Oncotarget: Urine protein biomarkers of bladder cancer
2021-05-24
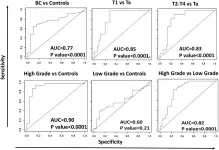
Oncotarget published "Urine protein biomarkers of bladder cancer arising from 16-plex antibody-based screens" which reported that the current study examines urine samples from 66 subjects, comprising of 31 Urology clinic controls and 35 bladder cancer patients, using a Luminex based screening platform.
ELISA validation was carried out for the top 4 prospective urine biomarkers using an independent cohort of 20 Urology clinic controls and 60 bladder cancer subjects.
Eight of these urine proteins were able to differentiate BC from control urine with ROC AUC values exceeding 0.70 at p < 0.0001, with specificity values exceeding 0.9. Upon ELISA validation, urine IL-1α, IL-1ra, and IL-8 were able to distinguish ...
Oncotarget: Retaining nanomolar potency in lung cancer with therapy-refractory mutations
2021-05-24
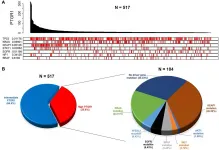
Oncotarget published "The acylfulvene alkylating agent, LP-184, retains nanomolar potency in non-small cell lung cancer carrying otherwise therapy-refractory mutations" which reported that KEAP1 mutant NSCLCs further activate NRF2 and upregulate its client PTGR1. LP-184, a novel alkylating agent belonging to the acylfulvene class is a prodrug dependent upon PTGR1.
The authors hypothesized that NSCLC with KEAP1 mutations would continue to remain sensitive to LP-184. LP-184 demonstrated highly potent anticancer activity both in primary NSCLC cell lines and in those originating from brain metastases of primary lung cancers.
LP-184 activity correlated with PTGR1 transcript levels but was independent of mutations in key oncogenes and tumor ...
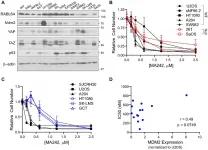
Oncotarget: The Hippo pathway, RABL6A, and p53-MDM2 axes in sarcomas
2021-05-24
Oncotarget published "Prognostic and therapeutic value of the Hippo pathway, RABL6A, and p53-MDM2 axes in sarcomas" which reported that herein the authors evaluate expression of TAZ and YAP, the p53-MDM2 axis, and RABL6A, a novel oncoprotein with potential ties to both pathways, in sarcomas of different histological types.
Immunohistochemical staining of a tissue microarray including 163 sarcomas and correlation with clinical data showed that elevated YAP and TAZ independently predict worse overall and progression-free survival, respectively.
In the absence of p53 expression, combined TAZ and YAP expression adversely affect overall, progression free, and metastasis free survival ...
No link between milk and increased cholesterol according to new study of 2 million people
2021-05-24
Regular consumption of milk is not associated with increased levels of cholesterol, according to new research.
A study published in the International Journal of Obesity looked at three large population studies and found that people who regularly drank high amounts of milk had lower levels of both good and bad cholesterol, although their BMI levels were higher than non-milk drinkers. Further analysis of other large studies also suggests that those who regularly consumed milk had a 14% lower risk of coronary heart disease.
The team of researchers took a genetic approach to milk consumption by looking at a variation in the lactase gene associated with digestion of milk sugars known as lactose.
The study identified that having the genetic variation where people can digest ...
New research suggests that night shift work is linked to menstrual irregularity and increased of developing endometriosis
2021-05-23
Press release - Abstract 1394: Alterations in clock genes expression in Eutopic and Ectopic Endometrial Tissue
New research suggests that night shift work is linked to menstrual irregularity and increased chance of developing endometriosis
According to a study being presented at the 23rd European Congress of Endocrinology (e-ECE 2021), on Sunday 23 May at 19:00 CET (http://www.ece2021.org), women working night shifts may be at a greater risk of menstrual irregularity and developing endometriosis. The research found a reduction in the expression of PER-2, CRY-1 and CLOCK genes along with an increase in REV-ERBb in ectopic compared to ...
