Lower rates of kidney transplant referrals at for- vs. non-profit dialysis facilities
2021-05-27
Highlights
Among patients receiving dialysis in the Southeastern United States, those at for-profit dialysis facilities were less likely to be referred for kidney transplantation than those at non-profit facilities.
Rates of starting medical evaluations soon after referral and placing patients on a waitlist after evaluations were similar between the groups.
Washington, DC (May 26, 2021) -- New research indicates that patients with kidney failure who receive care at for-profit dialysis facilities are less likely to be referred for kidney transplants that those receiving care at non-profit ...
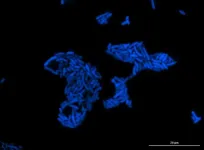
The first blood biomarker to distinguish between myocarditis and acute myocardial infarction
2021-05-27
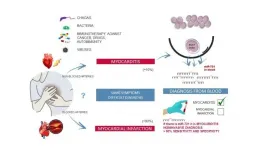
Scientists at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) have identified the first blood biomarker for myocarditis, a cardiac disease that is often misdiagnosed as myocardial infarction. Nevertheless, the diagnosis of myocarditis continues to be challenging in clinical practice.
The study, led by Dr. Pilar Martín and published today in The New England Journal of Medicine, has detected the presence of the human homolog of micro RNA miR-721 in the blood of myocarditis patients.
CNIC General Director Dr. Valentín Fuster emphasizes that these results of paramount importance because they establish the first validated blood marker with high sensitivity and specifity (>90%) for myocarditis. This will allow ...
Immediate skin-to-skin contact after birth improves survival of pre-term babies
2021-05-27
Continuous skin-to-skin contact starting immediately after delivery even before the baby has been stabilised can reduce mortality by 25 per cent in infants with a very low birth weight. This according to a study in low- and middle-income countries coordinated by the WHO on the initiative of researchers at Karolinska Institutet published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Continuous skin-to-skin contact between infant and mother, or "Kangaroo Mother Care" (KMC), is one of the most effective ways to prevent infant mortality globally. The current recommendation from the World Health Organization (WHO) is that skin-to-skin contact should commence ...
People prefer 'natural' strategies to reduce atmospheric carbon
2021-05-26
ITHACA, N.Y. - Soil carbon storage, carbon capture and storage, biochar - mention these terms to most people, and a blank stare might be the response.
But frame these climate change mitigation strategies as being clean and green approaches to reversing the dangerous warming of our planet, and people might be more inclined to at least listen - and even to back these efforts.
A cross-disciplinary collaboration led by Jonathon Schuldt, associate professor of communication at Cornell University, found that a majority of the U.S. public is supportive of soil carbon storage as a climate change mitigation strategy, particularly when that and similar approaches are seen as "natural" strategies.
"To me, that psychology part - that's really interesting," Schuldt ...
Unveiling what governs crystal growth
2021-05-26
With brilliant colors and picturesque shapes, many crystals are wonders of nature. Some crystals are also wonders of science, with transformative applications in electronics and optics. Understanding how best to grow such crystals is key to further advances.
Scientists from the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory, along with three universities, have revealed new insights into the mechanism behind how gallium nitride crystals grow at the atomic scale.
Gallium nitride crystals are already in wide use in light-emitting diodes, better known as LEDs. They might also be applied to form transistors for high-power switching electronics to make electric grids more energy efficient and smarter. The use of such "smart grids," which ...
Opiate overdoses linked to poor mental health
2021-05-26
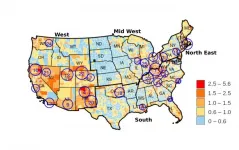
The opioid epidemic is taking a deadly toll on people in disproportionate clusters from Cape Cod to San Diego, according to a new study by the University of Cincinnati.
Fatal opiate overdoses are most prevalent among six states: Ohio, Pennsylvania, Kentucky, West Virginia, Indiana and Tennessee. But researchers identified 25 hot spots of fatal opioid overdoses nationwide using data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The study demonstrates how both widespread and localized the problem of substance use disorders can be, UC assistant professor and co-author Diego Cuadros ...
