The properties of non-racemic dihydrofurans have been studied at Samara Polytech
2021-05-28
The research team of the Department of Organic Chemistry of Samara Polytech under the leadership of Doctor of Chemical Sciences, Head of the Department Yuri Klimochkin and Doctor of Chemical Sciences, Professor Alexander Reznikov in cooperation with the crystallographic research group of Lomonosov Moscow State University (supervisor - candidate of chemical sciences, senior researcher Victor Rybakov) completed a study to obtain non-racemic 4,5-dihydrofurans based on Michael addition and study their chemical properties. The announcement of a scientific article with the results of the latest research is posted on the cover of the authoritative journal Tetrahedron.
"Studying the method of obtaining ...
'Good' bacteria show promise for clinical treatment of Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis
2021-05-28
CHAPEL HILL, NC - A new study published in Nature Communications demonstrates that a consortium of bacteria designed to complement missing or underrepresented functions in the imbalanced microbiome of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients, prevented and treated chronic immune-mediated colitis in humanized mouse models. The study's senior author, Balfour Sartor, MD, Midget Distinguished Professor of Medicine, Microbiology and Immunology, Co-Director of the UNC Multidisciplinary IBD Center, said the results are encouraging for future use treating Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis patients.
"The idea with this treatment is to restore the normal ...
The dark matter particle explorer has measured high-precision cosmic ray helium energy spectrum
2021-05-28
Dark Matter Particle Explorer (DAMPE) Collaboration directly observed a spectral softening of helium nuclei at about 34TeV for the first time. This work was based on measurements data of the helium spectrum with kinetic energies from 70 GeV to 80 TeV (17.5 GeV/n to 20 TeV/n for per nucleon) recorded by the DAMPE.
The relevant results were published in Physical Review Letters.
Galactic cosmic rays (GCRs) offers important ways to deeply understand the astrophysical particle origin and accelerators and the interstellar medium of the Galaxy. Helium nuclei, the second most abundant nuclear element of cosmic rays, is a distinguishing feature of space.
As for GCRs, the energy spectrum is supposed to follow a negative power law distribution when energies are below the "knee" (at ...
Detecting skin disorders based on tissue stiffness with a soft sensing device
2021-05-28
By putting a piece of soft, strain-sensing sheet on the skin may be able to detect skin disorders non-invasively and in real-time very soon. A research team co-led by a scientist from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has designed a simple electromechanical device that can be used for deep tissue pathology diagnosis, such as psoriasis, in an automated and non-invasive fashion. The findings will lay a foundation for future applications in the clinical evaluation of skin cancers and or dermatology diseases.
The research is co-led by Dr Yu Xinge, Assistant Professor from CityU's Department of Biomedical Engineering, and scientists from and Northwestern University in the US. Their findings have been published in the science journal Nature Biomedical Engineering, titled "Miniaturized ...
Revenge of the seabed burrowers
2021-05-28
New Haven, Conn. -- The ancient burrowers of the seafloor have been getting a bum rap for years.
These prehistoric dirt churners -- a wide assortment of worms, trilobites, and other animals that lived in Earth's oceans hundreds of millions of years ago -- are thought to have played a key role in creating the conditions needed for marine life to flourish. Their activities altered the chemical makeup of the sea itself and the amount of oxygen in the oceans, in a process called bioturbation.
But did that bioturbation help or hinder the expansion of complex animal life? A new Yale study, published in the journal Earth and Planetary Science Letters, found that ...
Ban on flavored vaping may have led teens to cigarettes, study finds
2021-05-28
New Haven, Conn. -- When San Francisco voters overwhelmingly approved a ballot measure banning the sale of flavored tobacco products in 2018, public health advocates celebrated. After all, tobacco use poses a significant threat to public health and health equity, and flavors are particularly attractive to youth.
