Better choice of contraceptives can prevent breast cancer
2021-05-28
Hormonal contraceptives, e.g. the pill, the patch, and the vaginal ring, contain synthetic hormones that prevent pregnancy by either stopping ovulation, changing the cervical mucus to stop sperm from passing through the cervix and finding an egg, or changing the womb's lining to prevent a fertilized egg from being implanted in it.
Despite their widespread use, hormonal contraceptives are known to increase the risk of breast cancer, which is the most common cause of cancer-related death among women worldwide, and also topped the list of most commonly diagnosed cancers in 2020.
The main component of hormonal contraceptives are progestins, ...
Moving one step closer to personalized anesthesia
2021-05-28
Anesthesia may be an exact science, but it's not yet fully personalized. Anesthesiologists use a variety of methods to calculate the right dose for a given patient: clinical studies, medical databases and laboratory measurements, for example. However, every individual responds to anesthetics in a different way, and there's no way of knowing what that response will be until the anesthetic is administered.
Personalizing dosage
Today patients often receive supplemental doses of an anesthetic during their operation based on their reaction. The role of anesthesiologists is to make sure that a patient doesn't wake up too soon and has no memory of the procedure, but they must use ...
Study identifies risk for some childhood cancer patients developing secondary leukaemia
2021-05-28
Scientists from the Wellcome Sanger Institute and the University of Cambridge found that in children with neuroblastoma - a cancer of immature nerve cells - treatment with platinum chemotherapy caused changes to the genome that could then cause leukaemia in some children later on.
The findings, published 27th May 2021 in Blood could lead to an ability to identify which children are more likely to develop the secondary cancer. This in turn could lead to changes in their treatment plan to either avoid these risks or take measures to prepare.
Secondary blood cancer is a challenging complication of childhood neuroblastoma cancer treatment. Every year around 100 children in the UK are diagnosed with neuroblastoma*, ...
40 top scientists to WHO: requirements for ventilation systems must be reinforced
2021-05-28
The group of experts includes Professor and Academician of Tallinn University of Technology Jarek Kurnitski, who said that improving ventilation can be regarded more broadly as a paradigm shift equal in scale to the transformation in the standards of drinking water supplies and food hygiene. "There has long been no doubt that you can get infection when you drink water or eat food that has been contaminated. Now we must work towards providing clean air so we can breathe safely," Kurnitski said.
He added, "Researchers see updating of ventilation standards, ventilation requirements based on the probability of infection and more efficient and flexible ventilation systems as a solution. High air change rates are required only in the event of an epidemic, at any ...
Immunity boost in the gut
2021-05-28
Varying immune response to vaccinations could be countered with microbiota-targeted interventions helping infants, older people and others to take full advantage of the benefits of effective vaccines, Australian and US experts say.
A comprehensive review in Nature Reviews Immunology concludes that evidence is mounting in clinical trials and other studies that the composition and function of individuals' gut microbiota are "crucial factors" in affecting immune responses to vaccinations.
"Never before has the need been greater for robust and long-lasting immunity from our vaccination programs, particularly in low and middle-income countries, and for populations at increased ...
Video platforms normalize exotic pets
2021-05-28
Researchers at the University of Adelaide are concerned video sharing platforms such as YouTube could be contributing to the normalisation of exotic pets and encouraging the exotic pet trade.
In a study, published in PLOS ONE, researchers analysed the reactions of people to videos on YouTube involving human interactions with exotic animals and found those reactions to be overwhelmingly positive.
The researchers analysed the reactions - via text and emoji usage - in comments posted on 346 popular videos starring exotic wild cats and primates in 'free handling situations'.
These situations involved exotic animals interacting with humans or other animals, such as domestic cats and dogs. The videos examined received ...
COVID-19 kept our parks busy, but not everyone ventured outside
2021-05-28
Public use of parks and reserves increased only slightly during last year's COVID-19 national lockdown despite gyms and sports facilities shutting down, a University of Queensland study found.
UQ School of Biological Sciences PhD candidate Violeta Berdejo-Espinola surveyed 1000 people in Brisbane, measuring their use of urban green space and the benefits people associated with visiting the areas during lockdown.
"People all around Brisbane, myself included, noticed a boom in park use in 2020, but while more people ventured into local parks, many folks were left indoors," Ms Berdejo-Espinola said.
"Thirty-six ...
Direct evidence of segregated oceanic crust trapped within the mantle transition zo
2021-05-28
Professor YAO Huajian's research group from the School of Earth and Space Sciences of the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC), in cooperation with Dr. Piero Poli from Grenoble-Alpes University of France, combined the unique resolution reflected body waves (P410P and P660P) retrieved from ambient noise interferometry with mineral physics modeling, to shed new light on transition zone physics. Relevant work was published in Nature Communications.
The subduction of oceanic slabs is an important process of the earth's internal material circulation. Studying the ...
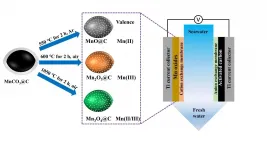
High-capacity electrodes by valence engineering developed for desalination
2021-05-28
Recently, the researchers from Institute of Solid State Physics, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, by using valence engineering, developed three manganese oxides as electrodes with different Mn valences for high-performance capacitive desalination.