Deep oceans dissolve the rocky shell of water-ice planets
2021-05-26
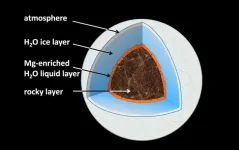
What is happening deep beneath the surface of ice planets? Is there liquid water, and if so, how does it interact with the planetary rocky "seafloor"? New experiments show that on water-ice planets between the size of our Earth and up to six times this size, water selectively leaches magnesium from typical rock minerals. The conditions with pressures of hundred thousand atmospheres and temperatures above one thousand degrees Celsius were recreated in a lab and mimicked planets similar, but smaller than Neptune and Uranus.
The mechanisms of water-rock interaction at the Earth's surface are well known, and the picture of ...
Keeping more ammonium in soil could decrease pollution, boost crops
2021-05-26
Modern-day agriculture faces two major dilemmas: how to produce enough food to feed the growing human population and how to minimize environmental damage associated with intensive agriculture. Keeping more nitrogen in soil as ammonium may be one key way to address both challenges, according to a new paper in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
Today's use of nitrogen fertilizers contributes heavily to greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, and water pollution, but they are also essential for growing crops. Reducing this pollution is critical, but nitrogen use is likely to grow with increased food production. At ...
Widespread coral-algae symbioses endured historical climate changes
2021-05-26
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- One of the most important and widespread reef-building corals, known as cauliflower coral, exhibits strong partnerships with certain species of symbiotic algae, and these relationships have persisted through periods of intense climate fluctuations over the last 1.5 million years, according to a new study led by researchers at Penn State. The findings suggest that these corals and their symbiotic algae may have the capacity to adjust to modern-day increases in ocean warming, at least over the coming decades.
Cauliflower corals -- which are in the genus Pocillopora -- are branching corals that provide critical habitat for one-quarter of the world's fish and many kinds of invertebrates, such as lobsters, sea urchins and giant clams. ...
Technology to monitor mental wellbeing might be right at your fingertips
2021-05-26
To help patients manage their mental wellness between appointments, researchers at Texas A&M University have developed a smart device-based electronic platform that can continuously monitor the state of hyperarousal, one of the signs of psychiatric distress. They said this advanced technology could read facial cues, analyze voice patterns and integrate readings from built-in vital signs sensors on smartwatches to determine if a patient is under stress.
Furthermore, the researchers noted that the technology could provide feedback and alert care teams if there is an abrupt deterioration in the patient's mental health.
"Mental health can change very rapidly, and a lot of these changes remain hidden from providers or counselors," said Dr. Farzan Sasangohar, assistant ...
This brain circuit signals when to stop eating; could regulating it help with obesity
2021-05-26
Like a good story, feeding has a beginning, a middle and an end. It begins with appetite prompting the search for food, continues with eating the food and it ends when satiation hits and the consumption of food is stopped.
At Baylor College of Medicine, Dr. Qi Wu, Dr. Yong Han and their colleagues have uncovered new aspects of the last part of this story that relate to the little-known neural circuits and neurotransmitters involved in ending food consumption.
The team discovered a novel circuit that connects a unique subset of dopamine-producing neurons with downstream neurons in the hindbrain (lower brainstem) ...
Few public-sector employees can contribute significantly to reaching sustainability goals
2021-05-26
The province of Quebec is one of only a few jurisdictions to enshrine sustainable development into law. In 2006 the then-Liberal government of Jean Charest adopted the END ...
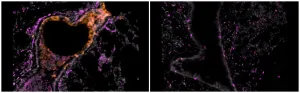
Head and neck cancer cells hijack nearby healthy tissue, promoting further invasion of cancer cells
2021-05-26
Up to half of patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma will experience tumor recurrence or new tumors--tumors that often spread and are difficult to treat.
A team of scientists led by the University of Michigan School of Dentistry identified a mechanism by which head and neck cancer cells subvert adjacent normal tissue, allowing small clusters of cancer cells to burrow beneath the healthy tissue.
The team decided to look at this particular mechanism in head and neck cancer because a specific gene, DMBT1, appeared on a screen of genes that are silenced during oral cancer, said principal investigator Nisha D'Silva, the Donald A. Kerr Endowed ...
