Enzymes of a feather: CRISPR-Cas components work together to enhance protection from viruses
2021-05-24
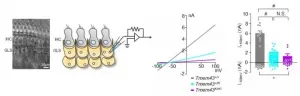
Researchers from Skoltech and their colleagues from Russia and the US have shown that the two components of the bacterial CRISPR-Cas immunity system, one that destroys foreign genetic elements such as viruses and another that creates "memories" of foreign genetic elements by storing fragments of their DNA in a special location of bacterial genome, are physically linked. This link helps bacteria to efficiently update their immune memory when infected by mutant viruses that learned to evade the CRISPR-Cas defense. The paper was published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
CRISPR-Cas, a defense mechanism that provides bacteria with resistance to their viruses (bacteriophages), destroys DNA from ...
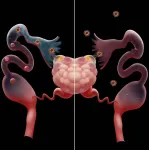
Lundquist investigator Wei Yan solves longstanding fallopian tube transport debate
2021-05-24
LOS ANGELES (May 24, 2021) -- Today, The Lundquist Institute announced that Wei Yan, MD, PhD, and his research group have solved a longstanding mystery and scientific debate about the mechanism underlying the gamete and embryo transport within the Fallopian tube. Using a mouse model where the animals lacked motile cilia in the oviduct, Dr. Yan's group demonstrated that motile cilia in the very distal end of the Fallopian tube, called infundibulum, are essential for oocyte pickup. Disruptions of the ciliary structure and/or beating patterns lead to failure in oocyte pickup and consequently, a loss of female fertility. Interestingly, motile cilia in other parts of the oviduct can facilitate sperm ...
Facilitating speech comprehension in rare inherited hearing loss patients
2021-05-24
Hearing loss is a disability that affects approximately 5% of the world's population. Clinically determining the exact site of the lesion is critical for choosing a proper treatment for hearing loss. For example, the subjects with damage in sound conduction or mild outer hair cell damage would benefit from hearing aids, while those with significant damage to outer or inner hair cells would benefit from the cochlear implant. On the other hand, the subjects with impairments in more central structures such as the cochlear nerve, brainstem, or brain do not benefit from either hearing aids or cochlear implants. However, the role of impairments in cochlear glial cells in hearing loss is not as well known. While it is known that connexin channels in cochlear glial ...
Dual impacts of extreme heat, ozone disproportionately hurt poorer areas
2021-05-24
Scientists at UC San Diego, San Diego State University and colleagues find that extreme heat and elevated ozone levels, often jointly present during California summers, affect certain ZIP codes more than others.
Those areas across the state most adversely affected tend to be poorer areas with greater numbers of unemployed people and more car traffic. The science team based this finding on data about the elevated numbers of people sent to the hospital for pulmonary distress and respiratory infections in lower-income ZIP codes.
The study identified hotspots throughout ...
Evacuating under dire wildfire scenarios
2021-05-24
In 2018, the Camp Fire ripped through the town of Paradise, California at an unprecedented rate. Officials had prepared an evacuation plan that required 3 hours to get residents to safety. The fire, bigger and faster than ever before, spread to the community in only 90 minutes.
As climate change intensifies, wildfires in the West are behaving in ways that were unimaginable in the past--and the common disaster response approaches are woefully unprepared for this new reality. In a recent study, a team of researchers led by the University of Utah proposed a framework for simulating dire scenarios, which the authors define as scenarios where there is less time to ...
Sterilizing skeeters
2021-05-24
Mosquitoes are one of humanity's greatest nemeses, estimated to spread infections to nearly 700 million people per year and cause more than one million deaths.
UC Santa Barbara Distinguished Professor Craig Montell has made a breakthrough in one technique for controlling populations of Aedes aegypti, a mosquito that transmits dengue, yellow fever, Zika and other viruses. The study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, documents the first use of CRISPER/Cas9 gene editing to target a specific gene tied to fertility in male mosquitoes. The researchers were then able to discern how this mutation can suppress ...
Corn ethanol reduces carbon footprint, greenhouse gases
2021-05-24
A study conducted by researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory reveals that the use of corn ethanol is reducing the carbon footprint and diminishing greenhouse gases.
The study, recently published in Biofuels, Bioproducts and Biorefining, analyzes corn ethanol production in the United States from 2005 to 2019, when production more than quadrupled. Scientists assessed corn ethanol's greenhouse gas (GHG) emission intensity (sometimes known as carbon intensity, or CI) during that period and found a 23% reduction in CI.
According ...
