Immune genetics and previous common cold infections might help protect Japan from COVID-19
2021-05-20
Protective immune memory--through B cells, which make antibodies, and/or T cells, which in the case of CD8+ T cells can kill virus-infected cells--can be induced by identical but also by related viruses. Related to the COVID-19 virus SARS-CoV-2, there are four common cold coronaviruses (CCCoVs) that together cause ~20% of common cold infections: OC43, HKU1, 229E, and NL63. Most adults have been infected with CCCoVs multiple times in their lives. Whether or not meaningful CCCoV-induced anti-SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies exist remains a matter of debate. Meanwhile, the generation of T cell memory should depend ...
Across US, COVID-19 death rate higher for those with IDD
2021-05-20
Syracuse, N.Y. - The COVID-19 death rate for people with intellectual and developmental disabilities (IDD) is higher than the general population in several states across the U.S., according to a new study published in Disability and Health Journal.
The research team that conducted the study analyzed data from 12 U.S. jurisdictions: Arizona, California, Connecticut, Illinois, Louisiana, Maryland, New Jersey, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Virginia, Washington and Washington, D.C.
The death rates were higher in all jurisdictions for those with IDD who live in congregate settings such as residential group homes. The results for ...
Global food, hunger challenges projected to increase mortality, disability by 2050
2021-05-20
RESEARCH TRIANGLE PARK, N.C. -- A new study by the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI), the USDA's Agricultural Research Service (USDA-ARS) and RTI International (RTI) projects that global chronic and hidden hunger will increase the overall years of life lost due to premature mortality and years lived with disability, also known as disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), globally by over 30 million by 2050 relative to 2010. Expected impacts of climate change on the availability and access to nutritious food will exacerbate this change in DALYs by almost 10 percent.
Researchers published the findings in an article in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, ...
Two complete responses and response rate of 41% for people with synovial sarcoma reported at ASCO in Adaptimmune's phase 2 SPEARHEAD-1 trial
2021-05-20
Data will support BLA filing for afamitresgene autoleucel next year -
Responses observed across a broad range of antigen expression -
Initial safety and durability are encouraging -
PHILADELPHIA, PA., and OXFORDSHIRE, U.K., May 20, 2021 -- Adaptimmune Therapeutics plc (Nasdaq:ADAP), a leader in cell therapy to treat cancer, will report initial data from its Phase 2 SPEARHEAD-1 trial, with afamitresgene autoleucel (afami-cel, formerly ADP-A2M4), at the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) congress. Full abstracts were released online today. Data will be presented in an oral presentation by Dr. Sandra D'Angelo of the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (Abstract #11504) on June 4th.
"Patients are seeing substantial ...
Less forest, more species
2021-05-20
Normally, mountain forests are among the most diverse habitats in alpine regions. Yet, as a team from the Alfred Wegener Institute discovered in the Tibetan Plateau, the higher, treeless areas are home to far more species. Their findings, which were just published in the journal Nature Communications, can help to predict how the biodiversity of alpine regions will decline in response to global warming - when the mountain forests spread to higher elevations.
As anyone who has ever hiked in the mountains knows, the landscape changes with the elevation. At first, for a long time, you trek uphill through forests, until they open up into the first meadows and pastures, where a wide range of plant species bloom in the spring. Farther up, the landscape becomes more barren. ...
Moon mission delays could increase risks from solar storms
2021-05-20
Planned missions to return humans to the Moon need to hurry up to avoid hitting one of the busiest periods for extreme space weather, according to scientists conducting the most in-depth ever look at solar storm timing.
Scientists at the University of Reading studied 150 years of space weather data to investigate patterns in the timing of the most extreme events, which can be extremely dangerous to astronauts and satellites, and even disrupt power grids if they arrive at Earth.
The researchers found for the first time that extreme space weather events are more likely to occur early in even-numbered solar cycles, and late in odd-numbered cycles - such as the one just starting. They are also ...
