Trust the machine -- it knows what it is doing
2021-06-01
Machine learning, when used in climate science builds an actual understanding of the climate system, according to a study published in the journal Chaos by Manuel Santos Gutiérrez and Valerio Lucarini, University of Reading, UK, Mickäel Chekroun, the Weizmann Institute, Israel and Michael Ghil, Ecole Normale Supérieure, Paris, France. This means we can trust machine learning and further its applications in climate science, say the authors. The study is part of the European Horizon 2020 TiPES project on tipping points in the Earth system. TiPES is administered from the University of Copenhagen, Denmark.
Man or ...
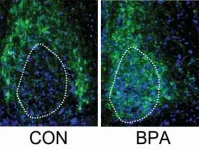
UCalgary study shows BPA exposure below regulatory levels can impact brain development
2021-06-01
Humans are exposed to a bath of chemicals every day. They are in the beds where we sleep, the cars that we drive and the kitchens we use to feed our families. With thousands of chemicals floating around in our environment, exposure to any number is practically unavoidable. Through the work of researchers like Dr. Deborah Kurrasch, PhD, the implications of many of these chemicals are being thoroughly explored.
"Manufacturers follow standards set by regulatory bodies, it's not up to the manufacturers to prove the chemicals in consumer products are safe," says Kurrasch, a researcher in the University of Calgary's Hotchkiss Brain ...
Right-wing rhetoric and the trivialization of pandemic casualties
2021-06-01
Right-wing voices set out powerful but misleading arguments to justify inaction by the Trump administration during the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a new study of the rhetoric used by high-level government officials and influential commentators in the US during the first half of 2020.
In a study published in the DeGruyter journal Open Anthropological Research, Professor Martha Lincoln of San Francisco State University examined how public officials openly pushed for people to accept widespread illness and death from the virus by adopting a tone that suggested premature death was normal and the scale of death acceptable in the grander ...
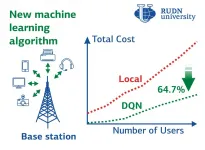
RUDN mathematician found a way to boost computations for IoT devices by three times
2021-06-01
RUDN mathematician and his colleagues from China, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, United Kingdom, and Qatar have developed an algorithm allowing the distribution of computing tasks between the IoT devices and the cloud in an optimal way. As a result, the power and time costs are reduced by about three times. The study was published in the Big Data.
With the development of technologies and devices, Internet of Things (IoT) applications require more and more computing power. The amount of data that the IoT devices need to process can be so large that it is reasonable to migrate computing to the cloud. Cloud computing provides flexible data processing and storage capabilities. But Computation offloading, meaning transferring of the resource-intensive processes ...
A new soft electronic material for human-machine-interfacing
2021-06-01
A DTU research team consisting of Malgorzata Gosia Pierchala, Firoz Babu Kadumundi, and Mehdi Mehrali from #TeamBioEngine headed by Alireza Dolatshahi-Pirouz, have developed a new material - CareGum - that among other things has potential for monitoring motor impairment associated with neurological disorders such as Parkinson's.
A green material with many properties
The CareGum property portfolio is incredibly broad with feats such as skin-like softness, it is stretchable up to 30,000 % and has self-healing capacities reminiscent of that of natural tissues. It is printable, moldable, and electrically conductive. Notably, the electrical conductivity enables the material to respond to external stimuli ...
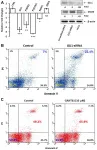
Oncotarget: STAT3 induces the expression of GLI1 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells
2021-06-01
Oncotarget published "STAT3 induces the expression of GLI1 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells" which reported that what induces GLI1 expression in GLI1-unmutated CLL cells is unknown.
Because signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 is constitutively activated in CLL cells and sequence analysis detected putative STAT3-binding sites in the GLI1 gene promoter, the authors hypothesized that STAT3 induces the expression of GLI1.
Western immunoblotting detected GLI1 in CLL cells from 7 of 7 patients, flow cytometry analysis confirmed that CD19 /CD5 CLL cells co-express GLI1 and confocal microscopy showed co-localization of GLI1 and phosphorylated STAT3. Chromatin immunoprecipitation showed ...