But according to a new study from the Yale School of Public Health (YSPH), that law may have had the opposite effect. Analyses found that, after the ban's implementation, high school students' odds of smoking conventional cigarettes doubled in San Francisco's school district relative to trends in districts without the ban, even when adjusting for individual demographics and other ...
Electrons waiting for their turn: New model explains 3D quantum material
2021-05-28
This new 3D effect can be the foundation for topological quantum phenomena, which are believed to be particularly robust and therefore promising candidates for extremely powerful quantum technologies. These results have just been published in the scientific journal Nature Communications.
Dr. Tobias Meng and Dr. Johannes Gooth are early career researchers in the Würzburg-Dresdner Cluster of Excellence ct.qmat that researches topological quantum materials since 2019. They could hardly believe the findings of a recent publication in "Nature" claiming that electrons in the topological metal zirconium pentatelluride (ZrTe5) move only in two-dimensional ...
Open, expressive family life may reduce social deprivation effects among adopted children
2021-05-28
WHAT:
An environment in which family members support one another and express their feelings can reduce the effects of social deprivation on cognitive ability and development among adopted children, suggests a small study by researchers at the National Institutes of Health. In contrast, rule-driven households where family members are in conflict may increase an adopted child's chances for cognitive, behavioral and emotional difficulties.
The study was conducted by Margaret F. Keil, Ph.D., and colleagues in the Section on Endocrinology and Genetics at NIH's Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD). It appears in Pediatric Research.
Researchers enrolled children who had spent at least eight ...
Natural gas pipeline density higher overall in more vulnerable US counties
2021-05-28
An analysis led by North Carolina State University researchers found counties with more socially vulnerable populations had a higher density of natural gas pipelines overall.
The findings suggest counties that are more socially vulnerable are also at greater risk of facing water and air pollution, public health and safety issues, and other negative impacts associated with the pipelines.
"We know that the network, as it stands today, is already distributed in such a way that any negative impacts fall disproportionately on vulnerable communities," ...
Better choice of contraceptives can prevent breast cancer
2021-05-28
Hormonal contraceptives, e.g. the pill, the patch, and the vaginal ring, contain synthetic hormones that prevent pregnancy by either stopping ovulation, changing the cervical mucus to stop sperm from passing through the cervix and finding an egg, or changing the womb's lining to prevent a fertilized egg from being implanted in it.
Despite their widespread use, hormonal contraceptives are known to increase the risk of breast cancer, which is the most common cause of cancer-related death among women worldwide, and also topped the list of most commonly diagnosed cancers in 2020.
The main component of hormonal contraceptives are progestins, ...
Moving one step closer to personalized anesthesia
2021-05-28
Anesthesia may be an exact science, but it's not yet fully personalized. Anesthesiologists use a variety of methods to calculate the right dose for a given patient: clinical studies, medical databases and laboratory measurements, for example. However, every individual responds to anesthetics in a different way, and there's no way of knowing what that response will be until the anesthetic is administered.
Personalizing dosage
Today patients often receive supplemental doses of an anesthetic during their operation based on their reaction. The role of anesthesiologists is to make sure that a patient doesn't wake up too soon and has no memory of the procedure, but they must use ...
Study identifies risk for some childhood cancer patients developing secondary leukaemia
2021-05-28
Scientists from the Wellcome Sanger Institute and the University of Cambridge found that in children with neuroblastoma - a cancer of immature nerve cells - treatment with platinum chemotherapy caused changes to the genome that could then cause leukaemia in some children later on.
The findings, published 27th May 2021 in Blood could lead to an ability to identify which children are more likely to develop the secondary cancer. This in turn could lead to changes in their treatment plan to either avoid these risks or take measures to prepare.
Secondary blood cancer is a challenging complication of childhood neuroblastoma cancer treatment. Every year around 100 children in the UK are diagnosed with neuroblastoma*, ...
