Will COVID-19 eventually become just a seasonal nuisance?
2021-05-21
Within the next decade, the novel coronavirus responsible for COVID-19 could become little more than a nuisance, causing no more than common cold-like coughs and sniffles. That possible future is predicted by mathematical models that incorporate lessons learned from the current pandemic on how our body's immunity changes over time. Scientists at the University of Utah carried out the research, now published in the journal Viruses.
"This shows a possible future that has not yet been fully addressed," says Fred Adler, PhD, professor of mathematics and ...
Scientists reveal structural details of how SARS-CoV-2 variants escape immune response
2021-05-21
LA JOLLA, CA--Fast-spreading variants of the COVID-19-causing coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2, carry mutations that enable the virus to escape some of the immune response created naturally or by vaccination. A new study from scientists at Scripps Research, along with collaborators in Germany and the Netherlands, has revealed key details of how these escape mutations work.
The scientists, whose study appears in Science, used structural biology techniques to map at high resolution how important classes of neutralizing antibodies bind to the original pandemic ...
Researchers use environmental data to assess prostate cancer diagnosis factors
2021-05-20
Environmental quality is associated with advanced-stage prostate cancer at diagnosis, according to a new study by University of Illinois Chicago researchers.
Prostate cancer is up to 57% heritable, with the remainder attributed to environmental exposures. However, studies on those environmental factors and prostate cancer aggressiveness have previously been limited. For their study, "Association between environmental quality and prostate cancer at diagnosis," published in the journal Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Disease, researchers paired data from the environmental quality index, or EQI, and the Surveillance, ...
Study: Culture influences mask wearing
2021-05-20
Around the world and within the U.S., the percentage of people wearing masks during the Covid-19 pandemic has varied enormously. What explains this? A new study co-authored by an MIT faculty member finds that a public sense of "collectivism" clearly predicts mask usage, adding a cultural and psychological perspective to the issue.
The study uses a series of datasets about mask usage and public attitudes, along with well-established empirical indices of collectivism, to evaluate the impact of those cultural differences on this element of the pandemic response. ...
Research suggests fly brains make predictions, possibly using universal design principles
2021-05-20
Flies predict changes in their visual environment in order to execute evasive maneuvers, according to new research from the University of Chicago. This reliance on predictive information to guide behavior suggests that prediction may be a general feature of animal nervous systems in supporting quick behavioral changes. The study was published on May 20 in PLOS Computational Biology.
Animals use their sensory nervous systems to take in information about their environments and then carry out certain behaviors in response to what they detect. However, the nervous system takes time ...
Novel immune checkpoints have applications for cancer, autoimmune disease treatment
2021-05-20
The immune system is a complex balancing act; if it overreacts or underreacts to foreign molecules, there can be serious health consequences.
For cancer patients, tumor progression is often accompanied by immunosuppression, meaning their bodies can't fight off pathogens the way they should. By contrast, for people with autoimmune diseases like type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis, their immune systems overreact and attack the body itself.
Both of these reactions are influenced by a series of molecular checkpoints found in both immune cells and cancer cells. In immune ...
What makes some oysters more resilient than others?
2021-05-20
Oysters live and grow in saltwater. However, the saltiness of their habitat can change dramatically, especially where the mighty Mississippi River flows into the Gulf of Mexico. Louisiana oysters from the northern Gulf of Mexico may experience some of the lowest salinity in the world due to the influx of fresh water from the Mississippi River. In addition, increased rainfall and large-scale river diversions for coastal protection will bring more fresh water that does not bode well for the eastern oyster. New research led by Louisiana State University (LSU) alumna Joanna Griffiths from Portland, Oregon, and her faculty advisor ...
AI-enabled EKGs find difference between numerical age and biological age significantly affects health
2021-05-20
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- You might be older - or younger - than you think. A new study found that differences between a person's age in years and his or her biological age, as predicted by an artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled EKG, can provide measurable insights into health and longevity.
The AI model accurately predicted the age of most subjects, with a mean age gap of 0.88 years between EKG age and actual age. However, a number of subjects had a gap that was much larger, either seemingly much older or much younger by EKG age.
The likelihood to die during follow-up was much ...
The doctor will see you (on the computer) now: telehealth's time has come
2021-05-20
During the pandemic, the old waiting room phrase "the doctor will see you now" has taken on a new meaning. So has the waiting room. Our kitchen table or living room couch is where many people do work lately, and that includes visits to the doctor. New research from Syracuse University's Falk College indicates this method of health care will continue even after COVID numbers are (hopefully) reduced.
"I was surprised by the results," said the study's lead author Bhavneet Walia, assistant professor of public health at Syracuse University. "I initially thought that, because of the challenges of telehealth, physicians would not be in favor of continuing post-pandemic. It turns out they do. But ...
