Researchers create machine learning model to predict treatment with dialysis or death for hospitalized COVID-19 patients
2021-05-28
Paper Title: Predictive Approaches for Acute Dialysis Requirement and Death in COVID-19
Journal: The Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology (published online May 24, 2021)
Authors: Girish Nadkarni, MD, Associate Professor in the Department of Medicine (Nephrology), Clinical Director of the Hasso Plattner Institute for Digital Health, and Co-Chair of the Mount Sinai Clinical Intelligence Center at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai; Lili Chan, MD, Assistant Professor in the Department of Medicine (Nephrology) at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai; Akhil Vaid, MD, postdoctoral fellow in the ...
Over half of UK's arts and cultural venues at risk from pandemic
2021-05-28
Over half of the UK's arts and cultural venues and organisations believe they are at risk due to the decline in income during the pandemic, a new study from the University of Sheffield, University of Kent, and the Chartered Institute of Fundraising has shown.
The only study of its kind, 'Dealing with the crisis: Creativity and resilience of arts and cultural fundraisers during Covid-19' (28 May 2021), gathered information about how arts and cultural fundraisers were impacted by, and managed the Covid-19 pandemic during 2020.
Many artists, organisations and venues rely on fundraising as a significant part of their income, using a range of events and activities to fund creative ...
New research could pave the way for safer and more efficient COVID-19 testing
2021-05-28
International research led by Monash University and the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity has achieved a proof of concept for a new, fast, portable saliva screening test that uses an infrared light technology to confirm infection with SARS-CoV-2.
The research is published today in Angewandte Chemie.
Professor Bayden Wood, from the Monash University School of Chemistry, Dr Phil Heraud formerly from the Monash Biomedicine Discovery Institute and collaborators Professors Dale Godfrey and Damian Purcell from the Doherty Institute, report on a new diagnostic approach, which involves the use of a portable infrared instrument to detect the SARS-CoV-2 virus ...
Key early steps in gene expression captured in real time by CSU researchers
2021-05-27
On scales too small for our eyes to see, the business of life happens through the making of proteins, which impart to our cells both structure and function. Cellular proteins get their marching orders from genetic instructions encoded in DNA, whose sequences are first copied and made into RNA in a multi-step process called transcription.
A research collaboration at Colorado State University specializes in high-resolution fluorescence microscopy and computational modeling to visualize and describe such stuff-of-life processes in exquisite detail, ...
Mouse pups' cries give clues about autism spectrum disorder
2021-05-27
SAN ANTONIO (May 27, 2021) -- One-fifth of babies who inherit a genetic variant located on chromosome 16 will develop autism spectrum disorder (ASD) by age 3. The variant is called 16p11.2 deletion.
Noboru Hiroi, PhD, of The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (also referred to as UT Health San Antonio), is studying mice that have this deletion. The team, which includes colleagues from Japan, Ireland and the U.S., is harnessing the power of machine learning to understand which vocalizations of the newborn mouse pups are most predictive of social abnormalities one month ...
Driving in the snow is a team effort for AI sensors
2021-05-27
Nobody likes driving in a blizzard, including autonomous vehicles. To make self-driving cars safer on snowy roads, engineers look at the problem from the car's point of view.
A major challenge for fully autonomous vehicles is navigating bad weather. Snow especially confounds crucial sensor data that helps a vehicle gauge depth, find obstacles and keep on the correct side of the yellow line, assuming it is visible. Averaging more than 200 inches of snow every winter, Michigan's Keweenaw Peninsula is the perfect place to push autonomous vehicle tech to its limits. In two papers presented at SPIE Defense + Commercial Sensing 2021, researchers from Michigan Technological University discuss solutions for snowy driving scenarios that ...
