Pollen-sized technology protects bees from deadly insecticides
2021-05-28
ITHACA, N.Y. - A Cornell University-developed technology provides beekeepers, consumers and farmers with an antidote for deadly pesticides, which kill wild bees and cause beekeepers to lose around a third of their hives every year on average.
An early version of the technology ¬- which detoxified a widely-used group of insecticides called organophosphates - is described in a new study, "Pollen-Inspired Enzymatic Microparticles to Reduce Organophosphate Toxicity in Managed Pollinators," published in Nature Food. The antidote delivery method has now been adapted to effectively ...
Study of Fe2+ ions contributes to further understanding of magnetoelectric coupling
2021-05-28
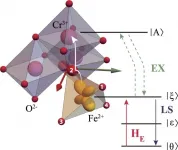
The authors, Kirill Vasin and Mikhail Eremin, contribute to the theory of electronic and structural properties of FeCr2O4 ferrimagnet. Due to the specific quantum state and the symmetry of FeO4 fragment, it has unusual electric and magnetic properties. Below TOO~150K, it lowers the symmetry with the macroscopic deformations due to the cooperative Jahn-Teller effect. The coupling between macroscopic deformation of the crystal FeCr2O4 and its inner ions shifts was revealed. The team enhanced the microscopic crystal field theory for 3D electrons with Kleiner's correction - the effect of penetrating charges density. It allows to have better prediction of electron-deformation ...
Nanofibrous filters for PM2.5 filtration
2021-05-28
In a paper published in NANO, the author reviewed many kinds of nanofibrous filters including the component, preparation process, and application performances to provide directional guidance for improvement of the air purification field.
Poor air quality is worldwide recognized as one of five health risks for causing adverse impacts on human health. Nanofibrous membrane is competitive to capture unclean nanoparticles since its lightweight, small diameter, high specific surface area, and easy to combine with functional additives. However, the trade-off between high filtration efficiency and low pressure drop posts challenge.
The removal mechanisms of fibrous filters to nanoparticles follow ...
A novel nitrogen-doped dual-emission carbon dots as an effective fluorescent probe for ratiometric detection dopamine
2021-05-28
How to construct the dual emission nitrogen-doped carbon dots (CDs) by a simple method? Professor Lili Ren with her collaborators proposed a new strategy to prepare such materials which were used to the detection of dopamine.
The traditional ratiometric fluorescence (FL) probe usually needs to combine different nanomaterials by chemical or physical methods and the manufacturing process is more complicated. While the dual-emission carbon dots (DECDs) can simplify the detection process. Therefore, it is of great significance to design a simple ratiometric fluorescence probe based on the DECDs for the accurate determination of DA concentration. ...
Using the environment to control quantum devices
2021-05-28
Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) researchers have uncovered how the environment can impact highly sensitive quantum behaviours like localisation. Their findings, published in Chaos, could lead to future innovations in the design of superconducting materials and quantum devices, including super precise sensors.
Quantum technology, in particular quantum sensing, promises to measure and capture our world at levels of precision never before possible. Such precision has diverse applications, from speedier and more sensitive medical imaging to recording time on high-frequency ...
Rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus during COVID-19 quarantine period
2021-05-28
In the Philippines, in the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic, there occurred a supply shortage of hydroxychloroquine and methotrexate. Limited access to medication and the life changes caused from the COVID-19 pandemic may prompt patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) to experience disease flares.
The researchers investigated self-reported symptoms of disease flares among patients with rheumatoid arthritis or systemic lupus erythematosus during the COVID-19 pandemic. They collected information through online surveys from 512 patients with SLE or RA. The data included ...
Results of the COLCORONA study published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine
2021-05-28
The Montreal Heart Institute (MHI) announces that the COLCORONA study results are published today in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine. The article, which is entitled Colchicine for community-treated patients with COVID-19 (COLCORONA): a phase 3, randomised, double-blinded, adaptive, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial, concludes that, given the lack of oral therapies available to prevent COVID-19 complications among non-hospitalized patients and the observed benefit of colchicine in patients with a PCR-confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19, this anti-inflammatory drug could be considered as a treatment for those at risk of ...