A fungus is major cause of death among people with HIV in the Brazilian Amazon
2021-06-01
A series of autopsies performed in an infectious disease hospital in the Brazilian Amazon reveals that infections by the Histoplasma fungus are a major cause of death in people with HIV. The study, led by Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), an institution supported by "la Caixa" Foundation, in collaboration with a team in Manaus, highlights the need of implementing sensitive methods to detect these infections in Histoplasma-endemic regions.
Histoplasmosis is a lung infection caused by inhalation of spores from a fungus (Histoplasma), and is frequent in some areas of the US, Africa, and Latin America.
In the majority of individuals with a functional immune system, the infection causes mild symptoms. However, in people who are immuno-compromised, such ...
Hi-CO unravels the complex packing of nucleosomes
2021-06-01
Scientists at Kyoto University's Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (iCeMS) in Japan have developed a technology that produces high-resolution simulations of one of the basic units of our genomes, called the nucleosome. Their findings were published in the journal Nature Protocols and should help improve understanding of how changes in nucleosome folding influence the inner workings of genes.
Nucleosomes are the basic structural units of DNA packaging inside the nucleus. They are formed of DNA wrapped around a small number of histone proteins. Nucleosomes move around inside the nucleus, folding and unfolding, changing their orientations, and moving closer together or further apart. These movements affect the accessibility of various molecules to DNA, determining ...
Childhood cancer discovery may stop tumour spread before it starts
2021-06-01
A new discovery in Ewing sarcoma, an aggressive and often fatal childhood cancer, has uncovered the potential to prevent cancer cells from spreading beyond their primary tumour site.
The breakthrough provides new insight into what triggers the process that allows cancer cells to survive while traveling through the body in the bloodstream.
Researchers with the University of British Columbia and BC Cancer have learned that Ewing sarcoma cells--and likely other types of cancer cells--are able to develop a shield that protects them from the harsh environment of the bloodstream and other locations as they search for a new place to settle, or metastasize. The study has just been published in Cancer Discovery.
"You ...
Browning could make lakes less productive, affecting food webs and fish
2021-06-01
TROY, N.Y. -- As more dissolved organic matter enters lakes across the northeast United States, darkening the lakes in a phenomena called "browning," new research shows that these waters may be growing less productive and able to sustain less life. In a study published today in Limnology and Oceanography Letters, scientists found that, rather than enriching lakes with nutrients as had previously been assumed, water more heavily laden with dissolved organic matter blocks sunlight and limits plant growth.
"A key question regarding lake browning is what impact it will have on aquatic food webs, including algal growth and fisheries," said Kevin Rose, co-author ...
Right off the bat: Navigation in extra-large spaces
2021-06-01
The brain is often likened to a computer: its hardware - neurons organized in complex circuits, its software - a plethora of codes that govern the neurons' behavior. But sometimes the brain performs exceptionally well even when its hardware seems inadequate for the task. For example, it's been puzzling how we and other mammals manage to navigate large-scale environments even though the brain's spatial perception circuits are seemingly suited to representing much smaller areas. A team of researchers from the Weizmann Institute of Science, led by Prof. Nachum Ulanovsky of the Neurobiology Department, tackled this riddle by thinking outside the experimental box. By combining an unusual research model - fruit bats - with an unusual setting - a 200 meters-long bat-tunnel - they were ...
Unraveling DNA packaging
2021-06-01
The genetic material of most organisms is carried by DNA, a complex organic molecule. DNA is very long -- for humans, the molecule is estimated to be about 2 m in length. In cells, DNA occurs in a densely packed form, with strands of the molecule coiled up in a complicated but efficient space-filling way. A key role in DNA's compactification is played by histones, structural-support proteins around which a part of a DNA molecule can wrap. The DNA-histone wrapping process is reversible -- the two molecules can unwrap and rewrap -- but little is known about the mechanisms at play. Now, by applying high-speed atomic-force microscopy (HS-AFM), Richard ...
Ethnically diverse research identifies more genetic markers linked to diabetes
2021-06-01
By ensuring ethnic diversity in a largescale genetic study, an international team of researchers, including a University of Massachusetts Amherst genetic epidemiologist, has identified more regions of the genome linked to type 2 diabetes-related traits.