Red meat intake, poor education linked to colorectal cancer
2021-05-20
A new paper in JNCI Cancer Spectrum, published by Oxford University Press, indicates that several non-genetic factors--including greater red meat intake, lower educational attainment, and heavier alcohol use--are associated with an increase in colorectal cancer in people under 50.
In the United States, incidence rates of early-onset colorectal cancer have nearly doubled between 1992 and 2013 (from 8.6 to 13.1 per 100,000), with most of this increase due to early-onset cancers of the rectum. Approximately 1 in 10 diagnoses of colorectal cancer in this country occur in people under 50.
Researchers ...
Walking in their shoes: Using virtual reality to elicit empathy in healthcare providers
2021-05-20
Philadelphia, May 20, 2021 - Research has shown empathy gives healthcare workers the ability to provide appropriate supports and make fewer mistakes. This helps increase patient satisfaction and enhance patient outcomes, resulting in better overall care. In an upcoming issue of the END ...
New tool factors effects of fossil-fuel emissions on ocean research
2021-05-20
A newly developed tool will allow scientists to better gauge how centuries of fossil fuel emissions could be skewing the data they collect from marine environments.
Researchers at the University of Alaska Fairbanks led the effort, which created a way for marine scientists to factor into their results the vast amounts of anthropogenic carbon dioxide that are being absorbed by oceans. Those human-caused carbon sources can muddy research results -- a problem known as the Suess effect -- leading to flawed conclusions about the health and productivity of marine ecosystems.
"The ...
Oncotarget: The comprehensive genomic profiling test, GEM ExTra®
2021-05-20
Oncotarget published "Analytic validation and clinical utilization of the comprehensive genomic profiling test, GEM ExTra®" which reported that the authors developed and analytically validated a comprehensive genomic profiling assay, GEM ExTra, for patients with advanced solid tumors that uses Next Generation Sequencing to characterize whole exomes employing a paired tumor-normal subtraction methodology.
The assay detects single nucleotide variants, indels, focal copy number alterations, TERT promoter region, as well as tumor mutation burden and microsatellite instability status.
Additionally, the assay incorporates ...
Technique uses fluctuations in video pixels to measure energy use of developing embryos
2021-05-20
Scientists have made a major breakthrough in the study of embryonic development and how it can be impacted by external factors such as climate change.
Researchers at the University of Plymouth have developed a cutting edge technique which enables them to instantly examine the biological traits and behaviours of developing embryos as an energy signature, rather than focusing on individual characteristics.
The method, outlined in a study published in BMC Bioinformatics, is built around timelapse video captured by the researchers of aquatic animals - specifically, the embryos of a freshwater pond snail Radix ...
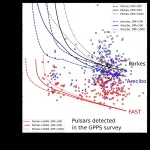
New FAST discoveries shed light on pulsars
2021-05-20
Using the Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST), a research team led by Prof. HAN Jinlin from National Astronomical Observatories of Chinese Academy of Sciences (NAOC) has discovered 201 pulsars, including many very faint pulsars, 40 millisecond pulsars (MSPs), and 16 pulsars in binaries.
These discoveries were published in Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics.
Pulsars are compact remnants of the death of bright, massive stars. They have the strongest magnetic field, highest density and fastest rotation of any celestial body in the Universe, and show significant ...
New pan-European research reveals double the concern about mental health impact of Lockdown and associated restrictions than physical inactivity
2021-05-20
Nearly two thirds (61%) expressed concern about their worsening mood in Lockdown and associated restrictions1.
34% said they felt more anxious and 28% felt more depressed during Lockdown and associated restrictions1.
Coffee helped lift nearly half (44%) of adult's negative moods in Lockdown and associated restrictions1.
A new pan-European survey funded by the Institute for Scientific Information on Coffee exploring the impact of COVID-19 Lockdowns and associated restrictions (in those countries where there has been no Lockdown), has found that nearly two thirds of adults (61%) expressed concern about their worsening mood; two times higher than those concerned about physical inactivity (24%)1.