World Vape Day: BAT's review highlights 10 years of scientific evidence on vaping
2021-05-28
Multiple scientific studies show switching completely to vaping with high-quality products has reduced health risks compared to smoking, contrary to many consumer beliefs
Study data indicates that vaping products can provide an alternative for smokers who would not otherwise quit
Review supports the important role for vaping products in Tobacco Harm Reduction
Reinforces the importance of BAT's unique consumer-centric model and how we are reducing the health impact of our business and building A Better Tomorrow™ through our multicategory approach
To mark World Vape Day, BAT has today published a comprehensive review of the scientific evidence ...
Alzheimer's: Blood oxygen levels could explain why memory loss is an early symptom
2021-05-28
In a world first, scientists from the University of Sussex have recorded blood oxygen levels in the hippocampus and provided experimental proof for why the area, commonly referred to as 'the brain's memory centre', is vulnerable to damage and degeneration, a precursor to Alzheimer's disease.
To understand why this region is so sensitive, the University of Sussex researchers, headed up by Dr Catherine Hall from the School of Psychology and Sussex Neuroscience, studied brain activity and blood flow in the hippocampus of mice. The researchers then used simulations to predict that the amount of oxygen supplied to hippocampal neurons furthest from blood vessels is only just enough for the cells to keep working normally.
Dr Catherine ...
Chimaeroid from Early Cretaceous reassessed in light of new data
2021-05-28
The basis for this new take on the classification was laid in 1985, when John Long attributed a fossil tooth plate to a new species, Edaphodon eyrensis. The species was named after Lake Eyre, near which the tooth was found in 1978.
Asscoiate Professor Evgeny Popov had his doubts about the attribution. However, he had to study the fossil personally to advance his theory. The opportunity presented itself during a trip to Australia in 2010. The tooth plate was stored in a museum in Adelaide, South Australia.
"I didn't plan to go there, but I was able to negotiate a temporary ...
Danish invention preserves muscle mass in COVID-19 patients
2021-05-28
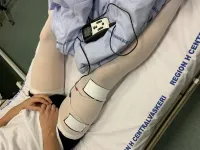
A research group from Aarhus University has developed a special biocompatible electrode for electrical muscle stimulation that the group has integrated and 3D-printed onto medical support stockings.
In the winter 2020/2021, the stockings were tested on hospitalised Covid patients. The studies were completed in March, but apart from a case study (Danish Medical Journal) data have not yet been published. However, the project group reveal that the results are very promising.
The stockings were tested on 16 Covid-19 patients who agreed to try the support stocking during their hospitalisation. The participants were hospitalised for five to seven days and were given a support stocking on each leg, but only ...
Research: Countries in violation of Baltic Sea Convention, polluting marine environment
2021-05-28
The countries around the Baltic Sea do not respect their binding international agreement to reduce agricultural pollution of the marine environment. Despite farming activities being the single most important source of nutrient pollution to the Baltic Sea.
An international research team presents evidence on these circumstances in a recent scientific article in the journal Ambio, published by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences.
The countries made a commitment 20 years ago to implement 10 specific reduction measures in their national legislation on agricultural pollution - e.g. featuring minimum storage capacity for manure and regulations on animal densities.
Now the researchers' study of legislations and regulations in place at national level, to address ...
Researchers build structured, multi-part nanocrystals with super light-emitting properties
2021-05-28
AMES, Iowa - Researchers have developed new types of materials that combines two or three types of nanoparticles into structures that display fundamental new properties such as superfluorescence.
"The whole goal of this research is to make new materials with new properties and/or exotic new structures," said Alex Travesset, an Iowa State University professor of physics and astronomy and an associate scientist for the U.S. Department of Energy's Ames Laboratory. "Those materials are made of very tiny materials, nanoparticles, and lead to properties not shared by more traditional materials made of atoms and molecules."
In this case, an international research team is combining perovskite nanocubes - tiny crystals with useful electrical or optical properties ...
