Intratumoral SIRPalpha-deficient macrophages activate tumor-specific cytotoxic T cells
2021-06-01
In a study that will be published in Nature Communications on May 28, 2021, a research team led by Dr. Yuan Liu from Georgia State University reports that intratumoral SIRPα-deficient macrophages activate tumor antigen-specific cytotoxic T cells to eliminate various syngeneic cancers under radiotherapy.
As a major component of the suppressive tumor microenvironment, tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are generally regarded as facilitators of tumor progression. It has been shown that depleting TAMs can enhance the response of tumors to radiotherapy (RT). However, Yuan's ...
Being born very preterm or very low birthweight is associated with continued lower IQ performance into adulthood
2021-06-01
The average IQ of adults born very preterm or very low birth weight was compared to those who were term born in the 1970s to 1990s in 8 longitudinal cohorts from 7 countries around the world
The IQ was significantly lower for very pre-term and very low birth weight adults in comparison to those term born, researchers from the University of Warwick have found
Action needs to be taken to ensure support is available for those born very preterm or very low birth weight
The average IQ of adults who were born very preterm (VP) or at a very low birth weight (VLBW) has been compared to adults born full term by researchers from the Department of Psychology at the University of Warwick. Researchers have found VP/VLBW children may require special ...
Genetic treasure trove for malaria researchers
2021-06-01
A new extensive genetic resource of rat-infecting malaria parasites may help advance the development of malaria prevention and treatment strategies. This trove of genome and phenome information has been published1 by a team of KAUST researchers, along with colleagues in Japan, and the datasets have been made publicly available for malaria researchers.
Rodent malaria parasites are closely related to human parasites but are easier to study because they can be grown in laboratory mice. "Investigations on rodent malaria parasites have played a key role in revealing many aspects of fascinating biology across ...
Looking at future of Antarctic through an Indigenous Māori lens
2021-06-01
It is time for the management and conservation of the Antarctic to begin focusing on responsibility, rather than rights, through an Indigenous Māori framework, a University of Otago academic argues.
In an article published in Nature Ecology & Evolution, Associate Professor Priscilla Wehi, of the Centre for Sustainability, says now is the time to be thinking of these potential changes.
"New Zealand is currently re-setting its priorities for future Antarctic research, and there may be review of the current international environmental conventions as we approach the 50-year anniversary of the protocols in 2048.
"We argue that Indigenous Māori frameworks offer powerful ways of thinking about how we protect the Antarctic, by focusing on ...
Biologists find invasive snails using new DNA-detection technique
2021-06-01
Invasive species, beware: Your days of hiding may be ending.
Biologists led by the University of Iowa discovered the presence of the invasive New Zealand mud snail by detecting their DNA in waters they were inhabiting incognito. The researchers employed a technique called environmental DNA (eDNA) to reveal the snails' existence, showing the method can be used to detect and control new, unknown incursions by the snail and other invasive species.
"eDNA has been used successfully with other aquatic organisms, but this is the first time it's been applied to detect a new invasive population of these snails, which are a destructive invasive species in fresh waters around the world," says Maurine Neiman, associate professor in the Department ...
Rush researchers develop new measure of brain health
2021-06-01
How old is your brain compared to your chronological age? A new measure of brain health developed by researchers at Rush University Medical Center may offer a novel approach to identifying individuals at risk of memory and thinking problems, according to research results published in Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association on June 1.
Dubbed the "cognitive clock" by the researchers, the tool is a measure of brain health based on cognitive performance. It may be used in the future to predict the likelihood of memory and thinking problems that develop ...
Unprecedented data sharing driving new rare disease diagnoses in Europe
2021-06-01
Rare disease experts detail the first results of an unprecedented collaboration to diagnose people living with unsolved cases of rare diseases across Europe. The findings are published today in a series of six papers in the European Journal of Human Genetics.
In the main publication, an international consortium, known as Solve-RD, explains how the periodic reanalysis of genomic and phenotypic information from people living with a rare disease can boost the chance of diagnosis when combined with data sharing across European borders on a massive scale. Using this new approach, a preliminary reanalysis of data from 8,393 individuals resulted in 255 new diagnoses, some with atypical manifestations of known diseases.
A complementary study ...
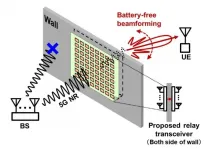
Lean and mean: Maximizing 5G communications with an energy-efficient relay network
2021-06-01
Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech) have developed a wirelessly powered relay network for 5G systems. The proposed battery-free communication addresses the challenges of flexible deployment of relay networks. This design is both economical and energy-efficient. Such advances in 5G communications will create tremendous opportunities for a wide range of sectors.
The ever-increasing demand for wireless data bandwidth shows no sign of slowing down in the near future. Millimeter wave, a short wavelength spectrum, has shown great potential in 5G communications and beyond. To leverage ...
