(Press-News.org) The risk of childhood undernutrition varies widely among villages in India, according to new research led by Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health in collaboration with researchers at Harvard's Center for Geographic Analysis, Harvard's Center for Population and Development Studies, Korea University, Microsoft, and the Government of India.
The study is the first to predict and map the burden of childhood undernutrition across all of the nearly 600,000 villages in rural India, and the methods developed to do so could be applied to other health indicators and help advance the field of "precision public health," in which interventions and policies are tailored to smaller populations that are disproportionally affected by specific health issues, according to the study's authors.
"By applying state-of-the-art data science techniques to existing public health indicators and census data, we created a framework that we hope can help local and regional decision makers better understand the substantial village disparities in childhood undernutrition," said S.V. Subramanian, corresponding author and professor of population health and geography at Harvard Chan School. "Mahatma Gandhi once said that India lives in its villages. Now we can bring the power of data science to aid public policy thru precision targeting and help ensure that children in all of India's villages are given an opportunity to grow healthy and thrive."
The study will be published April 26, 2021, in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Childhood undernutrition is a major problem in India; the country accounts for almost one-third of the global prevalence of childhood stunting. Precisely identifying areas with high levels of undernutrition, however, can be difficult because childhood nutrition data--and other key public health data--is typically analyzed at the district level. There are 640 districts in India per the 2011 census, a district can cover hundreds of square miles, and each district has an average rural population of 1.3 million people. Studying childhood nutrition data at this scale can result in oversimplified or misleading analyses that overlook substantial disparities within a district. Moreover, this approach can foster a lack of political accountability for the agencies responsible for crafting and implementing policies and interventions.
To obtain a more granular understanding of childhood undernutrition, the research team focused on India's 597,121 inhabited census villages. Villages are the smallest unit of governance in India, and the researchers said that mapping and analyzing nutrition data at the village level could provide a more accurate understanding of childhood health and result in more informed and effective local politics in India.
The team combined data from numerous sources including the 2011 census and the 2016 Indian Demographic and Health Survey, which contained anonymized GPS data on approximately 20,000 "clusters," or villages or groups of villages. The researchers then created a machine-learning prediction model to extrapolate the available data and estimate the prevalence of key indicators of undernutrition, including stunting, underweight, and wasting, for every village in the country.
The findings showed substantial variations in undernutrition across villages. For instance, the average predicted rate of stunting across all villages was 37.9%. In 691 villages, however, the average predicted rate of stunting was under 5%, while it exceeded 70% in 453 villages. In all districts, the authors noted, they found a mix of villages with high and low burdens of undernutrition.
The authors said the village-level model they created could potentially shift the paradigm of policy discussions in India by enabling policy makers and public health officials to better prioritize villages struggling with a high burden of undernutrition. The authors also created a publicly available dashboard that allows users to explore the village maps and associated data in an interactive manner.
"We focused on India, but this approach can be developed and applied to other countries to predict local health, nutrition and population estimates and better understand disparities," said first author Rockli Kim, assistant professor at Korea University and a visiting scientist at the Harvard Center for Population and Development Studies.
INFORMATION:
Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health brings together dedicated experts from many disciplines to educate new generations of global health leaders and produce powerful ideas that improve the lives and health of people everywhere. As a community of leading scientists, educators, and students, we work together to take innovative ideas from the laboratory to people's lives--not only making scientific breakthroughs, but also working to change individual behaviors, public policies, and health care practices. Each year, more than 400 faculty members at Harvard Chan School teach 1,000-plus full-time students from around the world and train thousands more through online and executive education courses. Founded in 1913 as the Harvard-MIT School of Health Officers, the School is recognized as America's oldest professional training program in public health.
One of the great mysteries of modern space science is neatly summed up by the view from NASA's Perseverance, which just landed on Mars: Today it's a desert planet, and yet the rover is sitting right next to an ancient river delta.
The apparent contradiction has puzzled scientists for decades, especially because at the same time that Mars had flowing rivers, it was getting less than a third as much sunshine as we enjoy today on Earth.
But a new study led by University of Chicago planetary scientist Edwin Kite, an assistant professor of geophysical sciences and an expert on climates of other worlds, uses a computer model to put forth a promising explanation: Mars ...
Understanding spoken words, developing normal speech - cochlear implants enable people with profound hearing impairment to gain a great deal in terms of quality of life. However, background noises are problematic, they significantly compromise the comprehension of speech of people with cochlear implants. The team led by Tobias Moser from the Institute for Auditory Neuroscience and InnerEarLab at the University Medical Center Göttingen and from the Auditory Neuroscience and Optogenetics Laboratory at the German Primate Center - Leibniz Institute for Primate Research (DPZ) is therefore working to improve cochlear implants. The scientists want to use genetic engineering methods to make the nerve cells in the ear ...
