Adult roles build skills for children of Latinx immigrants
2021-05-26
Children of Latinx immigrants who take on adult responsibilities exhibit higher levels of political activity compared with those who do not, according to University of Georgia researcher Roberto Carlos.
Immigrant communities often display low levels of political engagement, but a new study by Carlos indicates that when children of Latinx immigrants take on adult roles because of parents' long work hours, immigrant status or language deficiencies, they develop noncognitive skills associated with higher rates of political participation.
"There is thriving in spaces that we wouldn't necessarily expect because of the hardship related ...
No good decisions without good data: Climate, policymaking, the critical role of science
2021-05-26
"If you can't measure it, you can't improve it". This concept is also true within the context of climate policy, where the achievement of the objectives of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) is dependent on the ability of the international community to accurately measure greenhouse gas (GHG) emission trends and, consequently, to alter these trends.
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emission inventories represent the link between national and international political actions on climate change, and climate and environmental sciences. Research communities and inventory agencies have approached the problem of climate ...
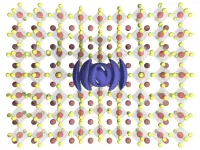
Study of promising photovoltaic material leads to discovery of a new state of matter
2021-05-26
Researchers at McGill University have gained new insight into the workings of perovskites, a semiconductor material that shows great promise for making high-efficiency, low-cost solar cells and a range of other optical and electronic devices.
Perovskites have drawn attention over the past decade because of their ability to act as semiconductors even when there are defects in the material's crystal structure. This makes perovskites special because getting most other semiconductors to work well requires stringent and costly manufacturing techniques to produce crystals that are as defect-free ...
A comprehensive profile of California's 'homegrown' coronavirus
2021-05-26
SAN FRANCISCO, CA--May 26, 2021--In January 2021, reports of a new coronavirus variant that had emerged in California raised many concerns. Preliminary data suggested that it is more transmissible than the unmutated strains of SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19) from which it evolved.
Now, a multifaceted collaboration between researchers at UC San Francisco, Gladstone Institutes, and other organizations across California provides a comprehensive portrait of the variant--including its interaction with the immune system and its potential to spread.
"Our ...
Significant otter helps couples communicate from the heart
2021-05-26
Even though people stayed in touch during the pandemic's stay-at-home orders and social distancing, it was easy to feel out of touch with loved ones.
Technology and the internet have expanded the way humans communicate and added much to that communication -- think emojis, GIFs and memes. But they can still fall short of being physically with someone.
"Our social cues are limited online," said Fannie Liu, a research scientist at Snap Inc who earned her Ph.D. from the Human-Computer Interaction Institute in Carnegie Mellon University's School of Computer Science. "We're exploring a new way to support digital connection through a deeper and more internal cue."
Liu was part of a team from CMU, Snap and the University ...
Study affirms that vaccines are safe for children and adults
2021-05-26
A new study looking across a large body of research finds further evidence for the safety of vaccines that are Food and Drug Administration-approved and routinely recommended for children, adults and pregnant women. The study updates a vaccine safety review that was released by the federal Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality in 2014.
"This in-depth analysis found no evidence of increased risk of serious adverse events following vaccines, apart from a few - previously known - associations," said Susanne Hempel, director of the Southern California Evidence Review Center.
The meta-analysis, ...
Stormwater could be a large source of microplastics and rubber fragments to waterways
2021-05-26
In cities, heavy rains wash away the gunk collecting on sidewalks and roads, picking up all kinds of debris. However, the amount of microplastic pollution swept away by this runoff is currently unknown. Now, researchers in ACS ES&T Water report that stormwater can be a large source of microplastics and rubber fragments to water bodies and, with a proof-of-concept experiment, show that a rain garden could keep these microscopic pieces out of a storm drain.
Most cities' storm drains end up discharging directly into wetlands, creeks or rivers. Rainwater running into these drains becomes a concoction of whatever is on the ground, including dirt and grass clippings, leaked car fluids, fertilizer and garbage. Recently, researchers also found that ...
Scientists find solution to measure harmful plastic particles in human sewage
2021-05-26
Scientists have got up close and personal with human sewage to determine how best to measure hidden and potentially dangerous plastics.
As the way microplastics are measured and counted varies from place to place, there is no agreed understanding of the weight of the problem. Until scientists can agree on one way of measuring them, life on land and sea will continue to ingest who knows how much plastic, affecting health for generations.
A new study, published today in Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, by the University of Portsmouth has examined one method, using a chemical solution called 'Fenton reagent' to ...