IBS patients' symptoms improved under COVID-19 lockdown orders
2021-05-23
Bethesda, MD (May 23, 2021) -- Patients' irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) symptoms unexpectedly improved when they were under COVID-19 stay-at-home orders, reaffirming the gut-brain connection in functional gastrointestinal disorders, according to research that was selected for presentation at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2021.
"One of our main hypotheses was that these patients were going to be worse because of pressure and stress due to COVID-19," said Juan Pablo Stefanolo, MD, a lead author on the study and a physician with the Neurogastroenterology and Motility section, Hospital de Clínicas José de San Martín, ...
Smart toilet may soon analyze stool for health problems
2021-05-22
Bethesda, MD (May 22, 2021) -- An artificial intelligence tool under development at Duke University can be added to the standard toilet to help analyze patients' stool and give gastroenterologists the information they need to provide appropriate treatment, according to research that was selected for presentation at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2021. The new technology could assist in managing chronic gastrointestinal issues such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
"Typically, gastroenterologists have to rely on patient self-reported information about their stool to help determine the cause of their ...
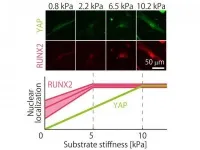
Finer touch for tuning stem cell "fate" with substrates of varying stiffness
2021-05-22
Tokyo, Japan - Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have been quantifying how different batches of mesenchymal stem cells respond to the mechanical stiffness of their environments. They focused on how certain proteins were "localized" in cell nuclei and found key trends in how this changed with stiffness. Their findings explain inconsistencies between previous findings and may guide how scientists control the state of stem cells for research and medical treatments.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are important "progenitor" cells that can transform into muscle, cartilage, bone or fat cells. In 2006, pioneering work by Engler and coworkers showed that they could control what cell type mesenchymal stem cells ...
Vast under-treatment of diabetes seen in global study
2021-05-22
Nearly half a billion people on the planet have diabetes, but most of them aren't getting the kind of care that could make their lives healthier, longer and more productive, according to a new global study of data from people with the condition.
Many don't even know they have the condition.
Only 1 in 10 people with diabetes in the 55 low- and middle-income countries studied receive the type of comprehensive care that's been proven to reduce diabetes-related problems, according to the new findings published in Lancet Healthy Longevity.
That comprehensive package of care ...
Business shutdowns reduce COVID-19 deaths
2021-05-22
Business shutdowns reduce COVID-19 deaths, though with rapidly diminishing returns, with study of Italian lockdowns estimating they saved over 9,400 lives in under a month.
INFORMATION:
Article Title: Closed for business: The mortality impact of business closures during the Covid-19 pandemic
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work.
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0251373
...
Preventing the spread of plant pandemics
2021-05-22
Plant diseases don't stop at national borders and miles of oceans don't prevent their spread, either. That's why plant disease surveillance, improved detection systems, and global predictive disease modeling are necessary to mitigate future disease outbreaks and protect the global food supply, according to a team of researchers in a new commentary published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The idea is to "detect these plant disease outbreak sources early and stop the spread before it becomes a pandemic," says lead-author Jean Ristaino, William Neal Reynolds Distinguished Professor of Plant Pathology at North Carolina State University. Once an epidemic occurs it is difficult to control, Ristaino says, likening the effort to the one undertaken ...
Neurotic personalities found the pandemic most traumatic
2021-05-22
Neurotic personalities found the pandemic most traumatic, while agreeable and conscientious personalities offered protection from the pandemic's negative impacts.
INFORMATION:
Article Title: Which personality traits can mitigate the impact of the pandemic? Assessment of the relationship between personality traits and traumatic events in the COVID-19 pandemic as mediated by defense mechanisms
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work.
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0251984
...
New COVID-19 rapid test kit receives scientific seal of approval
2021-05-22
Simon Fraser University researchers have validated a faster, cheaper COVID-19 test that could kickstart the expansion of more widespread rapid testing. Study results have been published in The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics.
