Puppies are born ready to communicate with people, study shows
2021-06-03
Anyone that's ever interacted with a dog knows that they often have an amazing capacity to interact with people. Now researchers reporting in the journal Current Biology on June 3 have found that this ability is present in dogs from a very young age and doesn't require much, if any, prior experience or training. But, some of them start off better at it than others based on their genetics.
"We show that puppies will reciprocate human social gaze and successfully use information given by a human in a social context from a very young age and prior to extensive experience with humans," said Emily E. Bray of the University of Arizona, Tucson. "For example, even before puppies have left their littermates to live ...
North Atlantic right whales have gotten smaller since the 1980s
2021-06-03
Whales are largely protected from direct catch, but many populations' numbers still remain far below what they once were. A study published in the journal Current Biology on June 3 suggests that, in addition to smaller population sizes, those whales that survive are struggling. As evidence, they find that right whales living in the North Atlantic today are significantly shorter than those born 30 to 40 years ago.
"On average, a whale born today is expected to reach a total length about a meter shorter than a whale born in 1980," said Joshua Stewart of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) in La Jolla, CA. That represents an average decline in length of about 7%. "But that's just the average--there are also some extreme cases where young whales are several ...
Predictive model identifies patients for genetic testing
2021-06-03
Patients who, perhaps unbeknownst to their health care providers, are in need of genetic testing for rare undiagnosed diseases can be identified en masse based on routine information in electronic health records (EHRs), a research team reported today in the journal Nature Medicine.
Findings from the Vanderbilt University Medical Center study suggest that, among the patients of any sizeable health care system, there are hundreds or thousands with undiagnosed rare diseases of the sort where a genetic test could lead to a diagnosis.
"Patients with rare genetic diseases often face ...
Changes in pregnancy, birth rates during COVID-19
2021-06-03
What The Study Did: Changes in pregnancy and birth rates before and after COVID-19 lockdown measures were estimated using electronic medical records.
Authors: Molly J. Stout, M.D., of the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11621)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this news release.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access ...
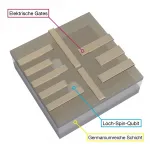
Quantum computing with holes
2021-06-03
Quantum computers with their promises of creating new materials and solving intractable mathematical problems are a dream of many physicists. Now, they are slowly approaching viable realizations in many laboratories all over the world. But there are still enormous challenges to master. A central one is the construction of stable quantum bits - the fundamental unit of quantum computation called qubit for short - that can be networked together.
In a study published in Nature Materials and led by Daniel Jirovec from the Katsaros group at IST Austria in close collaboration with researchers from the L-NESS Inter-university Centre in Como, Italy, scientists now have created a new and promising candidate system for reliable qubits.
Spinning Absence
The researchers created the qubit using the ...
Puppies are wired to communicate with people, study shows
2021-06-03
Dogs may have earned the title "man's best friend" because of how good they are at interacting with people. Those social skills may be present shortly after birth rather than learned, a new study by University of Arizona researchers suggests.
Published today in the journal Current Biology, the study also finds that genetics may help explain why some dogs perform better than others on social tasks such as following pointing gestures.
"There was evidence that these sorts of social skills were present in adulthood, but here we find evidence that puppies - sort of like humans - are biologically prepared to interact in these social ways," said lead study author Emily Bray, a postdoctoral research associate in the UArizona School of Anthropology in the College of Social and Behavioral ...
AI outperforms humans in creating cancer treatments, but do doctors trust it?
2021-06-03
(Toronto, June 3, 2021) -- The impact of deploying Artificial Intelligence (AI) for radiation cancer therapy in a real-world clinical setting has been tested by Princess Margaret researchers in a unique study involving physicians and their patients.
A team of researchers directly compared physician evaluations of radiation treatments generated by an AI machine learning (ML) algorithm to conventional radiation treatments generated by humans.
They found that in the majority of the 100 patients studied, treatments generated using ML were deemed to be clinically acceptable for patient treatments by physicians.
Overall, 89% of ML-generated treatments were considered clinically acceptable for treatments, ...