Grocery taxes put low-income families at risk for food insecurity
2021-05-26
ITHACA, N.Y. - Approximately one-third of all U.S. counties do not exempt grocery foods from the general sales tax, which means the lowest-income families living in those areas are most susceptible to food insecurity. New research from Cornell University finds that even a slight grocery tax-rate increase could be problematic for many.
"An increase of 1% to 4% may sound small, but after several trips to the grocery store, the extra costs can create serious burdens for the lowest-income families," said co-author Harry Kaiser, professor of applied economics and management in the Charles H. Dyson School of Applied ...
Ultrasensitive blood test detects viral protein, confirms vaccine activates robust immune response
2021-05-26
The carefully orchestrated dance between the immune system and the viral proteins that induce immunity against COVID-19 may be more complex than previously thought. A new study by investigators at Brigham and Women's Hospital used an ultrasensitive, single-molecule array (Simoa) assay to detect extremely low levels of molecules in the blood and measured how these levels change over the days and weeks following vaccination. The team found evidence of circulating protein subunits of SARS-CoV-2, followed by evidence of the body mounting its immune response and then clearing the viral protein to below the level of single-molecule detection. Results are published in Clinical Infectious Diseases.
"Because of ...
Novel sensor discovered that helps bacteria detect and respond to formaldehyde
2021-05-26
Bacteria called methylotrophs can use methane and methanol as fuel; in doing so, they produce large amounts of formaldehyde during growth, but until recently no one knew how they detected and responded to this toxic compound. Publishing on 26th May, 2021 in the Open Access journal PLOS Biology, Christopher Marx of the University of Idaho and colleagues describe their discovery of a novel formaldehyde sensor in the bacterium Methylorubrum extorquens, and other methylotrophs.
Some may remember the pungent smell of this toxic chemical from high school dissections of formaldehyde-preserved animals. From bacteria to humans, all organisms produce at least a little formaldehyde ...
Cleveland clinic researchers identify new drug target for treating aggressive prostate cancer
2021-05-26
May 26, 2021, CLEVELAND: According to new findings published in Science Translational Medicine, Cleveland Clinic researchers have identified a promising drug target for treating and preventing aggressive, drug-resistant prostate cancer.
The team, led by Nima Sharifi, M.D., of Cleveland Clinic's Lerner Research Institute, demonstrated that inhibiting the protein H6PD led to significantly reduced tumor sizes and improved survival among mouse models with drug-resistant prostate cancer. The H6PD levels also were elevated in biopsied patient tumors, suggesting the protein might be targeted ...
Identifying new, non-opioid based target for treating chronic pain
2021-05-26
Milwaukee, May 26, 2021 - A non-opioid based target has been found to alleviate chronic touch pain and spontaneous pain in mice. Researchers at the Medical College of Wisconsin (MCW) discovered that blocking transient receptor potential canonical 5 (TRPC5) activity reversed touch pain in mouse models of sickle cell disease, migraine, chemotherapy-related pain, and surgical pain.
TRPC5 is a protein that is expressed in both mouse and human neurons that send pain signals to the spinal cord. The findings were published in Science Translational Medicine. The senior and co-first authors of the manuscript, respectively, are MCW researchers ...
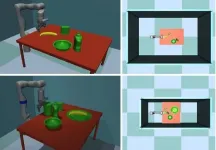
The path to more human-like robot object manipulation skills
2021-05-26
What if a robot could organize your closet or chop your vegetables? A sous chef in every home could someday be a reality.
Still, while advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning have made better robotics possible, there is still quite a wide gap between what humans and robots can do. Closing that gap will require overcoming a number of obstacles in robot manipulation, or the ability of robots to manipulate environments and adapt to changing stimuli.
Ph.D. candidate Jinda Cui and Jeff Trinkle, Professor and Chair of the Department of Computer Science and Engineering ...