An updated understanding of how to synthesize value-added chemicals
2021-05-20
Researchers have long been interested in finding ways to use simple hydrocarbons, chemicals made of a small number of carbon and hydrogen atoms, to create value-added chemicals, ones used in fuels, plastics, and other complex materials. Methane, a major component of natural gas, is one such chemical that scientists would like to find to ways to use more effectively, since there is currently no environmentally friendly and large-scale way to utilize this potent greenhouse gas.
A new paper in Science provides an updated understanding of how to add functional groups onto simple hydrocarbons like methane. Conducted by graduate students Qiaomu Yang and Yusen Qiao, postdoc Yu Heng Wang, and led by professors Patrick J. Walsh and Eric J. Schelter, this new and highly detailed mechanism ...
Thin is now in to turn terahertz polarization
2021-05-20
HOUSTON - (May 20, 2021) - It's always good when your hard work reflects well on you.
With the discovery of the giant polarization rotation of light, that is literally so.
The ultrathin, highly aligned carbon nanotube films first made by Rice University physicist Junichiro Kono and his students a few years ago turned out to have a surprising phenomenon waiting within: an ability to make highly capable terahertz polarization rotation possible.
This rotation doesn't mean the films are spinning. It does mean that polarized light from a laser or other source can now be manipulated in ways that were previously out of reach, making it completely visible or completely opaque with a device that's extremely ...
Survey measures health care delays during pandemic's beginning
2021-05-20
At the start of the COVID-19 outbreak, a University of Illinois Chicago researcher conducted a survey asking respondents if they experienced health care delays because of the pandemic. In addition to learning about the types of delays, the study also presented a unique opportunity to capture a historic moment at the pandemic's beginning.
Elizabeth Papautsky, UIC assistant professor of biomedical and health information sciences, is first author on "Characterizing Healthcare Delays and Interruptions in the U.S. During the COVID-19 Pandemic Using Data from an Internet-Based Cross-Sectional ...
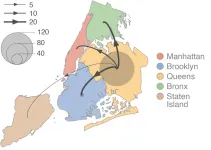
New research maps COVID-19 dispersal dynamics in New York's first wave of epidemic
2021-05-20
During the first phase of the COVID-19 epidemic, New York City experienced high prevalence compared to other U.S. cities, yet little is known about the circulation of SARS-CoV-2 within and among its boroughs. A study published in PLOS Pathogens by Simon Dellicour at Université Libre de Bruxelles, Belgium, Ralf Duerr and Adriana Heguy at New York University, USA, and colleagues describe the dispersal dynamics of COVID-19 viral lineages at the state and city levels, illustrating the relatively important role of the borough of Queens as a SARS-CoV-2 transmission hub.
To better understand how the virus dispersed throughout New York ...
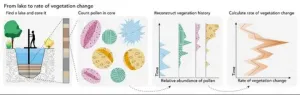
Global pollen samples reveal vegetation rate of change
2021-05-20
Ancient pollen samples and a new statistical approach may shed light on the global rate of change of vegetation and eventually on how much climate change and humans have played a part in altering landscapes, according to an international team of researchers.
"We know that climate and people interact with natural ecosystems and change them," said Sarah Ivory, assistant professor of geosciences and associate in the Earth and Environmental Systems Institute, Penn State. "Typically, we go to some particular location and study this by teasing apart these influences. In particular, we know that the impact people have goes back much earlier than what is typically ...
Compound commonly found in candles lights the way to grid-scale energy storage
2021-05-20
A compound used widely in candles offers promise for a much more modern energy challenge--storing massive amounts of energy to be fed into the electric grid as the need arises.
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Pacific Northwest National Laboratory have shown that low-cost organic compounds hold promise for storing grid energy. Common fluorenone, a bright yellow powder, was at first a reluctant participant, but with enough chemical persuasion has proven to be a potent partner for energy storage in flow battery systems, large systems that store energy for the grid.
Development of such storage is critical. When the grid goes offline due to severe weather, for instance, the large batteries under ...
Global acceleration in rates of vegetation change
2021-05-20
Wherever ecologists look, from tropical forests to tundra, ecosystems are being transformed by human land use and climate change. A hallmark of human impacts is that the rates of change in ecosystems are accelerating worldwide.
Surprisingly, a new study, published today in Science, found that these rates of ecological change began to speed up many thousands of years ago. "What we see today is just the tip of the iceberg" noted co-lead author Ondrej Mottl from the University of Bergen (UiB). "The accelerations we see during the industrial revolution and modern periods have a deep-rooted history stretching back in time."
Using a global network of over 1,000 fossil pollen records, the team found - and expected to find - a first peak ...
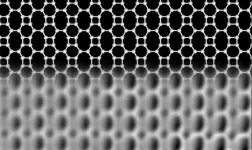
A new form of carbon
2021-05-20
Carbon exists in various forms. In addition to diamond and graphite, there are recently discovered forms with astonishing properties. For example graphene, with a thickness of just one atomic layer, is the thinnest known material, and its unusual properties make it an extremely exciting candidate for applications like future electronics and high-tech engineering. In graphene, each carbon atom is linked to three neighbours, forming hexagons arranged in a honeycomb network. Theoretical studies have shown that carbon atoms can also arrange in other flat network patterns, while still binding to three neighbours, but none of these predicted networks had been realized until now.
