer laboratory at IRB Barcelona, have described the alterations that occur during mammary gland formation when heterochromatin (the part of DNA that does not actively produce proteins) is poorly regulated. The results, which have been published in the journal Cell Stem Cell, indicate that incorrect DNA packaging makes retrotransposons (a type of transposable element originated in ancestral fragments of viruses integrated into the cell genome) more accessible.
As these fragments are more accessible, they can be "read" and copied ...
White roofs and more green areas would mitigate the effects of heat waves in cities
2021-05-18
The frequency and intensity of heat waves in cities is increasing due to climate change, with a great negative impact on the health and mortality rates of the population. Anthropogenic activities and urban materials affect heat accumulation in cities, and solar radiation stored throughout the day on asphalt and buildings is released slowly during the night, generating significant heat stress. To face this growing problem, cities must establish effective mitigation strategies that allow reducing the temperature during heat waves.
A study carried out by researchers from the Institut de Ciència i Tecnologia Ambientals ...
Time to capitalize on COVID-19 disruptions to lock-in greener behaviors
2021-05-18
As lockdown measures ease this week in the UK, environmental psychologists are urging that before rushing back to business as normal, we take advantage of the shifts observed over the past year to lock-in new, greener behaviours.
Writing in the journal END ...
Peatlands pose complex, poorly understood wildfire risk, researchers warn
2021-05-18
HAMILTON, ON May 18, 2021 -- Five years after the disastrous wildfire in Fort McMurray, Alberta, researchers are warning that the complex role of peatlands, a factor critical to projecting the risk and behaviour of future fires, is missing from the forecasting model.
The Fort McMurray fire burned out of control from May 1 to July 5, 2016, though it continued to smoulder until it was finally declared extinguished Aug. 2, 2017.
Peat deposits - which are prevalent across Canada, especially in Alberta - are complex threats that can complicate and magnify the risk of severe, long-lasting fires and heavy smoke, but they are not yet part of the standard assessment tools that fire managers use.
It's a critical ...
People who have had dengue are twice as likely to develop symptomatic COVID-19
2021-05-18
A study published this May in the journal Clinical Infectious Diseases suggests that people who have had dengue in the past are twice as likely to develop symptoms of COVID-19 if they are infected by the novel coronavirus.
The findings of the study were based on an analysis of blood samples from 1,285 inhabitants of Mâncio Lima, a small town in the state of Acre, part of Brazil’s Amazon region. The principal investigator was Marcelo Urbano Ferreira, a professor at the University of São Paulo’s Biomedical Sciences Institute (ICB-USP) in Brazil. The study was supported by FAPESP.
“Our results show that the populations most exposed to dengue, possibly owing to socio-demographic factors, are precisely ...
How a virtual program may help kids get ready for kindergarten
2021-05-18
COLUMBUS, Ohio - With pandemic lockdowns still in place last summer, The Ohio State University couldn't host its in-person Summer Success Program to help preschoolers from low-income families prepare for kindergarten.
Staff and teachers quickly pivoted to a fully virtual program, but they were worried: Could this really work with 4- and 5-year-olds who had no previous experience with preschool?
A new study suggested it did.
Researchers found that the reimagined Summer Success at Home program was feasible to operate, was popular with teachers and parents, and had at least modest success in helping the children learn ...
Socioeconomic status non-factor in worse COVID-19 for racial, ethnic groups in Twin Cities
2021-05-18
MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (03/18/2021) -- A research team, led by the University of Minnesota Medical School, found that regardless of socioeconomic status, Twin Cities residents of underrepresented racial and ethnic backgrounds endure worse COVID-19 outcomes compared to people who are white.
The study was just published in the Journal of General Internal Medicine and is one of the first papers to discuss which social and cultural factors, including non-English speaking, may or may not contribute to racial and ethnic health disparities related to COVID-19.
"For people of color, even in the highest socioeconomic status, our data shows they still have worse COVID-19 outcomes compared to people who are white," said Nicholas Ingraham, MD, a third-year fellow in the ...
Iran's groundwater depletion is reaching crisis levels, warn Concordia researchers
2021-05-18
More than three quarters of Iran's land is under extreme groundwater overdraft, where the rate of human uptake is higher than the rate of natural recharge. This is according to a new study led by Concordia researchers published in the Nature journal Scientific Reports.
The article was co-authored by Samaneh Ashraf, a former Horizon postdoctoral researcher now at the Université de Montréal, and Ali Nazemi, an assistant professor in the Department of Building, Civil and Environmental Engineering. Amir AghaKouchak of the University of California, ...
How Russia can protect its rights in the Artic
2021-05-18
Climate change-induced ice melting in the Arctic has led to contradictions in the assessment of Russia's rights in the region. As ice cover diminishes, Russia may be losing its influence on the territories that it has historically developed. This is partially due to the changing width of territorial waters by low-water lines. However, there are alternative legally valid ways to establish fair borders, which are described by researchers of the HSE Institute of Ecology in their paper 'Prospects for the evolution of the system of baselines in the Arctic' https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4441/13/8/1082/htm.
Baselines are one of the key factors shaping international maritime law. From these lines the breadth of a territorial sea is measured, over ...
Conn. medication-assisted opioid treatment programs retain patients at higher rates
2021-05-18
Medication-assisted treatment, or MAT, is an important tool in the ongoing fight against opioid use dependence in the United States. Employing certain medications in combination with counseling and behavioral therapy, MAT offers a comprehensive, "whole-patient" approach to addressing opioid use.
According to a new study from researchers at the UConn School of Social Work and the Connecticut Department of Mental Health and Addiction Services, Connecticut's MAT programs have higher-than-average patient retention rates - more people who enter Connecticut's programs stay in the program to completion.
But the study - recently published in the journal Substance Use and Misuse - also found that ...
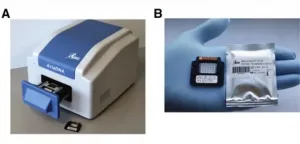
New testing platform for COVID-19 is an efficient and accurate alternative to gold-standard RT-qPCR tests
2021-05-18
Philadelphia, May 18, 2021 - Throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, supply chain shortages of reagents and test kits have limited the rapid expansion of clinical testing needed to contain the virus. Investigators have developed and validated a new microchip real-time technology platform that uses 10-fold less reagents compared to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)-approved tube-based RT-PCR tests, and reports results in as little as 30 minutes. Its accuracy was 100 percent predictive in clinical samples, investigators explain in the Journal of Molecular Diagnostics, published by Elsevier.
"Sensitivity is critical for early detection of COVID-19 ...
[1] ... [2305]
[2306]
[2307]
[2308]
[2309]
[2310]
[2311]
[2312]
2313
[2314]
[2315]
[2316]
[2317]
[2318]
[2319]
[2320]
[2321]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.