Understanding the effects of COVID-19 restrictions ...
A rapid antigen test for SARS-CoV-2 in saliva
2021-05-20
Scientists from Hokkaido University have shown that an antigen-based test for quantifying SARS-CoV-2 in saliva samples is simple, rapid, and more conducive for mass-screening.
More than a year into the COVID-19 pandemic, the RT-PCR test remains the gold standard for detection of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. This method requires trained personnel at every step, from collection of nasopharyngeal swab (NPS) samples to interpretation of the results; in addition, the entire process ranges from 24-48 hours on average. As the virus can be transmitted by an infected person before symptoms ...
Immunotherapy combination shows benefit for patients with advanced melanoma
2021-05-20
Fixed-dose combination of nivolumab and relatlimab holds the cancer in check significantly longer than nivolumab alone
This is the first regimen to demonstrate a statistical benefit over anti-PD-1 monotherapy in metastatic melanoma
BOSTON - A combination of two drugs that target different proteins on immune system T cells kept advanced melanoma in check significantly longer than one of the drugs alone in a phase 3 clinical trial involving 714 patients. Dana-Farber Cancer Institute investigators co-led the study. Findings will be presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, being held ...
Metabolic inhibitor IACS-6274 shows early antitumor effects in underserved patients
2021-05-20
HOUSTON -- The glutaminase (GLS1) inhibitor IACS-6274, discovered and developed by The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center's Therapeutics Discovery division, appears to be well-tolerated with successful target inhibition and early signs of anti-tumor activity in a biomarker-driven Phase I trial. Interim results of the study will be presented at the 2021 American Society for Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting on June 4.
On the trial, 17 of 20 evaluable patients achieved a best response of stable disease, with a disease control rate of 60% at 12 weeks. Six patients with biomarker-defined advanced cancers ...
Soy kits provide earning power for women entrepreneurs in Malawi
2021-05-19
URBANA, Ill. - Women's ability to work as entrepreneurs can help alleviate poverty and malnutrition in developing countries. As local governments and development organizations aim to encourage business opportunities, it's important to identify projects suited for women's lives in rural households.
The soy kit, which includes common household items such as a pot, spoon, thermometer, and cheese cloth, enables entrepreneurs to create value-added products from soy in small-scale household settings. The kit has potential to improve the economic conditions of Malawi women in a sustainable way, a University of Illinois study concludes.
"The larger issue is about adding value to agricultural products in the developing world as a means ...
The 'Great Dying'
2021-05-19
Boulder, Colo., USA: The Paleozoic era culminated 251.9 million years ago in the most severe mass extinction recorded in the geologic record. Known as the "great dying," this event saw the loss of up to 96% of all marine species and around 70% of terrestrial species, including plants and insects.
The consensus view of scientists is that volcanic activity at the end of the Permian period, associated with the Siberian Traps Large Igneous Province, emitted massive quantities of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere over a short time interval. This caused a spike in global temperatures and a cascade of other deleterious ...
Pets and their owners diet together, new study finds
2021-05-19
Keto, gluten-free, organic: If a pet owner is on a specific diet, chances are their dog is on it, too, a new U of G study reveals.
But when it comes to a grain-free diet, owners seem to choose it more for their dogs than themselves, the study also found.
"It demonstrates that many variables, not just dietary habits, influence the selection of dog food," said study lead author Sydney Banton, a master's student in U of G's Department of Animal Biosciences.
The international Pet Food Consumer Habit Survey is the first of its kind to examine factors involved in ...
White shark population is small but healthy off the coast of Central California
2021-05-19
NEWPORT, Ore. - The population of white sharks that call the Central California coast their primary home is holding steady at about 300 animals and shows some signs of growth, a new long-term study of the species has shown.