Hypertension during pregnancy is associated with increased risk of stroke in offspring
2021-06-01
Sophia Antipolis - 1 June 2021: A study in 5.8 million children has found a higher incidence of stroke four decades later in those whose mother had high blood pressure or pre-eclampsia while pregnant. The research is presented at ESC Heart & Stroke 2021, an online scientific conference of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
"Our findings indicate that hypertensive disorders during pregnancy are associated with increased risks of stroke and potentially heart disease in offspring up to the age of 41 years," said study author Dr. Fen Yang, PhD student, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden. "Studies with longer follow-up are needed to confirm the results and ...
Greenhouse gas emissions from reservoirs higher than previously expected
2021-06-01
VANCOUVER, Wash. - A new study in Global Biogeochemical Cycles shows per-area greenhouse gas emissions from the world's water reservoirs are around 29% higher than suggested by previous studies, but that practical measures could be taken to help reduce that impact.
Much of the increase in emissions comes from previously unaccounted for methane degassing, a process where methane passes through a dam and bubbles up downstream, according to the analysis by Washington State University and University of Quebec at Montreal scientists.
Overall, the researchers found ...
Seeds of economic health disparities found in subsistence society
2021-06-01
PULLMAN, Wash. - No billionaires live among the Tsimane people of Bolivia, although some are a bit better off than others. These subsistence communities on the edge of the Amazon also have fewer chronic health problems linked to the kind of dramatic economic disparity found in industrialized Western societies.
For a study in the journal eLife, a research team led by Aaron Blackwell of Washington State University and Adrian Jaeggi of University of Zurich tracked 13 different health variables across 40 Tsimane communities, analyzing them against each person's wealth and the degree of inequality in each community. While some have theorized that inequality's health impacts are universal, the researchers found only two robustly associated outcomes: higher blood pressure and ...
Light-shrinking material lets ordinary microscope see in super resolution
2021-06-01
Electrical engineers at the University of California San Diego developed a technology that improves the resolution of an ordinary light microscope so that it can be used to directly observe finer structures and details in living cells.
The technology turns a conventional light microscope into what's called a super-resolution microscope. It involves a specially engineered material that shortens the wavelength of light as it illuminates the sample--this shrunken light is what essentially enables the microscope to image in higher resolution.
"This material converts low resolution light to high resolution light," said Zhaowei Liu, a professor of electrical and computer engineering at UC San Diego. "It's very simple ...
Scientists say active early learning shapes the adult brain
2021-06-01
An enhanced learning environment during the first five years of life shapes the brain in ways that are apparent four decades later, say Virginia Tech and University of Pennsylvania scientists writing in the June edition of the Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience.
The researchers used structural brain imaging to detect the developmental effects of linguistic and cognitive stimulation starting at six weeks of age in infants. The influence of an enriched environment on brain structure had formerly been demonstrated in animal studies, but this is the first experimental study to find a similar result in humans.
"Our research shows a relationship between brain structure and five years of high-quality, educational and social experiences," said Craig Ramey, ...
Diabetes remission diet also lowers blood pressure and reduces need for medication
2021-06-01
New research has shown that if people achieve and maintain substantial weight loss to manage their type 2 diabetes, many can also effectively control their high blood pressure and stop or cut down on their anti-hypertensive medication.
A weight management programme, developed by researchers at the Universities of Glasgow and Newcastle for the Diabetes UK-funded DIabetes REmission Clinical Trial (DIRECT), has proved effective at lowering blood pressure and reducing the need for anti-hypertensive medications, as well as bringing remission of type 2 diabetes.
The programme involves an initial 12 weeks on a nutritionally complete formula diet (low calorie soups and shakes) which will induce weight loss ...
Tai chi about equal to conventional exercise for reducing belly fat in middle aged and older adults
2021-06-01
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
1. Tai chi about equal to conventional exercise for reducing belly fat in middle-aged and older adults
HD video soundbites ...
Study suggests tai chi can mirror healthy benefits of conventional exercise
2021-06-01
UCLA HEALTH RESEARCH BRIEF
FINDINGS
A new study shows that tai chi mirrors the beneficial effects of conventional exercise by reducing waist circumference in middle-aged and older adults with central obesity. The study was done by investigators at the University of Hong Kong, The Chinese University of Hong Kong; Chinese Academy of Sciences; and UCLA.
BACKGROUND
Central obesity is a major manifestation of metabolic syndrome, broadly defined as a cluster of cardiometabolic risk factors, including central obesity, dyslipidemia, hyperglycemia, low high-density lipoprotein ...
Overconfidence in news judgement
2021-05-31
A new study published in Proceedings of National Academics of Sciences finds that individuals who falsely believe they are able to identify false news are more likely to fall victim to it. In the article published today, Ben Lyons, assistant professor of communication at the University of Utah, and his colleagues examine the concern about the public's susceptibility to false news due to their inability to recognize their own limitations in identifying such information.
"Though Americans believe confusion caused by false news is extensive, relatively few indicate having seen or shared it," said Lyons. "If people incorrectly see themselves as highly skilled at identifying false news, they may unwittingly be more likely to consume, believe and share it, especially if it conforms to their ...
New 'Swiss Army knife' cleans up water pollution
2021-05-31
Phosphate pollution in rivers, lakes and other waterways has reached dangerous levels, causing algae blooms that starve fish and aquatic plants of oxygen. Meanwhile, farmers worldwide are coming to terms with a dwindling reserve of phosphate fertilizers that feed half the world's food supply.