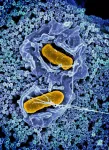
NIH scientists find that salmonella use intestinal epithelial cells to colonize the gut
2021-05-26
WHAT:
The immune system's attempt to eliminate Salmonella bacteria from the gastrointestinal (GI) tract instead facilitates colonization of the intestinal tract and fecal shedding, according to National Institutes of Health scientists. The study, published in Cell Host & Microbe, was conducted by National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) scientists at Rocky Mountain Laboratories in Hamilton, Montana.
Salmonella Typhimurium bacteria (hereafter Salmonella) live in the gut and often cause gastroenteritis in people. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates Salmonella bacteria cause about ...
Conquering COVID-19 with antivirals
2021-05-26
The COVID-19 pandemic has seen scientists perform incredible feats in a short amount of time, from developing tests to new types of vaccines. Despite these victories, experts are still working to develop an effective antiviral drug to kill the SARS-CoV-2 virus. A cover story in Chemical & Engineering News, the weekly newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society, details the challenges of and progress toward creating a drug that would help the world conquer COVID-19.
Creating a new antiviral drug is a tricky business. Viruses mutate and replicate quickly, and their structures differ greatly even within the same class, ...
Electric fish -- and humans -- pause before communicating key points
2021-05-26
American writer and humorist Mark Twain, a master of language and noted lecturer, once offered, "The right word may be effective, but no word was ever as effective as a rightly timed pause."
Electric fish and today's TED talk speakers take a page from Twain's playbook. They pause before sharing something particularly meaningful. Pauses also prime the sensory systems to receive new and important information, according to research from Washington University in St. Louis.
"There is an increased response in listeners to words -- or in this case, electrical pulses ...
Embryos of many species use sound to prepare for the outside world
2021-05-26
It's well known that reptiles depend on temperature cues while in the egg to determine a hatchling's sex. Now, researchers writing in the journal Trends in Ecology & Evolution on May 26 say that embryos of many different animal species also rely on acoustic signals in important ways. They call this phenomenon "acoustic developmental programming."
"Acoustic developmental programming occurs when a sound informs embryos about the environment they'll encounter postnatally and changes their development to better suit this environment," said Mylene Mariette (@MyleneMariette) of Deakin University in Australia.
Because this is a newly discovered phenomenon, the evidence is just beginning to accumulate. And, yet, it seems to ...
The ISSCR releases updated guidelines for stem cell research and clinical translation
2021-05-26
Skokie, IL - The International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR), today released updated guidelines for stem cell research and its translation to medicine. The update reflects emerging advances including, stem cell-based embryo models, human embryo research, chimeras, organoids, and genome editing.
"The 2021 update presents practical advice for oversight of research posing unique scientific and ethical issues for researchers and the public," said Robin Lovell-Badge, PhD, FRS, Chair, ISSCR Guidelines task force and Senior Group Leader and Head of the Division of Stem Cell Biology and Developmental Genetics at The Francis Crick Institute, UK. "They provide confidence to researchers, clinicians, and the public ...
Synthetic breakthrough for controlling functional group assembly over chaotic mixing
2021-05-26
The multifunctional porous solids with diverse functionalized linkers have been utilized as promising materials for various applications in energy, environmental and biomedical areas. Although their emerging properties are ascribed to varying pore types resulting from combinations of functional groups, the chemical environment of the pores remains an open question. A new synthetic platform where the population of pores can be identified and further controlled is of great interest in materials science.
A research team, led by Professor Wonyoung Choe and Professor Tae-Hyuk Kwon in Department of Chemistry ...
AI with swarm intelligence
2021-05-26
Communities benefit from sharing knowledge and experience among their members. Following a similar principle - called "swarm learning" - an international research team has trained artificial intelligence algorithms to detect blood cancer, lung diseases and COVID-19 in data stored in a decentralized fashion. This approach has advantage over conventional methods since it inherently provides privacy preservation technologies, which facilitates cross-site analysis of scientific data. Swarm learning could thus significantly promote and accelerate collaboration and information exchange in research, especially in the field of medicine. Experts from the DZNE, the University of Bonn, the information technology company Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) and other research institutions report on ...
Mobility data reveals universal law of visitation in cities
2021-05-26
New research published in Nature provides a powerful yet surprisingly simple way to determine the number of visitors to any location in a city.
Scientists* from the Santa Fe Institute, MIT, and ETH Zürich have discovered and developed a scaling law that governs the number of visitors to any location based on how far they are traveling and how often they are visiting. The visitation law opens up unprecedented possibilities for accurately predicting flows between locations, which could ultimately have applications in everything from city planning to preventing the spread of the next major pandemic.
"Imagine you are standing on a busy plaza, say in Boston, and you see people coming and going. This ...