New insights into switchable MOF structures
2021-05-28
Metal-organic framework compounds (MOFs) consist of inorganic and organic groups and are characterised by a large number of pores into which other molecules can be incorporated. MOFs are therefore interesting for many applications, for example for the storage of gases, but also for substance separation, sensor technology or catalysis. Some of these MOF structures react to different guest molecules by changing their structures. They are thus considered switchable.
One of these is "DUT-8", a material that has now been studied at the MX beamlines of BESSY II. "MOF crystals can be analysed very well at the MX beamlines," says HZB expert Dr. Manfred Weiss, who heads the MX team. ...
Pioneering single-dose radiotherapy for breast cancer treatment
2021-05-28
A breast cancer therapy that requires just one shot of radiotherapy is as effective as traditional radiotherapy, and avoids potential damage to nearby organs, according to a paper by UCL experts.
The results, published in the British Journal of Cancer, mean that eight out of ten patients who receive the treatment, TARGIT-IORT, will not need a long course of post-operative external beam radiotherapy (EBRT). These results strengthen and expand previously published outcomes.
Patients who received the treatment are less likely to go on to experience fatal cardiovascular disease such as heart attacks, lung problems or other cancers. As well as avoiding scattered radiation from EBRT that can damage nearby vital organs, delivering TARGIT-IORT during the lumpectomy procedure seems to ...
Watch me move it, move it: Gliding structure in Mycoplasma mobile revealed
2021-05-28
Much of human invention and innovation has been the result of our discovery and replication of natural phenomena, from birds serving to inspire human flight, to whales allowing us to dive deep into the ocean with submarines. For the first time ever, researchers have captured at the nanometer level the gliding machinery of the bacterium Mycoplasma mobile. Their findings were published in mBio. This brings us closer to understanding the origin and operating principle of motility, which could serve as a basis for the next generation of nanoscale devices and pharmaceuticals.
"My lab has been studying the molecular nature of bacteria from the Mycoplasma genus for years", ...
Research shows potential new sunscreen is coral-safe and provides more UVB/UVA protection
2021-05-28
(Bethesda, MD - May 25, 2021) A new study published in Nature Scientific Reports has found that Methylene Blue, a century old medicine, has the potential to be a highly effective, broad-spectrum UV irradiation protector that absorbs UVA and UVB, repairs ROS and UV irradiation induced DNA damages, and is safe for coral reefs. The study suggests that Methylene Blue could become an alternative sunscreen ingredient that supports the environment and protects human skin health.80% of today's sunscreens use Oxybenzone as a chemical UV blocker, despite multiple studies that have shown it expedites the destruction of coral reefs. Several states and countries have now banned the use of Oxybenzone and its derivatives to stop the devastating ...
How retroviruses become infectious
2021-05-28
Viruses are perfect molecular machines. Their only goal is to insert their genetic material into healthy cells and thus multiply. With deadly precision, they thereby can cause diseases that cost millions of lives and keep the world on edge. One example for such a virus, although currently less discussed, is HIV that causes the ongoing global AIDS-epidemic. Despite the progress made in recent years, 690 000 people died in 2019 alone as a result of the virus infection. "If you want to know the enemy, you have to know all its friends," says Martin Obr, postdoc at the Schur group at IST Austria. Together with his colleagues, he therefore studies a virus belonging to the same ...
Blood test detects childhood tumors based on their epigenetic profiles
2021-05-28
A new study exploits the characteristic epigenetic signatures of childhood tumors to detect, classify and monitor the disease. The scientists analyzed short fragments of tumor DNA that are circulating in the blood. These "liquid biopsy" analyses exploit the unique epigenetic landscape of bone tumors and do not depend on any genetic alterations, which are rare in childhood cancers. This approach promises to improve personalized diagnostics and, possibly, future therapies of childhood tumors such as Ewing sarcoma. The study has been published in Nature Communications.
A study led by scientists from St. Anna Children's Cancer Research Institute (St. Anna CCRI) in collaboration with CeMM Research Center for Molecular Medicine of the Austrian Academy of Sciences provides an innovative ...
