(Press-News.org) Children determine emotion by what they hear, rather than what they see, according to new research.
The first-of-its-kind study, by Durham University's Department of Psychology, looked at how children pick up on the emotions of a situation.
They found that whilst adults prioritised what they see, young children showed an auditory dominance and overwhelmingly prioritised what they could hear.
The researchers say their findings could benefit parents currently managing home learning and professional educators by increasing their understanding of how young children pick up on what is going on around them.
The research may also provide new avenues to understanding emotional recognition in children with developmental challenges such as autism.
The findings are published in the Journal of Experimental Child Psychology.
Lead author Dr Paddy Ross, in Durham University's Department of Psychology, said: "Our study found that young children over-rely on what they hear to make judgements about the emotions of a situation. With so many children spending much more time at home currently, there is huge value in considering what they may hear and pick up on.
"There could also be applications for how to make online learning more effective as well as our understanding of how children with challenges such as autism may detect and understand emotions."
The research was designed to test whether the previously identified 'Colavita effect', which had shown that from around the age of eight years old humans tend to respond more to visual rather than auditory stimuli, held true for more complex situations such as emotional recognition in young children.
The team undertook two experiments with volunteers in three age categories (seven and under, eight to 11, and 18+).
The volunteers were shown pictures of humans, with faces blurred, for the visual stimuli, and human voices for the auditory stimuli, which conveyed happy and fearful and sad and angry emotions.
The stimuli were presented both on their own, and in corresponding and contrasting combinations, and participants were asked what the over-riding emotion was in each.
The team found that when the visual and auditory stimuli were combined, adults based their emotional assessment on what they could see whereas young children overwhelmingly gave precedence to what they could hear.
All age groups scored over 90 per cent when presented with visual and auditory stimuli in isolation. A similar score was recorded when the stimuli were combined, and participants were asked to ignore the visual stimuli and identify the emotion from the voice.
However, when younger and older children were asked to ignore the voice and base their judgement on the body stimuli, the team found that they performed significantly worse than adults when presented with a combination where the emotions displayed in the visual and auditory stimuli did not match.
Children also scored significantly below chance level, indicating that they were not merely guessing, but selecting the spoken emotion, rather than the visual, despite being told to ignore it.
Dr Ross now plans to undertake further research to investigate whether young children still rely on what they can hear when human facial expressions are present, and when human voices are replaced with music conveying similar emotions.
INFORMATION:
Theories were introduced as far back as the 1960s about the possible existence of superheavy elements. Their most long-lived atomic nuclei could give rise to a so-called "island of stability" far beyond the element uranium. However, a new study, led by nuclear physicists at Lund University, shows that a 50-year-old nuclear physics manifesto must now be revised.
The heaviest element found in nature is uranium, with a nucleus containing 92 protons and 146 neutrons. The nuclei of heavier elements become more and more unstable due to the increased number of positively charged protons. They therefore decay faster and faster, usu-ally within a fraction of a second. ...
As the world prepares to commemorate International Holocaust Remembrance Day on January 27th, communities and memorials around the world are addressing how to meaningfully commemorate the day while protecting public health and safety. The day marking the anniversary of the liberation of Auschwitz is ordinarily commemorated with hundreds of individual memorial events across the globe. This year, most of those events will be impossible for any sizable gathering of people due to COVID-19.
With the goal of proposing relevant solutions to this challenge, Dr. Tobias Ebbrecht-Hartmann and research student Tom Divon of the Hebrew ...
ATLANTA - JANUARY 26, 2021 - A new study shows 4 in 10 cancer deaths are attributable to cigarette smoking in parts of the South region and Appalachia. For this study, appearing in Cancer Causes & Control, Farhad Islami, MD, PhD, and colleagues at the American Cancer Society examined the proportion of cancer deaths from 2013 to 2017 attributed to cigarette smoking in 152 metropolitan and micropolitan statistical areas (MMSAs).
Data show the proportion of cancer deaths attributable to cigarette smoking was greater in men than in women in all evaluated MMSAs. In both sexes combined, the proportion of smoking-related cancer deaths ranged from 8.8% in Logan ...
