Women's access to abortion care under Oregon's reproductive health equity act
2021-05-21
What The Study Did: Oregon's Reproductive Health Equity Act ensured coverage for family planning (abortion and contraception) using state funds for all low-income state residents regardless of citizenship status. Researchers in this study describe the first two years of abortion services covered and the distances traveled by women to receive care.
Authors: Maria I. Rodriguez, M.D., M.P.H., of Oregon Health & Science University in Portland, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2021.0402)
Editor's ...
Examining variation in SARS-CoV-2 infection risk, socioeconomic disadvantage in Mayan-Latinx population
2021-05-21
What The Study Did: Variation in SARS-CoV-2 infection risk and socioeconomic disadvantage among a Mayan-Latinx population in Fruitvale, California, was examined in this study.
Authors: Paul Wesson, Ph.D., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10789)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
Long-term gluten intake, cognitive function among women
2021-05-21
What The Study Did: This observational study found no association between long-term dietary intake of gluten and cognitive function among a large group of middle-age women without celiac disease.
Authors: Andrew T. Chan, M.D., M.P.H., of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.13020)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# ...
Brain's memory center stays active during 'infantile amnesia'
2021-05-21
One trait shared by all humans is that they don't remember specific life episodes that occurred before the age of 3 or 4. Many scientists have attributed this so-called "infantile amnesia" to a lack of development in the hippocampus, an area of the brain located in the temporal lobe that is crucial to encoding memory.
However, a new brain imaging study by Yale scientists shows that infants as young as three months are already enlisting the hippocampus to recognize and learn patterns. The findings were published May 21 in the journal Current Biology.
"A fundamental mystery ...
Efforts to treat COVID-19 patients chronicled in UC Health medications data
2021-05-21
Irvine, Calif. - A record of medicine utilization patterns assembled by an interdisciplinary team of researchers at the University of California, Irvine and the UC San Diego School of Medicine reveals the thought, care and scientific rigor clinicians at UC Health medical centers applied in their treatment of patients with COVID-19 in 2020.
For a study published today in Journal of the American Medical Association Network Open, the investigators examined data on the usage rates of 10 different medicines and medicine categories to map how drugs were used on people hospitalized with the viral infection.
The authors got their data ...
Water treatment: Removing hormones with sunlight
2021-05-21
Micropollutants such as steroid hormones contaminate drinking water worldwide and pose a significant threat to human health and the environment even in smallest quantities. Until now, easily scalable water treatment technologies that remove them efficiently and sustainably have been lacking. Scientists at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) developed a new chemical process for removing hormones. It takes advantage of the mechanisms of photocatalysis and transforms the pollutants into potentially safe oxidation products. The team reports on this in the scientific ...
Pivotal results from Trinity clinical trial for the chronic condition atopic dermatitis
2021-05-21
The findings of a clinical trial by Trinity College Dublin researchers of treatment for atopic dermatitis have been published today in The Lancet journal (Friday, 21st May, 2021). Results of the clinical trial at the School of Medicine, Trinity College and St James's Hospital, Dublin have shown the drug upadacitinib to be the most effective treatment to date for this chronic, relapsing inflammatory condition. The research is vital as there is an unmet need which exists for therapies that provide remission of symptoms in moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis.
The publication reports efficacy and safety results of upadacitinib compared with placebo for the treatment of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis in adults and adolescents. This pivotal Global Phase ...
Indigenous peoples and local communities, key to achieving biodiversity goals
2021-05-21
An international study led by the ICTA-UAB states that recognizing indigenous peoples' and local communities' rights and agency is critical to addressing the current biodiversity crisis
Policies established by the post-2020 Global Biodiversity Framework of the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) could be ineffective if the rights and agency of indigenous peoples and local communities are not recognized and fully incorporated into biodiversity management. This is supported by an international study led by the Institute of Environmental Science and Technology of the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (ICTA-UAB) and recently published in the journal Ambio.
The ...
Scientists created building materials effectively protecting from radiation
2021-05-21
Scientists at the Ural Federal University (UrFU, Russia) have created clay bricks that are able to attenuate ionizing radiation to a level that is safe for the human body. To the composition of bricks scientists add waste from the industry, which protects against radiation. The article describing the technology was published in the journal Applied Radiation and Isotopes.
"Bricks are a relatively cheap and convenient material with which we can quickly erect protective rooms, structures, walls around objects with radiation," says scientific head of the project, associate professor of the Department of Nuclear Power Plants and Renewable Energy Sources at UrFU Oleg Tashlykov. "The bricks ...
Itch insight: Skin itch mechanisms differ on hairless versus hairy skin
2021-05-21
Chronic skin itching drives more people to the dermatologist than any other condition. In fact, the latest science literature finds that 7% of U.S. adults, and between 10 and 20% of people in developed countries, suffer from dermatitis, a common skin inflammatory condition that causes itching.