"This research offers a cheaper, faster alternative to the most reliable and sensitive test currently used worldwide, without sacrificing sensitivity and reproducibility," says molecular biology and biochemistry professor Peter Unrau, who led the team evaluating the COVID-19 test kit.
The researchers suggest the test could be deployed in remote locations, clinics and airports due to its ease of use and portability.
The microchip real-time PCR test can provide ...
Researchers create world's most power-efficient high-speed ADC microchip
2021-05-21
To meet soaring demand for lightning-quick mobile technology, each year tech giants create faster, more powerful devices with longer-lasting battery power than previous models.
A major reason companies like Apple and Samsung can miraculously pull this off year after year is because engineers and researchers around the world are designing increasingly power-efficient microchips that still deliver high speeds.
To that end, researchers led by a team at Brigham Young University have just built the world's most power-efficient high-speed analog-to-digital converter (ADC) microchip. An ADC is a tiny piece of technology present in almost every electronic piece of equipment that converts analog ...
Clues from soured milk reveal how gold veins form
2021-05-21
For decades scientists have been puzzled by the formation of rare hyper-enriched gold deposits in places like Ballarat in Australia, Serra Palada in Brazil, and Red Lake in Ontario. While such deposits typically form over tens to hundreds of thousands of years, these "ultrahigh-grade" deposits can form in years, month, or even days. So how do they form so quickly?
Studying examples of these deposits from the Brucejack Mine in northwestern British Columbia, McGill Professor Anthony Williams-Jones of the Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences and PhD student Duncan McLeish have discovered that these gold deposits form much like soured milk. When milk goes sour, the butterfat particles clump together to form a jelly.
Q&A with Anthony Williams-Jones and Duncan McLeish
What did you ...
Study shows which North American mammals live most successfully alongside people
2021-05-21
A team of researchers led by scientists at UC Santa Cruz analyzed data from 3,212 camera traps to show how human disturbance could be shifting the makeup of mammal communities across North America.
The new study, published in the journal Global Change Biology, builds upon the team's prior work observing how wildlife in the Santa Cruz Mountains respond to human disturbance. Local observations, for example, have shown that species like pumas and bobcats are less likely to be active in areas where humans are present, while deer and wood rats become bolder and more active. But it's difficult to generalize findings like these across larger geographic areas because human-wildlife interactions are often regionally unique.
So, to get a continent-wide ...
Providing medications for free leads to greater adherence and cost-savings, study shows
2021-05-21
Free access to essential medicines increases patient adherence to taking medication by 35 per cent and reduces total health spending by an average of over $1,000 per patient per year, according to a two-year study that tested the effects of providing patients with free and convenient access to a carefully selected set of medications.
The findings, published May 21 in PLOS Medicine, come as advocates urge Canada to carve a path toward single-payer, public pharmacare. Canada is the only country with universal healthcare that does not have a universal pharmacare program.
A group of researchers led by St. Michael's Hospital of Unity Health ...
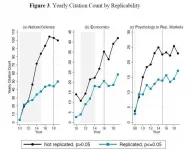
A new replication crisis: Research that is less likely to be true is cited more
2021-05-21
Papers in leading psychology, economic and science journals that fail to replicate and therefore are less likely to be true are often the most cited papers in academic research, according to a new study by the University of California San Diego's Rady School of Management.
Published in Science Advances, the paper explores the ongoing "replication crisis" in which researchers have discovered that many findings in the fields of social sciences and medicine don't hold up when other researchers try to repeat the experiments.
The paper reveals that findings from studies that ...
Superficial relationship: Enzymes protect the skin by ignoring microbes and viruses
2021-05-21
The human body is constantly exposed to various environmental actors, from viruses to bacteria to fungi, but most of these microbial organisms provoke little or no response from our skin, which is charged with monitoring and protecting from external dangers.
Until now, researchers weren't quite sure how that happened -- and why our skin wasn't constantly alarmed and inflamed.