Measuring the effects of radiotherapy on cancer may open up avenues for treatment
2021-05-27
Ionizing radiation is used for treating nearly half of all cancer patients. Radiotherapy works by damaging the DNA of cancer cells, and cells sustaining so much DNA damage that they cannot sufficiently repair it will soon cease to replicate and die. It's an effective strategy overall, and radiotherapy is a common frontline cancer treatment option. Unfortunately, many cancers have subsets of cells that are able to survive initial radiotherapeutic regimens by developing mechanisms that are able to repair the DNA damage. This often results in resistance to further radiation as cancerous growth recurs. But until recently, little was known about exactly what happens in the genomes of cancer cells following radiotherapy.
To probe the traits of post-radiotherapy cancer ...
Hip replacement surgery improves symptoms and biomechanics -- but not physical activity
2021-05-27
May 27, 2021 - Patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty (THA) show significant reduction in pain and other symptoms and improvement in walking gait biomechanics. However, those improvements do not lead to increased daily physical activity levels, reports a study in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio in partnership with Wolters Kluwer.
The findings "present a worrying picture that while patients have the opportunity to be more physically active through improvements in functional capacity, their physical behaviors do not change," according to the new research, led by Jasvir S. Bahl of the University of South Australia, Adelaide, in collaboration with the University of Adelaide, Flinders University, ...
Dark energy survey releases most precise look at the universe's evolution
2021-05-27
In 29 new scientific papers, the Dark Energy Survey examines the largest-ever maps of galaxy distribution and shapes, extending more than 7 billion light-years across the Universe. The extraordinarily precise analysis, which includes data from the survey's first three years, contributes to the most powerful test of the current best model of the Universe, the standard cosmological model. However, hints remain from earlier DES data and other experiments that matter in the Universe today is a few percent less clumpy than predicted.
New results from the Dark Energy Survey (DES) use the largest-ever sample ...
Versatile coronavirus antibody may be starting point for broader-acting vaccines
2021-05-27
LA JOLLA, CA--Even before the COVID-19 pandemic, most people in the United States already had been sick with a coronavirus, albeit a far less dangerous one. That's because at least four coronaviruses in the same general family as SARS-CoV-2 cause the benign yet annoying illness known as the common cold.
In a new study that appears in Nature Communications, scientists from Scripps Research investigated how the immune system's previous exposure to cold-causing coronaviruses impact immune response to COVID-19. In doing so, they discovered one cross-reactive coronavirus antibody that's triggered during a COVID-19 infection.
The findings will help in the pursuit of a vaccine or antibody ...
Bacterium causing rabbit fever remains virulent for months in cold water
2021-05-27
Although it is not spread through human contact, Francisella tularensis is one of the most infectious pathogenic bacteria known to science--so virulent, in fact, that it is considered a serious potential bioterrorist threat. It is thought that humans can contract respiratory tularemia, or rabbit fever--a rare and deadly disease--by inhaling as few as 10 airborne organisms.
Northern Arizona University professor David Wagner, director of the Pathogen and Microbiome Institute's (PMI) Biodefense and Disease Ecology Center, began a three-year project in 2018 to better understand the life cycle and behavior of F. tularensis, ...
Visits to 'crisis pregnancy centers' common in Ohio
2021-05-27
An estimated one in seven Ohio women of adult, reproductive age has visited a crisis pregnancy center, a new study has found.
In a survey of 2,529 women, almost 14% said they'd ever attended a center. The prevalence was more than twice as high among Black women and 1.6 times as high among those in the lowest socioeconomic group, found a research team from The Ohio State University. Their study appears in the journal Contraception.
Crisis pregnancy centers are often supported by religious organizations and are designed to discourage women with unintended pregnancies from choosing abortion, though they don't typically advertise themselves as anti-abortion. In Ohio, where more than 100 centers are spread throughout the state, they are funded by state dollars. In 2019, during ...
Local management crucial to helping coral reefs survive warming waters
2021-05-27
Local management of coral reefs to ease environmental stressors, such as overfishing or pollution, could increase reefs' chances of recovery after devastating coral bleaching events caused by climate change, a new study finds. The results suggest that caring for reefs on a local scale might help them persist globally. When waters warm, corals can die quickly and en masse in coral bleaching events. Marine warming due to climate change has resulted in sharp increases in both the frequency and magnitude of these mass mortality events, which have already caused severe ...