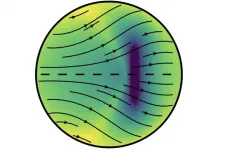
Is Earth's core lopsided? Strange goings-on in our planet's interior
2021-06-03
For reasons unknown, Earth's solid-iron inner core is growing faster on one side than the other, and it has been ever since it started to freeze out from molten iron more than half a billion years ago, according to a new study by seismologists at the University of California, Berkeley.
The faster growth under Indonesia's Banda Sea hasn't left the core lopsided. Gravity evenly distributes the new growth -- iron crystals that form as the molten iron cools -- to maintain a spherical inner core that grows in radius by an average of 1 millimeter per year.
But the enhanced growth on one side suggests that something in Earth's outer core or mantle under Indonesia is removing heat from the inner core at a faster rate than on the opposite side, under Brazil. Quicker cooling on one side would ...
CNIC scientists identify essential factors for limb formation
2021-06-03
Scientists at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC), working in partnership with researchers at the Institut de Recherches Cliniques de Montréal (IRCM) in Canada, have identified Meis transcription factors as essential biomolecules for the formation and antero-posterior patterning of the limbs during embryonic development.
In the study, published in Nature Communications, the research team carried out an in-depth characterization of the Meis family of transcription factors. Genetic deletion of all four family members showed that these proteins are essential for the formation of the limbs during embryonic development. "An embryo that develops in the absence of Meis does not ...
High-intensity strength and impact training attenuates skeletal aging
2021-06-03
Regular strength and impact-type training may decrease or even prevent age-related bone deterioration in men, new research at the University of Jyväskylä, Finland, shows. The tibial bone properties of middle-aged and older male sprint athletes were followed over 10 years. The study presents novel findings on maintaining the adaptability of the aging skeleton and on the importance of regular intensive training for maintaining bone health.
"Part of the age-related bone loss is probably explained by reduced levels of physical activity. Especially intensive, bone-loading exercise ...
Bilingualism as a natural therapy for autistic children
2021-06-03
Affecting more than one in a hundred children, autism spectrum disorder is one of the most common neurodevelopmental disorders. It has a particular impact on social interaction, including difficulties in understanding other people's perspectives, beliefs, desires and emotions, known as 'theory of mind'. Bilingual families with an autistic child often tend - and are sometimes encouraged - to forego the use of one of the home languages, so as not to further complicate the development of their child's communicative skills. A researcher from the University of Geneva (UNIGE, Switzerland), in collaboration with the Universities ...
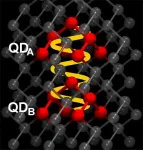
How quantum dots can 'talk' to each other
2021-06-03
So-called quantum dots are a new class of materials with many applications. Quantum dots are realized by tiny semiconductor crystals with dimensions in the nanometre range. The optical and electrical properties can be controlled through the size of these crystals. As QLEDs, they are already on the market in the latest generations of TV flat screens, where they ensure particularly brilliant and high-resolution colour reproduction. However, quantum dots are not only used as "dyes", they are also used in solar cells or as semiconductor devices, right up to computational building blocks, the qubits, of a quantum computer.
Now, a team led by Dr. Annika Bande at HZB has extended the understanding of the interaction between several quantum dots with an ...
Biomarker predicts bowel cancer recurrence
2021-06-03
A biomarker in the blood of patients with bowel cancer may provide valuable insight into the risk of cancer relapse after surgery and the effectiveness of chemotherapy.
Research published in PLOS found circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) measured before and after surgery provided a reliable marker for predicting whether the cancer would recur following chemotherapy treatment.
The ctDNA also provided a real-time measure of the effectiveness of chemotherapy, highlighting the potential for this test to provide an early indication of the success of chemotherapy in eradicating microscopic cancer.
At a glance
By measuring levels of ctDNA present in the blood of bowel cancer patients after surgery, researchers were able to predict the likelihood ...