Reverse osmosis and thermal distillation are widely used to treat salt water with high salt concentration, but they have disadvantages including high energy consumption and high cost.
As an alternative method, capacitive deionization (CDI) technology can remove charged ions ...
Tiniest of moments proves key for baby's healthy brain
2021-05-28
University of Virginia School of Medicine researchers have shed new light on how our brains develop, revealing that the very last step in cell division is crucial for the brain to reach its proper size and function.
The new findings identify a potential contributor to microcephaly, a birth defect in which the head is underdeveloped and abnormally small. That's because the head grows as the brain grows. The federal Centers for Disease Control estimates that microcephaly affects from 1 in 800 children to 1 in 5,000 children in the United States each year. The condition is associated with learning disabilities, developmental delays, ...
Waking just one hour earlier cuts depression risk by double digits
2021-05-28
Waking up just one hour earlier could reduce a person's risk of major depression by 23%, suggests a sweeping new genetic study published May 26 in the journal JAMA Psychiatry.
The study of 840,000 people, by researchers at University of Colorado Boulder and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, represents some of the strongest evidence yet that chronotype--a person's propensity to sleep at a certain time --influences depression risk.
It's also among the first studies to quantify just how much, or little, change is required to influence mental health. ...
A helping hand for working robots
2021-05-28
Until now, competing types of robotic hand designs offered a trade-off between strength and durability. One commonly used design, employing a rigid pin joint that mimics the mechanism in human finger joints, can lift heavy payloads, but is easily damaged in collisions, particularly if hit from the side. Meanwhile, fully compliant hands, typically made of molded silicone, are more flexible, harder to break, and better at grasping objects of various shapes, but they fall short on lifting power.
The DGIST research team investigated the idea that a partially-compliant ...
New drug combo found effective against high-risk leukaemia
2021-05-28
Australian scientists have found what could prove to be a new and effective way to treat a particularly aggressive blood cancer in children.
Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, or ALL, is the most common cancer diagnosed in children. Despite dramatic improvements in the survival of children with ALL over past several decades, children who develop 'high risk' ALL - subtypes that grow aggressively and are often resistant to standard treatments - often relapse, and many of these children die from their disease.
One common type of high-risk ALL for which new therapies are urgently needed is 'Philadelphia chromosome-like ALL' (Ph-like ALL), named for its similarity ...
Plant flowering in low-nitrogen soils: A mechanism revealed
2021-05-28
Scientists from Japan, Europe and the USA have described a pathway leading to the accelerated flowering of plants in low-nitrogen soils. These findings could eventually lead to increases in agricultural production.
Nitrogen is one of the three macronutrients required by plants for growth and development, along with phosphorus and potassium. Nitrogen-rich condition induces plant growth, particularly the growth of stems and leaves, while delaying flowering. On the other hand, in some plants, low-nitrogen conditions lead to a change from growth mode to reproductive mode, therefore accelerating flowering. However, the molecular mechanisms that regulate flowering under these conditions are not known.
A team of scientists led by Associate ...
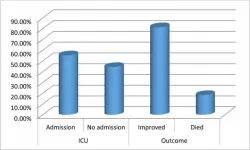
Prognostic value of troponin I in COVID-19 patients
2021-05-28
Corona Virus Disease (COVID -19) patients primarily appear with respiratory issues and viral pneumonia. The patients may also present cardiovascular issues includes early signs of acute myocardial injury. The researchers from Sohag University, Egypt, found that cardiac troponin I (cTnI) can prove to be a gold-standard biomarker for necrosis and myocardial risk assessment in COVID-19 sufferers.
The researchers aimed to assess the prognostic value of cTnI in COVID-19 sufferers. The study included ninety-two COVID-19 patients admitted in the El Helal ...
Reef-building corals and the microscopic algae within their cells evolve together
2021-05-28
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- The microscopic algae that live inside and provide nutrients to their reef-building coral hosts may be evolving in tandem with the corals they inhabit, so each partner is fine-tuned to meet one another's needs. A new study by Penn State biologists reveals that genetic differences within a species of these microalgal symbionts correspond to the coral species they inhabit, a discovery that could have implications for the conservation of these endangered corals.
"Acroporid corals are some of the primary reef-building species in the Caribbean, providing protection to coastlines and habitat for economically important species," said Iliana Baums, professor of biology at Penn State and leader of the research team. "However, these corals are critically ...
Japan's hands-off formula in disciplining schoolchildren works. Is it worth a try elsewhere?
2021-05-28
A study examining Japanese schools' hands-off approach when children fight showed it could create opportunities for autonomy and encourage ownership of solutions, suggesting a new strategy in handling kids squabbles in other countries.
Called mimamoru, the pedagogical strategy is a portmanteau of the Japanese words mi, meaning watch, and mamoru, meaning guard or protect. It is generally understood as "teaching by watching" -- where adults, including early childhood educators, intentionally let kids handle disagreements on their own to promote their learning through voluntary exploration and actions. While not an official part of Japan's early childhood ...