Solving a double murder arouses international interest
2021-05-28
The technology using DNA-based genealogy that solved a double murder in Linköping opens completely new possibilities in investigating serious crime. LiU researchers are now involved in spreading new knowledge about the technology, which brings hope to police forces and has aroused major international interest.
"We want to tell others about the problems that we faced when working with this pilot case, and how we dealt with them. We can prevent others reinventing the wheel, and make sure that the knowledge available is extended and improved", says Andreas Tillmar.
He is forensic geneticist at the National Board of Forensic Medicine, and adjunct senior lecturer ...
Data from 45 million mobile users further shows poorer people less able to stay at home COVID rules
2021-05-28
People living in deprived, less affluent neighborhoods spent less time indoors at home during lockdown, according to a study that tracked data from millions of mobile phone users across the United States.
The study, published in the journal Annals of the American Association of Geographers, adds to growing evidence that low earners are less likely to comply with stay-at-home orders, either because they simply can't afford to, or because they work in professions in which working from home is not possible.
The finding is concerning given the fact that vulnerable groups are already at greater risk from COVID.
In March 2020, the US like many countries in the world entered a state of lockdown, with its citizens advised to stay at home to curb the spread of Coronavirus. Non-essential ...
Plastic in Galapagos seawater, beaches and animals
2021-05-28
Plastic pollution has been found in seawater, on beaches and inside marine animals at the Galapagos Islands.
A new study - by the University of Exeter, Galapagos Conservation Trust (GCT) and the Galapagos Science Center - found plastic in all marine habitats at the island of San Cristobal, where Charles Darwin first landed in Galapagos.
At the worst "hotspots" - including a beach used by the rare "Godzilla" marine iguana - more than 400 plastic particles were found per square metre of beach.
Plastic was also found inside more than half of the marine invertebrates (such as barnacles and urchins) studied, and on the seabed.
The findings suggest most plastic pollution in Galapagos - a world-famous biodiversity haven - arrives on ocean currents.
The study also ...
When to release free and paid apps for maximal revenue
2021-05-28
Researchers from Tulane University and University of Maryland published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that examines the dynamic interplay between free and paid versions of an app over its lifetime and suggests a possible remedy for the failure of apps.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Managing the Versioning Decision over an App's Lifetime" and is authored by Seoungwoo Lee, Jie Zhang, and Michel Wedel.
Is it really over for paid mobile apps? The mobile app industry is unique because free apps are much more prevalent than paid apps in most app categories, contrary to many other product markets where free products primarily play a supportive role to the paid products. Apps have been trending toward the free version in the past decade, such ...
Helping doctors manage COVID-19
2021-05-28
Artificial intelligence (AI) technology developed by researchers at the University of Waterloo is capable of assessing the severity of COVID-19 cases with a promising degree of accuracy.
A study, which is part of the COVID-Net open-source initiative launched more than a year ago, involved researchers from Waterloo and spin-off start-up company DarwinAI, as well as radiologists at the Stony Brook School of Medicine and the Montefiore Medical Center in New York.
Deep-learning AI was trained to analyze the extent and opacity of infection in the lungs of COVID-19 patients based on chest x-rays. Its scores were then compared to assessments of the ...
Next-gen electric vehicle batteries: These are the questions we still need to answer
2021-05-28
The next generation of electric vehicle batteries, with greater range and improved safety, could be emerging in the form of lithium metal, solid-state technology.
But key questions about this promising power supply need to be answered before it can make the jump from the laboratory to manufacturing facilities, according to University of Michigan researchers. And with efforts to bring electric vehicles to a larger part of the population, they say, those questions need answering quickly.
Jeff Sakamoto and Neil Dasgupta, U-M associate professors of mechanical engineering, have been leading researchers on lithium metal, solid-state batteries over the past decade. In ...
[1] ... [2272]
[2273]
[2274]
[2275]
[2276]
[2277]
[2278]
[2279]
2280
[2281]
[2282]
[2283]
[2284]
[2285]
[2286]
[2287]
[2288]
... [8821]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.