"Itch is a significant clinical problem, often caused by underlying medical conditions in the skin, liver, or kidney. Due to our limited understanding of itch mechanisms, we don't have effective treatment for the majority of patients," said Liang Han, an assistant professor in the Georgia Institute of Technology's School of Biological Sciences who is also a researcher in the Parker H. Petit Institute for Bioengineering and Bioscience.
Until ...
Darwin foreshadowed modern scientific theories
2021-05-21
When Charles Darwin published Descent of Man 150 years ago, he launched scientific investigations on human origins and evolution. This week, three leading scientists in different, but related disciplines published "Modern theories of human evolution foreshadowed by Darwin's Descent of Man," in Science, in which they identify three insights from Darwin's opus on human evolution that modern science has reinforced.
"Working together was a challenge because of disciplinary boundaries and different perspectives, but we succeeded," said Sergey Gavrilets, lead author and professor in the Departments of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology and Mathematics at the University of Tennessee, Knoxville.
Their goal with this review summary was to apply the framework ...
SPRINT study confirms controlled blood pressure important in preventing heart disease and stroke
2021-05-21
CLEVELAND - Follow-up data from the landmark SPRINT study of the effect of high blood pressure on cardiovascular disease have confirmed that aggressive blood pressure management -- lowering systolic blood pressure to less than 120 mm Hg -- dramatically reduces the risk of heart disease, stroke, and death from these diseases, as well as death from all causes, compared to lowering systolic blood pressure to less than 140 mm Hg. Systolic blood pressure (SBP) is the upper number in the blood pressure measurement, 140/90, for example.
In findings published in the May 20, 2021 issue of the New England Journal of Medicine, investigators presented new evidence of the effectiveness of reducing SBP to a target range of less than 120 ...
Making the gray cells happy
2021-05-21
Depressive disorders are among the most frequent illnesses worldwide. The causes are complex and to date only partially understood. The trace element lithium appears to play a role. Using neutrons of the research neutron source at the Technical University of Munich (TUM), a research team has now proved that the distribution of lithium in the brains of depressive people is different from the distribution found in healthy humans.
Lithium is familiar to many of us from rechargeable batteries. Most people ingest lithium on a daily basis in drinking water. International studies have shown that ...
CVIA has just published a new issue, Volume 5 Issue 4
2021-05-21
Beijing, 19 May 2021: the journal Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications (CVIA) has just published a new issue, Volume 5 Issue 4.
This issue brings together important research from leading cardiologists in US and China in a combination of reviews, original research and case reports.
REVIEWS
Pei Huang, Yi Zhang, Yi Tang, Qinghua Fu, Zhaofen Zheng, Xiaoyan Yang and Yingli Yu
Progress in the Study of the Left Atrial Function Index in Cardiovascular Disease:
A Literature Review (https://tinyurl.com/3vruva37)
Nikhil H. Shah, Steven J. Ross, Steve A. Noutong Njapo, Justin Merritt, Andrew Kolarich, Michael Kaufmann, ...
Best predictor of arrest rates? The 'birth lottery of history'
2021-05-21
Social scientists have had a longstanding fixation on moral character, demographic information, and socioeconomic status when it comes to analyzing crime and arrest rates. The measures have become traditional markers used to quantify and predict criminalization, but they leave out a crucial indicator: what's going on in the changing world around their subjects.
An unprecedented longitudinal study, published today in the American Journal of Sociology, looks to make that story more complete and show that when it comes to arrests it can come down to when someone is rather than who someone is, a theory the researchers refer to as the birth lottery of history.
Harvard sociologist Robert J. Sampson and Ph.D. candidate Roland Neil followed arrests in the lives of more than ...
Pandemic paleo: A wayward skull, at-home fossil analyses, a first for Antarctic amphibians
2021-05-21
Paleontologists had to adjust to stay safe during the COVID-19 pandemic. Many had to postpone fossil excavations, temporarily close museums and teach the next generation of fossil hunters virtually instead of in person.
But at least parts of the show could go on during the pandemic -- with some significant changes.
"For paleontologists, going into the field to look for fossils is where data collection begins, but it does not end there," said Christian Sidor, a University of Washington professor of biology and curator of vertebrate paleontology ...
Researchers develop advanced model to improve safety of next-generation reactors
2021-05-21
When one of the largest modern earthquakes struck Japan on March 11, 2011, the nuclear reactors at Fukushima-Daiichi automatically shut down, as designed. The emergency systems, which would have helped maintain the necessary cooling of the core, were destroyed by the subsequent tsunami. Because the reactor could no longer cool itself, the core overheated, resulting in a severe nuclear meltdown, the likes of which haven't been seen since the Chernobyl disaster in 1986.
Since then, reactors have improved exponentially in terms of safety, sustainability and efficiency. Unlike the light-water reactors at Fukushima, which had liquid coolant and uranium ...
Finding the first flower from Northwest China
2021-05-21
"Abominable mystery" -- the early origin and evolution of angiosperms (flowering plants) was such described by Charles Robert Darwin. So far, we still have not completely solved the problem, and do not know how the earth evolved into such a colorful and blooming world.