In a study published May 21, 2021 in Science Immunology, scientists at University of California San Diego School of Medicine identify and describe two enzymes responsible for protecting our skin and body's overall health from countless potential microbial intruders. These enzymes, called histone deacetylases (HDACs), inhibit the body's inflammatory response in the skin.
"We have figured ...
Controllability of ionization energy of atoms promises advancements in chemical synthesis
2021-05-21
Ionization energy is one of the most important physicochemical parameters. It is defined in terms of the amount of energy required to rip an electron from an atom. The dependence of the ionization energy on the atomic number determines the periodic law of chemical elements, which is assumed to be fundamentally constant. Based on the previously predicted effect of changing the electron mass, the research team showed that the ionization energy of atoms placed in photonic crystals with an ultrahigh refractive index can be significantly changed.
Photonic crystals ...
New research examines why some firms prepare for natural disasters and others don't
2021-05-21
Despite the increasing frequency and severity of floods, storms, wildfires and other natural hazards, some firms in disaster-prone areas prepare while others do not.
That issue was examined in a new study by Jennifer Oetzel, professor, American University and Chang Hoon Oh, William & Judy Docking Professor of Strategy, University of Kansas published in the Strategic Management Journal (SMJ).
"Due to the increased frequency and severity of floods, storms, epidemics, wildfires and other natural hazards anticipated over the coming decades (according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration), there is growing pressure on managers and their ...
How human cells and pathogenic shigella engage in battle
2021-05-21
DALLAS - May 21, 2021 - One member of a large protein family that is known to stop the spread of bacterial infections by prompting infected human cells to self-destruct appears to kill the infectious bacteria instead, a new study led by UT Southwestern scientists shows. However, some bacteria have their own mechanism to thwart this attack, nullifying the deadly protein by tagging it for destruction.
The findings, published online today in Cell, could lead to new antibiotics to fight bacterial infections. And insight into this cellular conflict could shed light on a number of other conditions in which this protein is involved, including asthma, Type 1 diabetes, primary biliary cirrhosis, and Crohn's disease.
"This ...
OU researcher identifies new mode of transmission for bacteria
2021-05-21
OKLAHOMA CITY AND DENMARK - Campylobacter infection, one of the most common foodborne illnesses in the Western world, can also be spread through sexual contact, according to a new research discovery by an OU Hudson College of Public Health faculty member, working in conjunction with colleagues in Denmark.
The team's research has been published in Emerging Infectious Diseases, a journal published by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and is the first known study to prove this mode of transmission for Campylobacter. During a time when COVID-19 has dominated news about infectious diseases, the research is a reminder that many other pathogens affect lives around the world every day. The study was led by infectious disease epidemiologist Katrin ...
Sand's urban role demands key part on sustainability stage
2021-05-21
Over 20 Indonesian islands mysteriously disappear. One of the world's deadliest criminal syndicates rises to power. Eight cities the size of New York will be built every year for the next three decades. What connects them is sand, embedded in the concrete of nearly all of the world's buildings, roads, and cities, the glass in the windows, laptops and phone screens, and COVID-19 vaccine vials.
The unexamined true costs of sand - broadly, construction aggregates production -- has spurred a group of scientists to call for a stronger focus on understanding the physical dimension of sand use and extraction. They also suggest new ways to achieve economic and environmental justice.
Four years ago, an international group of scientists, including two from Michigan State University (MSU), called ...
Medication use in hospitalized patients with COVID-19
2021-05-21
What The Study Did: Medication use among hospitalized patients for COVID-19-related treatment in a large university health care system was examined in this study.
Authors: Jonathan H. Watanabe, Pharm.D., Ph.D., of the University of California, Irvine, School of Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10775)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: ...
[1] ... [2290]
[2291]
[2292]
[2293]
[2294]
[2295]
[2296]
[2297]
2298
[2299]
[2300]
[2301]
[2302]
[2303]
[2304]
[2305]
[2306]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.