Between 2011 and 2018, researchers were able to identify hundreds of individual adult and subadult white sharks, which are not fully mature but are old enough to prey on marine mammals. They used that information to develop estimates of the sharks' abundance.
"The finding, a result of eight years of photographing and identifying individual ...
Unexpected 'Black Swan' defect discovered in soft matter for first time
2021-05-19
In new research, Texas A&M University scientists have for the first time revealed a single microscopic defect called a "twin" in a soft-block copolymer using an advanced electron microscopy technique. This defect may be exploited in the future to create materials with novel acoustic and photonic properties.
"This defect is like a black swan -- something special going on that isn't typical," said Dr. Edwin Thomas, professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering. "Although we chose a certain polymer for our study, I think the twin defect will be fairly universal across a bunch of similar soft matter systems, like oils, surfactants, biological materials and natural polymers. Therefore, our findings will be valuable to diverse research across the soft matter field."
The ...
Nuclear terrorism could be intercepted by neutron-gamma detector that pinpoints source
2021-05-19
Scanning technology aimed at detecting small amounts of nuclear materials was unveiled by scientists in Sweden today, with the hope of preventing acts of nuclear terrorism.
Bo Cederwall, a professor of physics at KTH Royal Institute of Technology, says the technology can be used in airports and seaports for routine inspection of passengers and goods. The research is published and featured in the journals Science Advances and Science, respectively.
A form of tomography, the system enables quick 3D imaging of the source of neutron and gamma ray emissions from weapons-grade plutonium and other special nuclear materials, Cederwall says.
The so-called Neutron-Gamma Emission Tomography (NGET) system goes beyond the capabilities of existing radiation portal monitors, ...
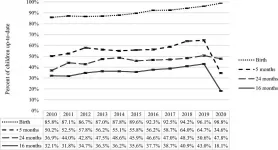
Study shows sharp decrease in Texas childhood vaccination rates during pandemic
2021-05-19
Despite expert recommendations that children continue to get regularly scheduled vaccines during the pandemic, vaccination rates have decreased in several states.
A new study by researchers from the Texas A&M University School of Public Health and several other research institutions looked at childhood immunization rates in Texas to see what effect the COVID-19 pandemic may have had on childhood immunizations in 2020. In the study, led by public health doctoral student Tasmiah Nuzhath and published in the journal Vaccine, the researchers used data from a statewide immunization registry ...
In severe ankle arthritis, total ankle replacement yields better function than ankle arthrodesis
2021-05-19
May 19, 2021 - For patients with severe arthritis of the ankle, total ankle arthroplasty (TAA) provides better long-term function than ankle arthrodesis (AA), reports a study in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio in partnership with Wolters Kluwer.
"Both established treatments for end-stage ankle arthritis are effective at pain relief and improved patient-reported outcomes," according to the research by Bruce Sangeorzan MD, and colleagues at the University of Washington and VA Puget Sound Health Care System. "However, it appears TAA leads to greater improvement in most patient-reported outcome measures at 48 months after surgery."
Study adds to evidence supporting TAA for ankle arthritis
End-stage ankle arthritis is characterized ...
Silicon chips combine light and ultrasound for better signal processing
2021-05-19
The continued growth of wireless and cellular data traffic relies heavily on light waves. Microwave photonics is the field of technology that is dedicated to the distribution and processing of electrical information signals using optical means. Compared with traditional solutions based on electronics alone, microwave photonic systems can handle massive amounts of data. Therefore, microwave photonics has become increasingly important as part of 5G cellular networks and beyond. A primary task of microwave photonics is the realization of narrowband filters: the selection of specific data, at specific frequencies, out of immense volumes that are carried over light.
Many microwave photonic systems are built ...
[1] ... [2298]
[2299]
[2300]
[2301]
[2302]
[2303]
[2304]
[2305]
2306
[2307]
[2308]
[2309]
[2310]
[2311]
[2312]
[2313]
[2314]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.