40 top scientists to WHO: requirements for ventilation systems must be reinforced
2021-05-28
The group of experts includes Professor and Academician of Tallinn University of Technology Jarek Kurnitski, who said that improving ventilation can be regarded more broadly as a paradigm shift equal in scale to the transformation in the standards of drinking water supplies and food hygiene. "There has long been no doubt that you can get infection when you drink water or eat food that has been contaminated. Now we must work towards providing clean air so we can breathe safely," Kurnitski said.
He added, "Researchers see updating of ventilation standards, ventilation requirements based on the probability of infection and more efficient and flexible ventilation systems as a solution. High air change rates are required only in the event of an epidemic, at any ...
Immunity boost in the gut
2021-05-28
Varying immune response to vaccinations could be countered with microbiota-targeted interventions helping infants, older people and others to take full advantage of the benefits of effective vaccines, Australian and US experts say.
A comprehensive review in Nature Reviews Immunology concludes that evidence is mounting in clinical trials and other studies that the composition and function of individuals' gut microbiota are "crucial factors" in affecting immune responses to vaccinations.
"Never before has the need been greater for robust and long-lasting immunity from our vaccination programs, particularly in low and middle-income countries, and for populations at increased ...
Video platforms normalize exotic pets
2021-05-28
Researchers at the University of Adelaide are concerned video sharing platforms such as YouTube could be contributing to the normalisation of exotic pets and encouraging the exotic pet trade.
In a study, published in PLOS ONE, researchers analysed the reactions of people to videos on YouTube involving human interactions with exotic animals and found those reactions to be overwhelmingly positive.
The researchers analysed the reactions - via text and emoji usage - in comments posted on 346 popular videos starring exotic wild cats and primates in 'free handling situations'.
These situations involved exotic animals interacting with humans or other animals, such as domestic cats and dogs. The videos examined received ...
COVID-19 kept our parks busy, but not everyone ventured outside
2021-05-28
Public use of parks and reserves increased only slightly during last year's COVID-19 national lockdown despite gyms and sports facilities shutting down, a University of Queensland study found.
UQ School of Biological Sciences PhD candidate Violeta Berdejo-Espinola surveyed 1000 people in Brisbane, measuring their use of urban green space and the benefits people associated with visiting the areas during lockdown.
"People all around Brisbane, myself included, noticed a boom in park use in 2020, but while more people ventured into local parks, many folks were left indoors," Ms Berdejo-Espinola said.
"Thirty-six ...
Direct evidence of segregated oceanic crust trapped within the mantle transition zo
2021-05-28
Professor YAO Huajian's research group from the School of Earth and Space Sciences of the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC), in cooperation with Dr. Piero Poli from Grenoble-Alpes University of France, combined the unique resolution reflected body waves (P410P and P660P) retrieved from ambient noise interferometry with mineral physics modeling, to shed new light on transition zone physics. Relevant work was published in Nature Communications.
The subduction of oceanic slabs is an important process of the earth's internal material circulation. Studying the ...
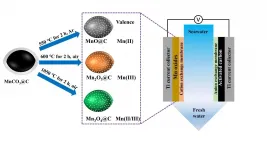
High-capacity electrodes by valence engineering developed for desalination
2021-05-28
Recently, the researchers from Institute of Solid State Physics, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, by using valence engineering, developed three manganese oxides as electrodes with different Mn valences for high-performance capacitive desalination.
Reverse osmosis and thermal distillation are widely used to treat salt water with high salt concentration, but they have disadvantages including high energy consumption and high cost.
As an alternative method, capacitive deionization (CDI) technology can remove charged ions ...
Tiniest of moments proves key for baby's healthy brain
2021-05-28
University of Virginia School of Medicine researchers have shed new light on how our brains develop, revealing that the very last step in cell division is crucial for the brain to reach its proper size and function.
The new findings identify a potential contributor to microcephaly, a birth defect in which the head is underdeveloped and abnormally small. That's because the head grows as the brain grows. The federal Centers for Disease Control estimates that microcephaly affects from 1 in 800 children to 1 in 5,000 children in the United States each year. The condition is associated with learning disabilities, developmental delays, ...