Overdose-associated cardiac arrests during COVID-19 pandemic
2021-05-26
What The Study Did: This study included data from more than 11,000 emergency medical services (EMS) agencies in 49 states to describe racial/ethnic, social and geographic changes in EMS-observed overdose-associated cardiac arrests during the COVID-19 pandemic through 2020 in the United States.
Authors: Joseph Friedman, M.P.H., of the University of California, Los Angeles, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2021.0967)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author ...
Frequency, variety of persistent symptoms among patients with COVID-19
2021-05-26
What The Study Did: Researchers conducted a review of studies examining the frequency and variety of persistent symptoms after COVID-19 infection.
Authors: Steven N. Goodman, M.D., M.H.S., Ph.D., of Stanford University in Stanford, California, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11417)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media ...
Study reveals a universal travel pattern across four continents
2021-05-26
What explains how often people travel to a particular place? Your intuition might suggest that distance is a key factor, but empirical evidence can help urban studies researchers answer the question more definitively.
A new paper by an MIT team, drawing on global data, finds that people visit places more frequently when they have to travel shorter distances to get there.
"What we have found is that there is a very clear inverse relationship between how far you go and how frequently you go there," says Paolo Santi, a research scientist at the Senseable City Lab at MIT and a co-author of the new paper. "You only seldom go to faraway places, and usually you tend to visit places close to you more often. It tells us how we organize our lives."
By examining cellphone data ...
Accessibility, usability of state health department COVID-19 vaccine websites
2021-05-26
What The Study Did: Researchers analyzed each state's department of health website for accessibility and usability challenges. Findings suggest state health department COVID-19 vaccine website accessibility and usability challenges create frustration, may promote health disparities and contribute to overall ineffective and inequitable distribution.
Authors: Raj M. Ratwani, Ph.D., of the Medstar Health National Center for Human Factors in Healthcare in Washington, D.C., is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.14861)
Editor's ...
Brain tumors caused by normal neuron activity in mice predisposed to such tumors
2021-05-26
Seeing, hearing, thinking, daydreaming -- doing anything at all, in fact -- activates neurons in the brain. But for people predisposed to developing brain tumors, the ordinary buzzing of their brains could be a problem. A study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and Stanford University School of Medicine shows that the normal day-to-day activity of neurons can drive the formation and growth of brain tumors.
The researchers studied mice genetically prone to developing tumors of their optic nerves, the bundle of neurons that carries ...
Measuring opioid-related mortality in Canada during COVID-19 pandemic
2021-05-26
What The Study Did: Researchers quantified the added burden of fatal opioid overdoses occurring in Ontario, Canada, during the first six months of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Authors: Tara Gomes, Ph.D., of the Keenan Research Centre of the Li Ka Shing Knowledge Institute, St. Michael's Hospital in Toronto, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.12865)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding support disclosures. ...
Reporting of race, sex, socioeconomic status in randomized clinical trials in medical journals
2021-05-26
What The Study Did: Researchers compared reporting practices for race, sex and socioeconomic status in randomized clinical trials published in general medical journals in 2015 with those published in 2019.
Authors: Asad Siddiqui, M.D., of the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11516)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this news ...
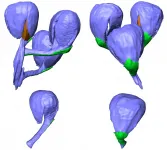
Dinosaur-age fossils provide new insights into origin of flowering plants
2021-05-26
Flowering plants (angiosperms) dominate most terrestrial ecosystems, providing the bulk of human food. However, their origin has been a mystery since the earliest days of evolutionary thought.
Angiosperm flowers are hugely diverse. The key to clarifying the origin of flowers and how angiosperms might be related to other kinds of plants is understanding the evolution of the parts of the flower, especially angiosperm seeds and the fruits in which the seeds develop.
Fossil seed-bearing structures preserved in a newly discovered Early Cretaceous silicified peat in Inner Mongolia, China, provide a partial answer to the origin of flowering plants, according to a study led by Prof. SHI Gongle from the Nanjing ...
University of Kentucky researchers discover fundamental roles of glucosamine in brain
2021-05-26
LEXINGTON, Ky. (May 26, 2021) - Using novel imaging methods for studying brain metabolism, University of Kentucky researchers have identified the reservoir for a necessary sugar in the brain. Glycogen serves as a storage depot for the sugar glucose. The laboratories of Ramon Sun, Ph.D., assistant professor of neuroscience, Markey Cancer Center at the University of Kentucky College of Medicine, and Matthew Gentry, Ph.D., professor of molecular and cellular biochemistry and director of the Lafora Epilepsy Cure Initiative at the University of Kentucky College ...
[1] ... [2279]
[2280]
[2281]
[2282]
[2283]
[2284]
[2285]
[2286]
2287
[2288]
[2289]
[2290]
[2291]
[2292]
[2293]
[2294]
[2295]
... [8821]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.