The findings, published May 31 in Nature Genetics, broaden the understanding of the biological basis of type 2 diabetes and demonstrate that expanding research into different ancestries yields better results. Ultimately the goal is to improve patient care worldwide by identifying genetic targets to treat the chronic metabolic disorder. Type 2 diabetes affects and sometimes debilitates more than 460 million adults worldwide, according to the International Diabetes Federation. About 1.5 million deaths were directly ...
Suitable thread type and stitch density for Ghanaian public basic school uniforms
2021-06-01
The quality of a sewn garment is dependent on the quality of its seams that are the basic structural element. The factors affecting seam quality in garments include sewing thread type and stitch density. Making the right choice of these helps in getting quality seams in garments. However, the choice of suitable sewing threads and stitch densities for particular fabrics can only be determined through testing.
Dr. Patience Danquah Monnie, from the University of Cape Coast, Ghana, with fellow researchers, conducted research aimed to determine sewing thread brand and stitch density suitable for seams for a selected fabric (79% polyester and 21% cotton) for public basic school uniforms in Ghana. For the research, a 2×3 factorial ...
Scientists identify protein that activates plant response to nitrogen deficiency
2021-06-01
Nitrates are critical for the growth of plants, so plants have evolved sophisticated mechanisms to ensure sufficient nitrate uptake from their environments. In a new study published in Nature Plants, researchers at Nagoya University, Japan, have identified a plant enzyme that is key to activating a nitrate uptake mechanism in response to nitrogen starvation. This finding explains how plants meet their needs in challenging environments, opening doors to improving agriculture in such environments.
When nitrate levels are plentiful in a plant's environment, a plant can achieve adequate nitrate uptake levels by relying ...
Mind the nanogap: Fast and sensitive oxygen gas sensors
2021-06-01
Oxygen (O2) is an essential gas not only for us and most other lifeforms, but also for many industrial processes, biomedicine, and environmental monitoring applications. Given the importance of O2 and other gases, many researchers have focused on developing and improving gas-sensing technologies. At the frontier of this evolving field lie modern nanogap gas sensors--devices usually comprised of a sensing material and two conducting electrodes that are separated by a minuscule gap in the order of nanometers (nm), or thousand millionths of a meter. When molecules of specific gases get inside this gap, they electronically interact with the sensing layer and the electrodes, altering measurable ...
Declining deer population likely due to natural regulation
2021-06-01
The Yakushima sika deer (yakushika: Cervus nippon yakushimae), a subspecies of the Japanese sika deer (Cervus nippon), evolved without natural predators on the island of Yakushima, in Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan. It inhabits the forests on the island which were declared a World Heritage Site in 1993. Within the site, the yakushika has not been hunted in the past 50 years; however, since 2014, their population has been decreasing. This phenomenon is especially curious, as Japanese researchers believed that sika deer populations in Japan would not decrease without human intervention.
A group of three scientists, including Hokkaido ...
Overweight or obesity worsens liver-damaging effects of alcohol
2021-06-01
Led by the University of Sydney's Charles Perkins Centre, the study looked at medical data from nearly half a million people and found having overweight or obesity considerably amplified the harmful effects of alcohol on liver disease and mortality.
"People in the overweight or obese range who drank were found to be at greater risk of liver diseases compared with participants within a healthy weight range who consumed alcohol at the same level," said senior author and research program director Professor Emmanuel Stamatakis from the Charles Perkins Centre and the Faculty of Medicine and Health.
"Even for people who drank within alcohol guidelines, participants classified as obese were at over 50 percent greater risk of liver disease."
The researchers ...
The secret to stickiness of mussels underwater
2021-06-01
Mussels survive by sticking to rocks in the fierce waves or tides underwater. Materials mimicking this underwater adhesion are widely used for skin or bone adhesion, for modifying the surface of a scaffold, or even in drug or cell delivery systems. However, these materials have not entirely imitated the capabilities of mussels.
A joint research team from POSTECH and Kangwon National University (KNU) - led by Professor Hyung Joon Cha and Ph.D. candidate Mincheol Shin of the Department of Chemical Engineering at POSTECH with Professor Young Mee Jeong and Dr. Yeonju Park of the Department ...