Waking just one hour earlier cuts depression risk by double digits
2021-05-28
Waking up just one hour earlier could reduce a person's risk of major depression by 23%, suggests a sweeping new genetic study published May 26 in the journal JAMA Psychiatry.
The study of 840,000 people, by researchers at University of Colorado Boulder and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, represents some of the strongest evidence yet that chronotype--a person's propensity to sleep at a certain time --influences depression risk.
It's also among the first studies to quantify just how much, or little, change is required to influence mental health. ...
A helping hand for working robots
2021-05-28
Until now, competing types of robotic hand designs offered a trade-off between strength and durability. One commonly used design, employing a rigid pin joint that mimics the mechanism in human finger joints, can lift heavy payloads, but is easily damaged in collisions, particularly if hit from the side. Meanwhile, fully compliant hands, typically made of molded silicone, are more flexible, harder to break, and better at grasping objects of various shapes, but they fall short on lifting power.
The DGIST research team investigated the idea that a partially-compliant ...
New drug combo found effective against high-risk leukaemia
2021-05-28
Australian scientists have found what could prove to be a new and effective way to treat a particularly aggressive blood cancer in children.
Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, or ALL, is the most common cancer diagnosed in children. Despite dramatic improvements in the survival of children with ALL over past several decades, children who develop 'high risk' ALL - subtypes that grow aggressively and are often resistant to standard treatments - often relapse, and many of these children die from their disease.
One common type of high-risk ALL for which new therapies are urgently needed is 'Philadelphia chromosome-like ALL' (Ph-like ALL), named for its similarity ...
Plant flowering in low-nitrogen soils: A mechanism revealed
2021-05-28
Scientists from Japan, Europe and the USA have described a pathway leading to the accelerated flowering of plants in low-nitrogen soils. These findings could eventually lead to increases in agricultural production.
Nitrogen is one of the three macronutrients required by plants for growth and development, along with phosphorus and potassium. Nitrogen-rich condition induces plant growth, particularly the growth of stems and leaves, while delaying flowering. On the other hand, in some plants, low-nitrogen conditions lead to a change from growth mode to reproductive mode, therefore accelerating flowering. However, the molecular mechanisms that regulate flowering under these conditions are not known.
A team of scientists led by Associate ...
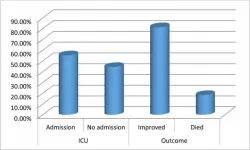
Prognostic value of troponin I in COVID-19 patients
2021-05-28
Corona Virus Disease (COVID -19) patients primarily appear with respiratory issues and viral pneumonia. The patients may also present cardiovascular issues includes early signs of acute myocardial injury. The researchers from Sohag University, Egypt, found that cardiac troponin I (cTnI) can prove to be a gold-standard biomarker for necrosis and myocardial risk assessment in COVID-19 sufferers.
The researchers aimed to assess the prognostic value of cTnI in COVID-19 sufferers. The study included ninety-two COVID-19 patients admitted in the El Helal ...
Reef-building corals and the microscopic algae within their cells evolve together
2021-05-28
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- The microscopic algae that live inside and provide nutrients to their reef-building coral hosts may be evolving in tandem with the corals they inhabit, so each partner is fine-tuned to meet one another's needs. A new study by Penn State biologists reveals that genetic differences within a species of these microalgal symbionts correspond to the coral species they inhabit, a discovery that could have implications for the conservation of these endangered corals.
"Acroporid corals are some of the primary reef-building species in the Caribbean, providing protection to coastlines and habitat for economically important species," said Iliana Baums, professor of biology at Penn State and leader of the research team. "However, these corals are critically ...
[1] ... [2268]
[2269]
[2270]
[2271]
[2272]
[2273]
[2274]
[2275]
2276
[2277]
[2278]
[2279]
[2280]
[2281]
[2282]
[2283]
[2284]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.