Reducing metabolic cost of walking while generating electricity using an exoskeleton
2021-05-27
An exoskeleton can reduce the metabolic cost of walking not by adding energy or by recycling energy from one gait phase to another, as other exoskeletons have done, but by removing the kinetic energy of a striding person's swinging leg so they don't have to tense their muscles so much. Tested in ten healthy males, it also converted the extracted kinetic energy to useable electricity. Although humans are exceptional walkers, walking is metabolically expensive and requires more energy than any other activity of daily living. Exoskeletons and exosuits - wearable devices designed to work along with the body's musculoskeletal system - have been shown to reduce this cost by adding or recycling energy to assist the body's movement. These and other ...
Seabirds sound alarm: Breeding success corresponds to hemispheric rates of ocean warming
2021-05-27
There is heightened public awareness that the world's oceans are under duress, with over-fishing and plastic pollution as some of the more tangible problems. Now, seabirds are calling attention to another problem and have delivered a warning message.
Serving as translators of the birds' message, an international team of 40 scientists led by William Sydeman at the Farallon Institute in northern California published findings on May 28 in the journal Science that some seabirds are struggling to raise young where the globe is most rapidly warming - in the northern hemisphere.
Using over 50 years of data from 67 seabird species across the globe, the team found ...
Seabirds' success reveals asymmetry in ocean health
2021-05-27
In a study that uniquely evaluates marine ecosystem responses to a changing climate by hemisphere, researchers report that the fish-eating, surface-foraging bird species of the Northern Hemisphere suffered greater breeding productivity stresses over the last half-century than their Southern Hemisphere counterparts. The findings suggest the need for ocean management at hemispheric scales and underscore the importance of long-term seabird monitoring programs - some of which are already under threat - by illustrating the critical role that seabirds play as sentinels of global marine change. To date, global understanding of ocean change has not explicitly considered differences, ...
Managing global climate change--and local conditions--key to coral reefs' survival
2021-05-27
Australian researchers recently reported a sharp decline in the abundance of coral along the Great Barrier Reef. Scientists are seeing similar declines in coral colonies throughout the world, including reefs off of Hawaii, the Florida Keys and in the Indo-Pacific region.
The widespread decline is fueled in part by climate-driven heat waves that are warming the world's oceans and leading to what's known as coral bleaching, the breakdown of the mutually beneficial relationship between corals and resident algae.
But other factors are contributing to the decline ...
Biologists construct a 'periodic table' for cell nuclei
2021-05-27
HOUSTON - (May 27, 2021) - One hundred fifty years ago, Dmitri Mendeleev created the periodic table, a system for classifying atoms based on the properties of their nuclei. This week, a team of biologists studying the tree of life has unveiled a new classification system for cell nuclei and discovered a method for transmuting one type of cell nucleus into another.
The study, which appears this week in the journal Science, emerged from several once-separate efforts. One of these centered on the DNA Zoo, an international consortium spanning dozens of institutions including Baylor College of ...
Seabirds face dire threats from climate change, human activity — especially in Northern Hemisphere
2021-05-27
Many seabirds in the Northern Hemisphere are struggling to breed -- and in the Southern Hemisphere, they may not be far behind. These are the conclusions of a study, published May 28 in Science, analyzing more than 50 years of breeding records for 67 seabird species worldwide.
The international team of scientists -- led by William Sydeman at the Farallon Institute in California -- discovered that reproductive success decreased in the past half century for fish-eating seabirds north of the equator. The Northern Hemisphere has suffered greater impacts from human-caused climate change and other human activities, like overfishing.
Seabirds include albatrosses, puffins, murres, penguins and other birds. Whether they ...