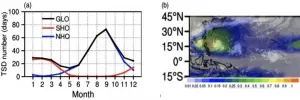
Researchers connect climate features to the variability of global tropical storm days from 1965 to 2019
2021-06-01
Nearly two billion people live in a region where tropical cyclones (TC) are an annual threat. TCs are deadly and can cause billions of dollars in economic losses worldwide. During peak season in the Northern Hemisphere, typically July through October, about two TCs develop or are ongoing every day. However, this and overall TC frequency vary substantially year-to-year.
To quantify this variability, scientists developed a metric called the tropical storm day (TSD). TSD is a collective measure of how frequently tropical cyclones develop, storm track, and cyclone lifespan, which reflects overall activity. Despite this advancement, researchers have not often studied tropical cyclone variability on a global scale.
Now, ...
Biopolymer-based electrolyte for the dream of zero-pollution battery
2021-06-01
In a paper published in NANO, researchers from Guizhou Meiling Power Sources Co., Ltd., China have reviewed the recent progress in biopolymer-based electrolyte. The biopolymer materials with unique characteristics including water solubility, film-forming capability and adhesive property played a key role in the design of zero pollution lithium battery. The biopolymers mentioned in this review were polysaccharide, protein, natural rubber and other polymers.
For polysaccharide, cellulose with good wettability, low cost and good mechanical properties can enhance the mechanical strength of membranes and improve interfacial stability between electrolyte and electrode. However, the porosity control of cellulose-based membranes was ...
Urban life is not to everyone's taste
2021-06-01
Habitat change, for example through urbanisation, is one of the most important causes of biodiversity decline. By 2050, settlements and cities across the globe are predicted to increase by two to three million square kilometres - about half the size of Greenland. Natural and semi-natural habitats will thus gradually be replaced by urban habitats.
How wildlife can adapt to such fundamental changes has mostly been studied for a few species groups, such as mammals and birds.
"In order to make predictions about the development of biodiversity as a whole and to combat current phenomena such as insect declines, robust knowledge is also needed for other species groups," ...
Researchers measure tritium production rates in mock-up of water-cooled ceramic breeder blanket
2021-06-01
To realize tritium self-sustaining cycle through tritium breeding blanket has been one of the core technologies of future fusion reactor. Therefore the design and function of blanket must be validated by neutronic experiment under D-T neutron environment. But due to the scarcity of DT neutron source, and highly radioactivity during neutronic experiments, it is very difficult to validate the nuclear response of the blanket, the data of tritium production rate mainly rely on Monte Carlo simulation.
Recently, a research group led by ZHU Qingjun from Institute of Plasma Physics, ...
Memory, learning and decision-making studied in worms
2021-06-01
As anyone who has ever procrastinated knows, remembering that you need to do something and acting on that knowledge are two different things. To understand how learning changes nerve cells and leads to different behaviors, researchers studied the much simpler nervous system of worms.
"In this study, we can now translate neuronal activity to behavioral response," said Project Researcher Hirofumi Sato, a neuroscientist at the University of Tokyo and first author of the research paper recently published in Cell Reports.
The discovery was made possible using technology that researchers describe as a "robot microscope," first developed in 2019 by researchers at Tohoku University in Miyagi Prefecture, northeastern Japan.
The technique involves genetically modifying the worms ...
Small 'snowflakes' in the sea play a big role
2021-06-01
A team of scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology, the Max Planck Institute for Meteorology and the GEOMAR - Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel have been studying biogeochemical processes in the oxygen minimum zone of the eastern South Pacific off Peru, one of the largest low oxygen regions of the world ocean. The researchers focused on so-called marine snow particles of different sizes, which are composed of algal debris and other organic material, aiming to understand how these particles affect the nitrogen cycle in the oxygen minimum zone. Thereby, they solved ...
[1] ... [2264]
[2265]
[2266]
[2267]
[2268]
[2269]
[2270]
[2271]
2272
[2273]
[2274]
[2275]
[2276]
[2277]
[2278]
[2279]
[2280]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.