Researchers at the University of Marburg ...
ALMA discovers the most ancient galaxy with spiral morphology
2021-05-20
Analyzing data obtained with the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), researchers found a galaxy with a spiral morphology by only 1.4 billion years after the Big Bang. This is the most ancient galaxy of its kind ever observed. The discovery of a galaxy with a spiral structure at such an early stage is an important clue to solving the classic questions of astronomy: "How and when did spiral galaxies form?"
"I was excited because I had never seen such clear evidence of a rotating disk, spiral structure, and centralized mass structure in a distant galaxy in any previous ...
Accounting for finance is key for climate mitigation pathways
2021-05-20
A new study published in the journal Science, highlights the opportunity to complement current climate mitigation scenarios with scenarios that capture the interdependence among investors' perception of future climate risk, the credibility of climate policies, and the allocation of investments across low- and high-carbon assets in the economy.
Climate mitigation scenarios are key to understanding the transition to a low-carbon economy and inform climate policies. These scenarios are also important for financial investors to assess the risk of missing out on the transition or making the transition happen too late and in a disorderly fashion. In this respect, the scenarios developed by the platform of financial authorities ...
Total deaths due to COVID-19 underestimated by 20% in US counties
2021-05-20
Deaths caused by indirect effects of the pandemic emphasize the need for policy changes that address widening health and racial inequities.
More than 15 months into the pandemic, the U.S. death toll from COVID-19 is nearing 600,000. But COVID-19 deaths may be underestimated by 20%, according to a new, first-of-its-kind study from Boston University School of Public Health (BUSPH), the University of Pennsylvania, and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation.
Published in the journal PLOS Medicine, the study uses data from the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention ...
New smartphone app predicts vineyard yields earlier, more accurately
2021-05-20
ITHACA, N.Y. - Cornell University engineers and plant scientists have teamed up to develop a low-cost system that allows grape growers to predict their yields much earlier in the season and more accurately than costly traditional methods.
The new method allows a grower to use a smartphone to record video of grape vines while driving a tractor or walking through the vineyard at night. Growers may then upload their video to a server to process the data. The system relies on computer-vision to improve the reliability of yield estimates.
Traditional methods for estimating grape ...
The impact of real-time feedback in employee reviews
2021-05-20
INFORMS Journal Information Systems Research Study Key Takeaways:
In real-time feedback the relationship source (peer, subordinate or supervisor) plays a role: the feedback tends to be more critical when it is from supervisors.
Favoritism and retribution are impacted in real-time feedback: Supervisors adopt tit-for-tat strategies, but peers do not.
Men rate women higher than men, and women rate men and women similar to how men rate men.
Positive real-time feedback has a stronger effect on future ratings than negative feedback.
CATONSVILLE, MD, May 20, 2021 - To deliver real-time feedback to support employee development and rapid innovation, many companies are replacing formal, review-based performance management with systems that enable frequent and continuous employee evaluation. ...
Hubble tracks down fast radio bursts to galaxies' spiral arms
2021-05-20
Astronomers using NASA's Hubble Space Telescope have traced the locations of five brief, powerful radio blasts to the spiral arms of five distant galaxies.
Called fast radio bursts (FRBs), these extraordinary events generate as much energy in a thousandth of a second as the Sun does in a year. Because these transient radio pulses disappear in much less than the blink of an eye, researchers have had a hard time tracking down where they come from, much less determining what kind of object or objects is causing them. Therefore, most of the time, astronomers don't know exactly where to look.
Locating where these blasts ...
Older adults with functional impairments linked to prescription drug use/misuse
2021-05-20
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, approximately 22 percent of older adults in the United States suffer from a functional impairment, defined as difficulties performing daily activities, such as bathing or getting dressed, or problems with concentration or decision-making affected by physical, mental or emotional conditions.
In a new study published in the May 20, 2021 online edition of the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine found that functional impairments among adults aged 50 and older are associated with a higher risk of medical cannabis use; and prescription opioid and tranquilizer/sedative use and misuse.
"Our ...
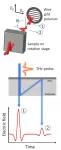
New biosensor developed to aid early diagnosis of breast cancer
2021-05-20
A team of Spanish researchers have developed, at the laboratory level, a prototype of a new biosensor to help detect breast cancer in its earliest stages. One of the team coordinators has been Ramón Martínez Máñez, a professor at the Universitat Politècnica de València (UPV) and the scientific director of the Networking Biomedical Research Centre in Bioengineering, Biomaterials and Nanomedicine (CIBER BBN). The other one has been Ana Lluch, a Valencian oncologist, co-coordinator of the Breast Cancer Biology Research Group ...
[1] ... [2293]
[2294]
[2295]
[2296]
[2297]
[2298]
[2299]
[2300]
2301
[2302]
[2303]
[2304]
[2305]
[2306]
[2307]
[2308]
[2309]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.