MADISON, Wis. -- In October of 2020, Jennifer Doudna and Emmanuelle Charpentier were awarded the Nobel Prize in chemistry for their discovery of an adaptable, easy way to edit genomes, known as CRISPR, which has transformed the world of genetic engineering.
CRISPR has been used to fight lung cancer and correct the mutation responsible for sickle cell anemia in stem cells. But the technology was also used by a Chinese scientist to secretly and illegally edit the genomes of twin girls -- the first-ever heritable mutation of the human germline made with genetic engineering.
"We've moved away from an era of science where we understood the risks that came with new technology and where decision stakes were ...
New findings detailing the world's first-of-its-kind estimate of how many people live in high-altitude regions, will provide insight into future research of human physiology.
Dr. Joshua Tremblay, a postdoctoral fellow in UBC Okanagan's School of Health and Exercise Sciences, has released updated population estimates of how many people in the world live at a high altitude.
Historically the estimated number of people living at these elevations has varied widely. That's partially, he explains, because the definition of "high altitude" does not have a fixed cut-off.
Using novel techniques, Dr. Tremblay's publication in the Proceedings of the National ...
New research reveals a genetic quirk in a small species of songbird in addition to its ability to carry a tune. It turns out the zebra finch is a surprisingly healthy bird.
A study published today in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences reveals that zebra finches and other songbirds have a low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) gene surprisingly different than other vertebrates.
The function of LDLR, which is responsible for cellular uptake of LDL-bound cholesterol, or "bad cholesterol," has been thought to be conserved across vertebrates. OHSU scientists found that in the case ...
Stomata, formed by a pair of kidney-shaped guard cells, are tiny pores in leaves. They act like mouths that plants use to "eat" and "breathe." When they open, carbon dioxide (CO2) enters the plant for photosynthesis and oxygen (O2) is released into the atmosphere. At the same time as gases pass in and out, a great deal of water also evaporates through the same pores by way of transpiration.
These "mouths" close in response to environmental stimuli such as high CO2 levels, ozone, drought and microbe invasion. The protein responsible for closing these "mouths" is an anion channel, called SLAC1, which moves negatively charged ions across the guard cell membrane to reduce turgor pressure. Low pressure causes the guard cells to collapse and subsequently the stomatal pore to ...
(Boston)--Lung carcinomas are the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States and worldwide. Lung squamous cell carcinomas (non-small cell lung cancers that arise in the bronchi of the lungs and make up approximately 30 percent of all lung cancers) are poorly understood, particularly with respect to the cell type and signals that contribute to disease onset.
According to the researchers, treatments for lung squamous cell carcinomas are limited and research into the etiology of the disease is required to create new ways to treat it.
"Our study offers insight into how damage ...
A multi-institutional team of researchers has identified both the genetic abnormalities that drive pre-cancer cells into becoming an invasive type of head and neck cancer and patients who are least likely to respond to immunotherapy.
"Through a series of surprises, we followed clues that focused more and more tightly on specific genetic imbalances and their role in the effects of specific immune components in tumor development," said co-principal investigator Webster Cavenee, PhD, Distinguished Professor Emeritus at University of California San Diego School of Medicine.
"The genetic ...
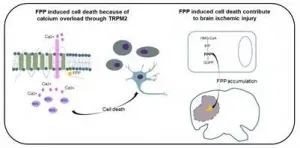
A vital intermediate in normal cell metabolism is also, in the right context, a trigger for cell death, according to a new study from Wanli Liu and Yonghui Zhang of Tsinghua University, and Yong Zhang of Peking University in Beijing, publishing 26th April 2021 in the open access journal PLOS biology. The discovery may contribute to a better understanding of the damage caused by stroke, and may offer a new drug target to reduce that damage.
Farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) is an intermediate in the mevalonate pathway, a series of biochemical reactions in every cell that contributes to protein synthesis, energy production, and construction of cell membranes. During a search for regulators of immune cell function, the authors unexpectedly discovered that FPP, when present at high concentrations ...
Patients hospitalized with COVID-19 may be at risk of developing heart failure even if they do not have a previous history of heart disease or cardiovascular risk factors, a new Mount Sinai study shows.
Researchers say that while these instances are rare, doctors should be aware of this potential complication. The study, published in the April 26 online issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, may prompt more monitoring of heart failure symptoms among patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
"This is one of the largest studies to date to specifically capture instances of new heart failure diagnosis among patients hospitalized ...