DNA-based material with tunable properties
2021-05-28
While DNA is often idealised as the "molecule of life", it is also a highly sophisticated polymer that can be used for next-generation materials. Beyond the fact that it can store information, further fascinating aspects of DNA are its geometric and topological properties, such as knotting and super-coiling. Indeed, very much like a twisted telephone cord, DNA is often found coiled up inside bacteria and other cells and even knotted in viruses. Now, a collaboration of scientists from the Universities of Edinburgh, San Diego and Vienna have started to harness these properties to craft "topologically ...
UM research suggests social factors important for human-wildlife coexistence
2021-05-28
MISSOULA - In bear country, it's normal to find bruins munching down on temptations left out by humans - from a backyard apple tree to leftovers in the trash bin - but these encounters can cause trouble for humans and bears alike. One method to reduce human-bear conflicts is to secure attractants like garbage and livestock feed.
While effective when implemented, this approach requires people to change their behavior, and that makes things a little more complicated.
University of Montana researchers recently published a new study in the Journal of Wildlife Management analyzing why landowners do or don't secure attractants in bear country. ...
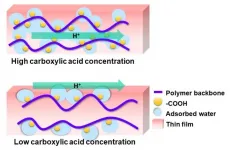
Proton's travel route in polymers could lead the way to clean fuels
2021-05-28
Ishikawa, Japan - Protons--subatomic particles with a positive electric charge--are one of the first particles to have formed after the universe began and are a constituent of every atom today out there. The movement of protons plays a key role in energy conversion processes, such as photosynthesis and respiration, in biological systems. In addition, proton conduction is an important factor for hydrogen fuel cells, which are often touted as the ideal clean energy source for the next generation.
High proton conduction observed in biomaterials such as sugar and protein derivatives is attributed to the presence of proton-donating functional groups (substituents in a molecule that governs its characteristic ...
Pollen-sized technology protects bees from deadly insecticides
2021-05-28
ITHACA, N.Y. - A Cornell University-developed technology provides beekeepers, consumers and farmers with an antidote for deadly pesticides, which kill wild bees and cause beekeepers to lose around a third of their hives every year on average.
An early version of the technology ¬- which detoxified a widely-used group of insecticides called organophosphates - is described in a new study, "Pollen-Inspired Enzymatic Microparticles to Reduce Organophosphate Toxicity in Managed Pollinators," published in Nature Food. The antidote delivery method has now been adapted to effectively ...
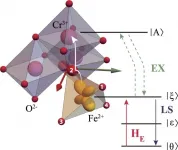
Study of Fe2+ ions contributes to further understanding of magnetoelectric coupling
2021-05-28
The authors, Kirill Vasin and Mikhail Eremin, contribute to the theory of electronic and structural properties of FeCr2O4 ferrimagnet. Due to the specific quantum state and the symmetry of FeO4 fragment, it has unusual electric and magnetic properties. Below TOO~150K, it lowers the symmetry with the macroscopic deformations due to the cooperative Jahn-Teller effect. The coupling between macroscopic deformation of the crystal FeCr2O4 and its inner ions shifts was revealed. The team enhanced the microscopic crystal field theory for 3D electrons with Kleiner's correction - the effect of penetrating charges density. It allows to have better prediction of electron-deformation ...
Nanofibrous filters for PM2.5 filtration
2021-05-28
In a paper published in NANO, the author reviewed many kinds of nanofibrous filters including the component, preparation process, and application performances to provide directional guidance for improvement of the air purification field.
Poor air quality is worldwide recognized as one of five health risks for causing adverse impacts on human health. Nanofibrous membrane is competitive to capture unclean nanoparticles since its lightweight, small diameter, high specific surface area, and easy to combine with functional additives. However, the trade-off between high filtration efficiency and low pressure drop posts challenge.
The removal mechanisms of fibrous filters to nanoparticles follow ...
A novel nitrogen-doped dual-emission carbon dots as an effective fluorescent probe for ratiometric detection dopamine
2021-05-28
How to construct the dual emission nitrogen-doped carbon dots (CDs) by a simple method? Professor Lili Ren with her collaborators proposed a new strategy to prepare such materials which were used to the detection of dopamine.
The traditional ratiometric fluorescence (FL) probe usually needs to combine different nanomaterials by chemical or physical methods and the manufacturing process is more complicated. While the dual-emission carbon dots (DECDs) can simplify the detection process. Therefore, it is of great significance to design a simple ratiometric fluorescence probe based on the DECDs for the accurate determination of DA concentration. ...
Using the environment to control quantum devices
2021-05-28
Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) researchers have uncovered how the environment can impact highly sensitive quantum behaviours like localisation. Their findings, published in Chaos, could lead to future innovations in the design of superconducting materials and quantum devices, including super precise sensors.
Quantum technology, in particular quantum sensing, promises to measure and capture our world at levels of precision never before possible. Such precision has diverse applications, from speedier and more sensitive medical imaging to recording time on high-frequency ...
[1] ... [2286]
[2287]
[2288]
[2289]
[2290]
[2291]
[2292]
[2293]
2294
[2295]
[2296]
[2297]
[2298]
[2299]
[2300]
[2301]
[2302]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.