How more inclusive lab meetings lead to better science
2021-05-27
A new paper, published recently in PLOS Computational Biology by a team including UMass Amherst researchers, seeks to help scientists structure their lab-group meetings so that they are more inclusive, more productive and, ultimately, lead to better science.
The word "scientist" might conjure images of lab-coated researchers tending bubbling beakers or building supercomputers, but an enormous amount of scientific work takes place around a conference table during weekly group meetings. "There is plenty of good research showing that diversity and inclusion make the science itself better," says Kadambari Devarajan, one of the paper's co-lead authors and a graduate ...
Changes in how cholesterol breaks down in the body may accelerate progression of dementia
2021-05-27
The blood-brain barrier is impermeable to cholesterol, yet high blood cholesterol is associated with increased risk of Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia. However, the underlying mechanisms mediating this relationship are poorly understood. A study published in the open-access journal PLOS Medicine by Vijay Varma and colleagues at the National Institute on Aging, part of the National Institutes of Health, in Baltimore, Maryland, suggests that disturbances in the conversion of cholesterol to bile acids (called cholesterol catabolism) may play a role in the development of dementia.
Little ...
Astonishing quantum experiment in Science raises questions
2021-05-27
Quantum systems are considered extremely fragile. Even the smallest interactions with the environment can result in the loss of sensitive quantum effects. In the renowned journal Science, however, researchers from TU Delft, RWTH Aachen University and Forschungszentrum Jülich now present an experiment in which a quantum system consisting of two coupled atoms behaves surprisingly stable under electron bombardment. The experiment provide an indication that special quantum states might be realised in a quantum computer more easily than previously thought.
The so-called decoherence is one of the greatest enemies of the quantum physicist. Experts understand by this the decay of quantum states. This inevitably occurs when the system interacts with its environment. In ...
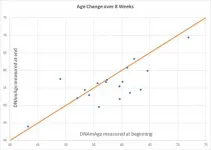
Three years younger in just eight weeks? A new study suggests yes!
2021-05-27
A groundbreaking clinical trial shows we can reduce biological age (as measured by the Horvath 2013 DNAmAge clock) by more than three years in only eight weeks with diet and lifestyle through balancing DNA methylation. A first-of-its-kind, peer-reviewed study provides scientific evidence that lifestyle and diet changes can deliver immediate and rapid reduction of our biological age. Since aging is the primary driver of chronic disease, this reduction has the power to help us live better, longer. The study, released on April 12, utilized a randomized controlled clinical trial conducted among 43 healthy adult males between the ages of 50-72. The 8-week treatment program included diet, sleep, exercise and relaxation ...
The new species of bacteria killing palms in Australia
2021-05-27
The bacterium, which they named Candidatus Phytoplasma dypsidis was found to cause a fatal wilt disease. This new discovery was reported in the International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology.
In 2016, several ornamental palms within a conservatory in the Cairns Botanic Gardens, Queensland, died mysteriously. A sample was taken from one of the diseased plants and investigated by Dr Richard Davis and colleagues from the Australian Government Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment, and state and local government. They compared the characteristics and genome of the bacterium identified as the cause of the disease and found the ...
Exploring optimization of duplex velocity criteria for diagnosis of ICA stenosis
2021-05-27
Study Exploring Optimization of Duplex Velocity Criteria for Diagnosis of Internal Carotid Artery (ICA) Stenosis Published Online
Online first in Vascular Medicine, researchers from the Intersocietal Accreditation Commission (IAC) Vascular Testing division report findings of their multi-centered study of duplex ultrasound for diagnosis of internal carotid artery (ICA) stenosis. 1
The study was developed in response to wide variability in the diagnostic criteria used to classify severity of ICA stenosis across vascular laboratories nationwide and following a survey of members of IAC-accredited ...
[1] ... [2273]
[2274]
[2275]
[2276]
[2277]
[2278]
[2279]
[2280]
2281
[2282]
[2283]
[2284]
[2285]
[2286]
[2287]
[2288]
[2289]
... [8821]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.