Ultra-low doses of inhaled nanobodies effective against COVID-19 in hamsters
2021-05-26
PITTSBURGH, May 26, 2021 - In a paper published today in Science Advances, researchers from the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine showed that inhalable nanobodies targeting the spike protein of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus can prevent and treat severe COVID-19 in hamsters. This is the first time the nanobodies--which are similar to monoclonal antibodies but smaller in size, more stable and cheaper to produce--were tested for inhalation treatment against coronavirus infections in a pre-clinical model.
The scientists showed that low doses of an aerosolized nanobody named Pittsburgh inhalable Nanobody-21 (PiN-21) protected hamsters from the dramatic weight loss ...
An inhalable nanobody-based treatment prevented and treated SARS-CoV-2 infections in hamsters
2021-05-26
An inhalable nanobody-based treatment may effectively prevent and treat SARS-CoV-2 infections when administered at ultra-low doses, according to a new study in Syrian hamsters. This novel therapy, Pittsburgh inhalable Nanobody 21 (PiN-21), could provide an affordable, needle-free alternative to monoclonal antibodies for treating early infections. Sham Nambulli and colleagues recently developed PiN-21, which uses single-domain antibody fragments that are cheaper to produce than monoclonal antibodies. However, until this study, the efficacy of PiN-21 had not been reported in living organisms. To advance the development of this treatment, Nambulli et al. administered a 0.6 milligram per kilogram ...
Salmon virus originally from the Atlantic, spread to wild Pacific salmon from farms: Study
2021-05-26
Piscine orthoreovirus (PRV) - which is associated with kidney and liver damage in Chinook salmon - is continually being transmitted between open-net salmon farms and wild juvenile Chinook salmon in British Columbia waters, according to a new genomics analysis published today in Science Advances.
The collaborative study from the University of British Columbia (UBC) and the Strategic Salmon Health Initiative (SSHI) -- a partnership between Fisheries and Oceans Canada (DFO), Genome BC and the Pacific Salmon Foundation -- traces the origins of PRV to Atlantic salmon farms in Norway and finds that the virus is now almost ubiquitous in salmon farms in B.C.
It also shows that wild Chinook salmon are more likely to be infected with ...
Targeting plasmacytoid dendritic cells can reduce cutaneous lupus symptoms
2021-05-26
Jodi Karnell and colleagues have developed a monoclonal antibody, VIB7734, that reduces symptom severity in people with cutaneous lupus by targeting and depleting plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDC) in blood and skin. In two phase I clinical trials involving a total of 67 people with autoimmune diseases such as lupus, treatment with VIB7734 was as safe as a placebo and significantly reduced pDC frequencies, the researchers found. The antibody also reduced the activity of a group of key immune proteins called type 1 interferons in skin. Both pDCs and type 1 interferons are suspected ...
Good bacteria can temper chemotherapy side effects
2021-05-26
In the human gut, good bacteria make great neighbors.
A new Northwestern University study found that specific types of gut bacteria can protect other good bacteria from cancer treatments -- mitigating harmful, drug-induced changes to the gut microbiome. By metabolizing chemotherapy drugs, the protective bacteria could temper short- and long-term side effects of treatment.
Eventually, the research could potentially lead to new dietary supplements, probiotics or engineered therapeutics to help boost cancer patients' gut health. Because chemotherapy-related microbiome changes in children are ...
Study finds ongoing evolution in Tasmanian Devils' response to transmissible cancer
2021-05-26
MOSCOW, Idaho -- May 26, 2021 -- University of Idaho researchers partnered with other scientists from the United States and Australia to study the evolution of Tasmanian devils in response to a unique transmissible cancer.
The team found that historic and ongoing evolution are widespread across the devils' genome, but there is little overlap of genes between those two timescales. These findings, published in Proceedings of the Royal Society B, suggest that if transmissible cancers occurred historically in devils, they imposed natural selection on different sets of genes.
Tasmanian devils suffer from a transmissible cancer called devil facial tumor disease (DFTD). Unlike typical cancers, tumor cells from transmissible cancers are directly transferred from one individual ...
[1] ... [2278]
[2279]
[2280]
[2281]
[2282]
[2283]
[2284]
[2285]
2286
[2287]
[2288]
[2289]
[2290]
[2291]
[2292]
[2293]
[2294]
... [8821]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.