Recently, a new angiosperm was reported based on numerous exceptionally well-preserved fossils from the Lower Cretaceous of Jiuquan Basin, West Gansu Province, Northwest China. The new discovery is the earliest and unique record of early angiosperms in Northwest China. The study has been accepted for publication in the journal National Science Review and is currently available online at https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwab084.
The new angiosperm was named Gansufructus saligna, and all the fossil specimens ...
Russian wildfires and tropospheric ozone pollution over Northern Tibetan Plateau
2021-05-21
Atmospheric ozone, which can regulate the amount of incoming ultraviolet radiation on the Earth's surface, is important for the atmospheric environment and ecosystems. Tropospheric ozone, primarily originating from photochemical reactions, is the third most prominent greenhouse gas causing climate warming.
A research team led by Dr. Jinqiang Zhang from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics (IAP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences tried to analyze vertical ozone distributions and explore the influence of deep stratospheric intrusions and wildfires on ozone variation in the northern Tibetan Plateau (TP) during the Asian summer monsoon period.
Their findings were published in Atmospheric Research.
Ozone variation over the TP can influence weather and climate change. ...
New method of seeing graphene growing using a standard electron microscope
2021-05-21
Researchers from the University of Surrey have revealed a new method that enables common laboratory scanning electron microscopes to see graphene growing over a microchip surface in real time.
This discovery, published in ACS Applied Nano Materials, could create a path to control the growth of graphene in production factories and lead to the reliable production of graphene layers.
Dispensing with the use of expensive bespoke systems, the new technique not only produces graphene sheets reliably but also allows to use fast-acting catalysts that reduce growth times from several hours to only a few minutes.
With the use of video imagining, the team from Surrey's Advanced Technology Institute (ATI) have shown graphene growing over an iron catalyst, using a silicon nitride ...
Who's in this ocean? Tracking down species on the go using environmental DNA
2021-05-21
Sloughed off skin and bodily fluids are things most people would prefer to avoid.
But for marine biologist like Cheryl Lewis Ames, Associate Professor of Applied Marine Biology in the Graduate School of Agricultural Science at Tohoku University (Japan), such remnants of life have become a magical key to detecting the unseen.
Any organism living in the ocean will inevitably leave behind traces containing their DNA - environmental DNA (eDNA) - detectable in water samples collected from the ocean
Only recently has molecular sequencing technology become ...
Missing role of finance in climate mitigation scenarios
2021-05-21
Researchers at the University of Zurich show how climate mitigation scenarios can be improved by taking into account that the financial system can play both an enabling or a hampering role on the path to a sustainable economic system.
To limit global warming, a profound transformation of energy, production and consumption in our economies is required. The scale of the transformation means that the financial system must have a proactive role. New green investments are needed, as well as a reallocation of capital from high to low-carbon activities. The Central Banks and Supervisors Network for Greening the Financial ...
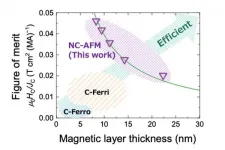
A new spintronic phenomenon: Chiral-spin rotation found in non-collinear antiferromagnet
2021-05-21
Researchers at Tohoku University and the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) have discovered a new spintronic phenomenon - a persistent rotation of chiral-spin structure.
Their discovery was published in the journal Nature Materials on May 13, 2021.
Tohoku University and JAEA researchers studied the response of chiral-spin structure of a non-collinear antiferromagnet Mn3Sn thin film to electron spin injection and found that the chiral-spin structure shows persistent rotation at zero magnetic field. Moreover, their frequency can be tuned by the applied current.
"The electrical control of magnetic ...
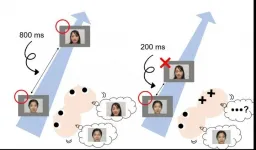
Infants recognize rapid images, just like adults
2021-05-21
It has previously been reported that human visual system has a temporal limitation in processing visual information when perceiving things that occur less than half a second apart. This temporal deficit is known as "attentional blink" and has been demonstrated in a large number of studies. These studies reported that adults could recognize two things when these two were temporally separated over 500 ms, but adults overlooked the second thing when the temporal interval was less than 500 ms. Recently, this attentional blink phenomenon has been observed in even preverbal infants less than one-year old.
In the study ...
Researchers identify a gene that causes canine hereditary deafness in puppies
2021-05-21
Finnish researchers have been the first to determine the cause for the nonsyndromic early-onset hereditary canine hearing loss in Rottweilers. The gene defect was identified in a gene relevant to the sense of hearing. The study can also promote the understanding of mechanisms of hearing loss in human.
Hearing loss is the most common sensory impairment and a complex problem in humans, with varying causes, severity and age of onset. Deafness and hearing loss are fairly common also in dogs, but gene variants underlying the hereditary form of the disorder are so far poorly ...
[1] ... [2291]
[2292]
[2293]
[2294]
[2295]
[2296]
[2297]
[2298]
2299
[2300]
[2301]
[2302]
[2303]
[2304]
[2305]
[2306]
[2307]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.