Inspired by Chicago's many nearby bodies of water, a Northwestern University-led team has developed a way to repeatedly remove and reuse phosphate from polluted waters. The researchers liken the development to a "Swiss Army knife" for pollution remediation as they tailor their membrane to absorb ...
Extreme CO2 greenhouse effect heated up the young Earth
2021-05-31
Very high atmospheric CO2 levels can explain the high temperatures on the still young Earth three to four billion years ago. At the time, our Sun shone with only 70 to 80 per cent of its present intensity. Nevertheless, the climate on the young Earth was apparently quite warm because there was hardly any glacial ice. This phenomenon is known as the 'paradox of the young weak Sun.' Without an effective greenhouse gas, the young Earth would have frozen into a lump of ice. Whether CO2, methane, or an entirely different greenhouse gas heated up planet Earth is a matter of debate among scientists. New research by Dr ...
Duetting songbirds 'mute' the musical mind of their partner to stay in sync
2021-05-31
Art Garfunkel once described his legendary musical chemistry with Paul Simon, "We meet somewhere in the air through the vocal cords ... ." But a new study of duetting songbirds from Ecuador, the plain-tail wren (Pheugopedius euophrys), has offered another tune explaining the mysterious connection between successful performing duos.
It's a link of their minds, and it happens, in fact, as each singer mutes the brain of the other as they coordinate their duets.
In a study published May 31 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, a team of researchers studying brain ...
Researchers report reference genome for maize B chromosome
2021-05-31
Three groups (Dr. James Birchler's group from University of Missouri, Dr. Jan Barto's group from Institute of Experimental Botany of the Czech Academy of Sciences and Dr. HAN Fangpu's group from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences) recently reported a reference sequence for the supernumerary B chromosome in maize in a study published online in PNAS (doi:10.1073/pnas.2104254118).
Supernumerary B chromosomes persist in thousands of plant and animal genomes despite being nonessential. They are maintained in populations by mechanisms of "drive" that make them inherited at higher than typical Mendelian rates. Key properties such as its origin, evolution, and the molecular mechanism for its accumulation in ...
Newly discovered African 'climate seesaw' drove human evolution
2021-05-31
While it is widely accepted that climate change drove the evolution of our species in Africa, the exact character of that climate change and its impacts are not well understood. Glacial-interglacial cycles strongly impact patterns of climate change in many parts of the world, and were also assumed to regulate environmental changes in Africa during the critical period of human evolution over the last ~1 million years. The ecosystem changes driven by these glacial cycles are thought to have stimulated the evolution and dispersal of early humans.
A paper published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) this week challenges this view. Dr. Kaboth-Bahr ...
Using fossil plant molecules to track down the Green Sahara
2021-05-31
The Sahara has not always been covered by only sand and rocks. During the period from 14,500 to 5,000 years ago large areas of North Africa were more heavily populated, and where there is desert today the land was green with vegetation. This is evidenced by various sites with rock paintings showing not only giraffes and crocodiles, but even illustrating people swimming in the "Cave of Swimmers". This period is known as the Green Sahara or African Humid Period. Until now, researchers have assumed that the necessary rain was brought from the tropics through an enhanced summer monsoon. The northward shift of the monsoon was attributed to rotation of the Earth's tilted axis that produces higher levels of ...
Emotional regulation technique may be effective in disrupting compulsive cocaine addiction
2021-05-31
An emotion regulation strategy known as cognitive reappraisal helped reduce the typically heightened and habitual attention to drug-related cues and contexts in cocaine-addicted individuals, a study by Mount Sinai researchers has found. In a paper published in PNAS, the team suggested that this form of habit disruption, mediated by the prefrontal cortex (PFC) of the brain, could play an important role in reducing the compulsive drug-seeking behavior and relapse that are the hallmarks, and long-standing challenges, of addiction.
"Relapse in addiction is often precipitated by heightened attention-bias to drug-related cues, which could consist of sights, smells, ...
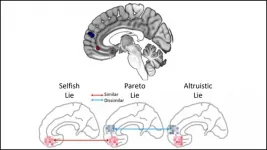
Brain activity reveals when white lies are selfish
2021-05-31
You may think a little white lie about a bad haircut is strictly for your friend's benefit, but your brain activity says otherwise. Distinct activity patterns in the prefrontal cortex reveal when a white lie has selfish motives, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
White lies -- formally called Pareto lies -- can benefit both parties, but their true motives are encoded by the medial prefrontal cortex (MPFC). This brain region computes the value of different social behaviors, with some subregions focusing on internal motivations and others on external ones. Kim and Kim predicted activity patterns in these subregions could elucidate the true motive behind white lies.
The research team deployed a stand in for white lies, having participants tell lies to earn a reward ...
[1] ... [2265]
[2266]
[2267]
[2268]
[2269]
[2270]
[2271]
[2272]
2273
[2274]
[2275]
[2276]
[2277]
[2278]
[2279]
[2280]
[2281]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.