(Press-News.org) An estimated 48 million cases of foodborne illness are contracted in the United States every year, causing about 128,000 hospitalizations and 3,000 deaths, according to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC). In some instances, the source is well known, such as a batch of tainted ground beef that infected 209 people with E. Coli in 2019. But 80 percent of food poisoning cases are of unknown origin, making it impossible to inform consumers of hazardous food items.
David Goldberg, assistant professor of management information systems at San Diego State University, wants to improve the traceability and communication of risky food products. In a new study published by the journal Risk Analysis, his research team proposes a new Food Safety Monitoring System (FSMS) that utilizes consumer comments posted on websites to identify products associated with food-related illnesses.
The researchers utilized an AI technology called text mining to analyze comments and reviews from two websites: Amazon.com, the world's largest e-commerce retailer, and IWasPoisoned.com, a site where consumers alert others to cases of food poisoning. The database consisted of 11,190 randomly selected Amazon reviews of "grocery and canned food" items purchased between 2000 and 2018, along with 8,596 reviews of food products posted on IWasPoisoned.com. These two datasets allowed the researchers to test the text mining tools before analyzing 4.4 million more Amazon reviews.
The computers were programmed to recognize words associated with foodborne illness such as "sick," "vomiting," "diarrhea," "fever," and "nausea." This resulted in a list of flagged products that included specific brands of protein bars, herbal teas, and protein powder. Two of the products flagged by the computers had already been recalled.
An important final step in the monitoring system was a manual review by a panel of 21 food safety experts. Their job was to verify the risk level of a product and suggest a remediation strategy for the manufacturer. For example, in the case of an allergic reaction, experts would recommend investigating alternative ingredients or revising product packaging to include a consumer warning.
In future work, Goldberg hopes to create a way of alerting consumers to food product risks when they are shopping online. Amazon reviewers can give products a star rating and post comments, but it is difficult and time consuming to sort through those reviews looking for health risks. "If there were a panel that popped up on their screen, it would make them more informed as a consumer and allow them to make a purchasing decision that may ultimately make them feel safer," says Goldberg.
INFORMATION:
About SRA
The Society for Risk Analysis is a multidisciplinary, interdisciplinary, scholarly, international society that provides an open forum for all those interested in risk analysis. SRA was established in 1980 and has published Risk Analysis: An International Journal, the leading scholarly journal in the field, continuously since 1981. For more information, visit http://www.sra.org.
Overview:
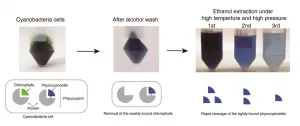
Phycocyanobilin (PCB) is a natural blue chromophore found in cyanobacteria. PCB is expected to be applied as food colorants and pharmaceuticals with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. PCB also functions as the chromophore of photoswitches that control biological functions in synthetic biology. PCB is covalently bound to phycocyanin, a component of photosynthetic antenna protein, and its extraction requires specialized expertise, time-consuming procedures, and/or expensive reagents. A research group led by Assistant Professor Yuu Hirose at Toyohashi University of Technology succeeded in developing a highly efficient and rapid extraction method for PCB by treating cyanobacterial cells with alcohol ...
The use of online messaging and social media apps among Singapore residents has spiked during the COVID-19 pandemic, a Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) study has found.
Three in four respondents (75%) said that their use of WhatsApp during the pandemic increased. This was followed by Telegram (60.3%), Facebook (60.2%) and Instagram (59.7%).
Accompanying this spike is videoconferencing fatigue, found the NTU Singapore study, which surveyed 1,606 Singapore residents from 17 to 31 December last year. Nearly one in two Singapore residents (44%) said they felt drained from videoconferencing activities, which ...
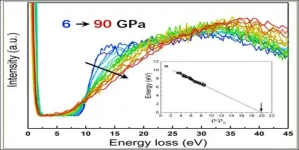
Utilizing a newly developed state-of-the-art synchrotron technique, a group of scientists led by Dr. Ho-kwang Mao, Director of HPSTAR, conducted the first-ever high-pressure study of the electronic band and gap information of solid hydrogen up to 90 GPa. Their innovative high pressure inelastic X-ray scattering result serves as a test for direct measurement of the process of hydrogen metallization and opens a possibility to resolve the electronic dispersions of dense hydrogen. This work is published in the recent issue of Physical Review Letters.
The pressure-induced evolution of hydrogen's electronic band from a wide gap insulator to a closed gap metal, or metallic ...
A group of KAIST researchers and collaborators have engineered a tiny brain implant that can be wirelessly recharged from outside the body to control brain circuits for long periods of time without battery replacement. The device is constructed of ultra-soft and bio-compliant polymers to help provide long-term compatibility with tissue. Geared with micrometer-sized LEDs (equivalent to the size of a grain of salt) mounted on ultrathin probes (the thickness of a human hair), it can wirelessly manipulate target neurons in the deep brain using light.
This study, led by Professor Jae-Woong Jeong, is a step forward from the wireless head-mounted ...
The prevalence of inflammatory bowel diseases has significantly increased both in Finland and globally. These disorders cannot be entirely cured. Instead, they are treated with anti-inflammatory drugs and, at times, through surgery.
If conventional drug therapies based on anti-inflammatory drugs are ineffective, the diseases can be treated using infliximab, a biological TNF-α blocker that is administered intravenously. Infliximab is an antibody that prevents TNF-α, a pro-inflammatory factor, from binding with inflammatory cells in the intestine. It is effective in reducing inflammation and improving the patient's condition, while also controlling the disease well.
Although infliximab therapy is often effective, roughly 30-40% of patients either do not respond ...
An international research team succeeded in gaining new insights into the artificially produced superheavy element flerovium, element 114, at the accelerator facilities of the GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung in Darmstadt, Germany. Under the leadership of Lund University in Sweden and with significant participation of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) as well as the Helmholtz Institute Mainz (HIM) in Germany and other partners, flerovium was produced and investigated to determine whether it has a closed proton shell. The results suggest that, contrary to expectations, flerovium is not a so-called "magic nucleus". The results were published in ...
Two family members test positive for COVID-19 -- how do we know who infected whom? In a perfect world, network science could provide a probable answer to such questions. It could also tell archaeologists how a shard of Greek pottery came to be found in Egypt, or help evolutionary biologists understand how a long-extinct ancestor metabolized proteins.
As the world is, scientists rarely have the historical data they need to see exactly how nodes in a network became connected. But a new paper published in Physical Review Letters offers hope for reconstructing the missing information, using a new method to evaluate the rules that generate network models.
"Network models are like impressionistic ...
A new paper from UC Santa Cruz researchers, published in END ...
Overview:
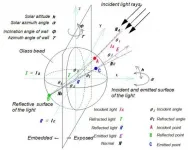
Jihui Yuan (Assistant Professor, Department of Architecture and Civil Engineering, Toyohashi University of Technology) proposed a numerical bead model to predict the upward-to-downward reflection ratio of glass bead retro-reflective (RR) material purposed for urban heat island (UHI) mitigation and reducing energy consumption. It revealed that the retro-reflectivity of glass bead RR material gradually increases from morning to noon, at which time it begins to gradually decrease. These results will contribute to existing research on the absorption or reflection of solar radiation to improve urban thermal and lighting ...
WASHINGTON--Poor social conditions caused by systemic racism contribute to health disparities in people with diabetes, according to a paper published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Minorities are disproportionately affected by diabetes because of poor social conditions that contribute to negative health outcomes such as poverty, unsafe housing, lack of access to healthy food and safe physical activity, and inadequate employment and educational opportunities. These are known as the social determinants of health and are the result of residential ...