Tick for insomnia treatment
2021-06-03
If insomnia keeps you awake at night, Flinders University researchers recommend a trip to the doctor - not for a sleeping pill prescription but for a short course of intensive behavioural therapy.
Researchers have developed new clinical guidelines for Australian doctors to give family GPs insights into the most effective treatment for insomnia - Cognitive Behavioural Therapy for insomnia (or 'CBTi').
CBTi improves insomnia, mental health and quality of life, and can be more successful than sleeping pills, say Adelaide Institute for Sleep Health (AISH) sleep experts from Flinders University in a new paper in the Australian Journal of General Practice.
Most patients with insomnia managed in general practice are prescribed potentially addictive ...
Five million years of climate change preserved in one place
2021-06-03
Paleo researcher Charlotte Prud'homme, who until recently worked at the Max Planck Institute for Chemistry and is now a researcher at the Université Lausanne, explains: "The 80-meter-thick sedimentary sequence we found at Charyn Canyon in southeast Kazakhstan provides us with a virtually continuous record of five million years of climate change. This is a very rare occurrence on land!" The alternating dust and soil layers provide the first reliable evidence, in one place, of long-term interactions between major climate systems on the Eurasian continent. "Over the past five million years, the land surfaces of Eurasia appear to ...
One in 20 workers are in 'worthless' jobs -- far fewer than previously thought
2021-06-03
The so-called 'bullshit jobs theory' - which argues that a large and rapidly increasing number of workers are undertaking jobs that they themselves recognise as being useless and of no social value - contains several major flaws, argue researchers from the universities of Cambridge and Birmingham.
Even so, writing in Work, Employment and Society, the academics applaud its proponent, American anthropologist David Graeber, who died in September 2020, for highlighting the link between a sense of purpose in one's job and psychological wellbeing.
Graeber initially put forward the concept of 'bullshit jobs' - jobs that even those who do them view as worthless - in his 2013 essay ...
Novel antibody drug wakes up the body's defense system in advanced-stage cancer
2021-06-03
Researchers at the University of Turku, Finland, showed that the antibody treatment reactivates the immune defense in patients with advanced-stage cancer. The treatment alters the function of the body's phagocytes and facilitates extensive activation of the immune system.
The immune defense is the body's own defense system equipped to combat cancer. However, cancer learns to hide from immune attacks and harnesses this system to promote its own growth. Therefore, it would be beneficial to be able to return the immune defense back to restricting the advancement of cancer.
Macrophages, a type of white blood cell, are central in the fight against cancer. Cancer educates ...
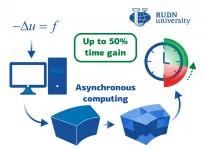
RUDN mathematician boosted domain decomposition method for asynchronous parallel computing
2021-06-03
RUDN University mathematician and his colleagues from France and Hungary developed an algorithm for parallel computing, which allows solving applied problems, such as electrodynamics or hydrodynamics. The gain in time is up to 50%. The results are published in the Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics.
Parallel computing methods are often used to process practical problems in physics, engineering, biology, and other fields. It involves several processors joined in a net to simultaneously solve a single problem -- each has its own small part. The way to distribute the work between the processors and make them "communicate" with each other is a choice based on the specifics of a particular problem. ...
Stone Age raves to the beat of elk tooth rattles?
2021-06-03
"Ornaments composed of elk teeth suspended from or sown on to clothing emit a loud rattling noise when moving," says auditory archaeologist and Academy of Finland Research Fellow Riitta Rainio from the University of Helsinki. "Wearing such rattlers while dancing makes it easier to immerse yourself in the soundscape, eventually letting the sound and rhythm take control of your movements. It is as if the dancer is led in the dance by someone."
Rainio is well versed in the topic, as she danced, for research purposes, for six consecutive hours, wearing elk tooth ornaments produced according to the Stone Age model. Rainio and artist Juha Valkeapää held a performance to ...