The battle to stop false news and online misinformation is not going to end any time soon, but a new finding from MIT scholars may help ease the problem.
In an experiment, the researchers discovered that fact-checking labels, when attached to online news headlines, actually work better after people read false headlines, compared to when they precede the headline or accompany it.
"We found that whether a false claim was corrected before people read it, while they read it, or after they read it influenced the effectiveness of the correction," says David Rand, an MIT professor and co-author of a new paper detailing the study's results.
Specifically, the researchers found, when "true" and "false" labels were shown immediately after participants in the experiment read headlines, ...
A new neural network developed by researchers at the University of Eastern Finland and Kuopio University Hospital enables an easy and accurate assessment of sleep apnoea severity in patients with cerebrovascular disease. The assessment is automated and based on a simple nocturnal pulse oximetry, making it possible to easily screen for sleep apnoea in stroke units.
Up to 90% of patients experiencing a stroke have sleep apnoea, according to earlier studies conducted at Kuopio University Hospital. If left untreated, sleep apnoea can reduce the quality of life and rehabilitation of patients with stroke and increase ...
An estimated 48 million cases of foodborne illness are contracted in the United States every year, causing about 128,000 hospitalizations and 3,000 deaths, according to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC). In some instances, the source is well known, such as a batch of tainted ground beef that infected 209 people with E. Coli in 2019. But 80 percent of food poisoning cases are of unknown origin, making it impossible to inform consumers of hazardous food items.
David Goldberg, assistant professor of management information systems at San Diego State University, wants to improve the traceability and ...
Overview:
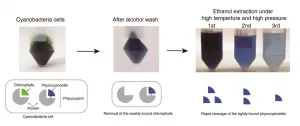
Phycocyanobilin (PCB) is a natural blue chromophore found in cyanobacteria. PCB is expected to be applied as food colorants and pharmaceuticals with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. PCB also functions as the chromophore of photoswitches that control biological functions in synthetic biology. PCB is covalently bound to phycocyanin, a component of photosynthetic antenna protein, and its extraction requires specialized expertise, time-consuming procedures, and/or expensive reagents. A research group led by Assistant Professor Yuu Hirose at Toyohashi University of Technology succeeded in developing a highly efficient and rapid extraction method for PCB by treating cyanobacterial cells with alcohol ...
The use of online messaging and social media apps among Singapore residents has spiked during the COVID-19 pandemic, a Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) study has found.
Three in four respondents (75%) said that their use of WhatsApp during the pandemic increased. This was followed by Telegram (60.3%), Facebook (60.2%) and Instagram (59.7%).
Accompanying this spike is videoconferencing fatigue, found the NTU Singapore study, which surveyed 1,606 Singapore residents from 17 to 31 December last year. Nearly one in two Singapore residents (44%) said they felt drained from videoconferencing activities, which ...
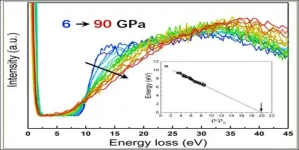
Utilizing a newly developed state-of-the-art synchrotron technique, a group of scientists led by Dr. Ho-kwang Mao, Director of HPSTAR, conducted the first-ever high-pressure study of the electronic band and gap information of solid hydrogen up to 90 GPa. Their innovative high pressure inelastic X-ray scattering result serves as a test for direct measurement of the process of hydrogen metallization and opens a possibility to resolve the electronic dispersions of dense hydrogen. This work is published in the recent issue of Physical Review Letters.
The pressure-induced evolution of hydrogen's electronic band from a wide gap insulator to a closed gap metal, or metallic ...
A group of KAIST researchers and collaborators have engineered a tiny brain implant that can be wirelessly recharged from outside the body to control brain circuits for long periods of time without battery replacement. The device is constructed of ultra-soft and bio-compliant polymers to help provide long-term compatibility with tissue. Geared with micrometer-sized LEDs (equivalent to the size of a grain of salt) mounted on ultrathin probes (the thickness of a human hair), it can wirelessly manipulate target neurons in the deep brain using light.
This study, led by Professor Jae-Woong Jeong, is a step forward from the wireless head-mounted ...