Protect the sea, neglect the people? Social impact of marine conservation schemes revealed
2021-06-03
As G7 governments renew commitments to protecting marine spaces and biodiversity, global conservation initiatives such as 30x30 are feared to pay too little attention to the livelihood impacts on communities
Close-up inspection of an upcoming marine conservation area in Cambodia shows mixed livelihood consequences ranging from improving relationships to the state to increased anxiety and social division
In the long term and on a regional scale in Southeast Asia, communities exposed to marine conservation are poorer and experience higher child mortality
Researchers warn that the rapid global expansion of nominal marine protected area (MPA) coverage can undermine community livelihoods if it proceeds with a sole focus on marine resource conservation, a disregard of local ...
How to obtain immune bovine milk to strengthen the body against COVID-19
2021-06-03
Physiologically, milk contains biocomponents that are highly protective against infections. In light of this, the AGR-149-Infectious Diseases group at the University of Cordoba's Department of Animal Health is doing research that focuses on cow's milk as a possible source of Covid-19 control. The results have been published, partially, in the journal Frontiers in Immunology.
This is possible due to "crossed immunity", and there is already evidence of the protection it provides, explained one of the principal investigators, Mari Carmen Borge. "It has been shown that the immune cells that the vaccinated animal generates against bovine coronavirus ...
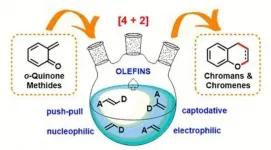
Samara Polytech has summarized all data on methods of synthesis of chromanes and chromene
2021-06-03
O-quinone methides have been studied at the Samara Polytech for more than ten years. Vitaly Osyanin, Doctor of Chemistry, Professor of the Department of Organic Chemistry, is in charge of scientific work in this area. The results of the latest research were published in the authoritative Russian journal "Russian Chemical Reviews" (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1070/RCR4971).
Thus Professor Osyanin and the Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor of the Department Dmitry Osipov and the Candidate of Chemical Sciences, the graduate of the Department Anton Lukashenko prepared a review article in which the main known examples of the transformation of o-quinone methides into chromene and ...
Skoltech researchers unveil complex defect structure of Li-ion cathode material
2021-06-03
Skoltech scientists have studied the hydroxyl defects in LiFePO4, a widely used cathode material in commercial lithium-ion batteries, contributing to the overall understanding of the chemistry of this material. This work will help improve the LiFePO4 manufacturing process to avoid formation of adverse intrinsic structural defects which deteriorate its performance. The paper was published in the journal Inorganic Chemistry.
Lithium iron phosphate, LiFePO4, is a safe, stable and affordable cathode material for Li-ion batteries that has been very well optimized for practical applications despite its low conductivity and medium energy density. Yet scientists continue to study the various properties of this material, and in particular the impact ...
Study sheds new light on link between COVID pressures and suicidal thoughts
2021-06-03
There has been concern at how the pandemic has not only hit physical health and the economy but has also impacted our mental health with the possibility of increased rates of suicide.
Now a new study - a collaboration between Swansea University, Cardiff University, and the NHS in Wales - has investigated exactly which Covid-related stressors are most likely to trigger suicidal thoughts and behaviours.
The researchers also discovered the important role that hope for the future can play - along with individuals' levels resilience - when it comes to coping with these stressors.
More than 12,000 people responded to the Wales Wellbeing survey which asked volunteers to share their experiences during the ...
Extreme rainfall: More accurate predictions in a changing climate
2021-06-03
To limit the impacts of climate change it is essential to predict them as accurately as possible. Regional Climate Models are high-resolution models of the Earth's climate that are able to improve simulations of extreme weather events that may be affected by climate change and thus contribute to limiting impacts through timely action.
At their highest resolutions, Regional Climate Models are capable of simulating atmospheric convection, a key process in many extreme weather events which is often the cause of very intense and localized precipitations. Although "convection permitting" models are widely used in weather forecasting, they require large supercomputing ...
[1] ... [2269]
[2270]
[2271]
[2272]
[2273]
[2274]
[2275]
[2276]
2277
[2278]
[2279]
[2280]
[2281]
[2282]
[2283]
[2284]
[2285]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.