Chemical changes to peptide siRNA-carrier enhance gene silencing for future cancer drugs
2021-05-24
MUSC Hollings Cancer Center researchers are exploring the use of peptide carriers for the delivery of small RNA drugs as a novel treatment for cancer. The team's recent work, published online March 19 in the Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids journal, lays the foundation for developing a clinically relevant peptide carrier RNAi-based drug treatment strategy for human oral cancer.
According to the American Cancer Society, the estimated risk of developing oral cancer in the U.S. is 1 in 60 for men and 1 in 140 for women. Cancer therapies face multiple challenges, including off-target side effects and low efficacy. ...
Ludwig Cancer research study finds way to revive potent immune cells for cancer therapy
2021-05-24
MAY 24, 2021, NEW YORK - A Ludwig Cancer Research study has discovered how to revive a powerful but functionally inert subset of anti-cancer immune cells that are often found within tumors for cancer therapy.
Led by Ludwig Lausanne's Ping-Chih Ho and Li Tang of the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, the study describes how an immune factor known as interleukin-10 orchestrates the functional revival of "terminally exhausted" tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes (TILs), which have so far proved impervious to stimulation by immunotherapies. It also demonstrates that the factor, when applied in combination with cell therapies, can eliminate tumors in mouse models of melanoma and colon cancer. The findings are reported in the current issue of Nature ...
New study shines light on hazards of Earth's largest volcano
2021-05-24
MIAMI - Scientists from the University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science analyzed ground movements measured by Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) satellite data and GPS stations to precisely model where magma intruded and how magma influx changed over time, as well as where faults under the flanks moved without generating significant earthquakes. The GPS network is operated by the U.S. Geological Survey's Hawaii Volcano Observatory.
"An earthquake of magnitude-6 or greater would relieve the stress imparted by the influx of magma along ...
Study: Diet to lower blood pressure also improved other factors in cardiac health
2021-05-24
BOSTON - Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in the United States. Public health advocates frequently site Americans' high-sodium diet as one factor in the nation's cardiac health. While sodium has been definitively linked to high-blood pressure -- a key risk factor for CVD -- few rigorously controlled studies make the direct causal link between high sodium intake and cardiovascular damage, heart attack, or stroke.
In a new analysis, researchers from Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) examined three cardiovascular biomarkers, which are measurable indicators ...
Impact of school nutrition policies in California varies by children's ethnicity
2021-05-24
California state school nutrition policies and federal policies for school meals have mixed impacts on childhood obesity in children of Pacific Islander (PI), Filipino (FI) and American Indian/Alaska native (AIAN) origins, according to a new study published this week in the open access journal PLOS Medicine by Mika Matsuzaki of Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, USA, and colleagues.
Children of PI, FI and AIAN origin are some of the most understudied subgroups experiencing high rates of overweight/obesity. California has enacted policies on foods and beverages available in schools through a series of standards ...
Built environments don't play expected role in weight gain
2021-05-24
People don't gain or lose weight because they live near a fast-food restaurant or supermarket, according to a new study led by the University of Washington. And, living in a more "walkable", dense neighborhood likely only has a small impact on weight.
These "built-environment" amenities have been seen in past research as essential contributors to losing weight or tending toward obesity. The idea appears obvious: If you live next to a fast-food restaurant, you'll eat there more and thus gain weight. Or, if you have a supermarket nearby, you'll shop there, eat healthier and thus lose weight. Live in a neighborhood that makes walking and biking easier and you'll get out, exercise more and burn more calories. ...
Weight-loss treatment prevents accumulation of lipid linked to cardiac mortality
2021-05-24
Researchers at the Karolinska Institutet, University of Oxford and University of Copenhagen have shown that elevated levels of lipids known as ceramides can be associated with a ten-fold higher risk of death from cardiovascular disease. Treatment with liraglutide could keep the ceramide levels in check, compared with placebo. The results have been published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Approximately 16 percent of the Swedish population suffers from obesity (BMI over 30), which is one of the greatest risk factors for cardiovascular diseases such as myocardial infarction and stroke. The World Health ...
Specialized inhibitory cluster gates plasticity in fear learning
2021-05-24
Has your heart ever started to race at the thought of an upcoming deadline for work? Or has the sight of an unknown object in a dark room made you jump? Well, you can probably thank your amygdala for that.
The small almond-shaped brain structure is central to how we perceive and process fear. As we start to learn to associate fear with cues in our environment, neuronal connections within the amygdala are dynamically altered in a process called synaptic plasticity. Although this physiological mechanism is important for facilitating fear learning, it has mostly been studied in the context of excitatory neurons within the amygdala. Far less is known about the role inhibitory cells ...
COVID-19 infection rates of dentists remain lower than other health professionals
2021-05-24
CHICAGO, May 24, 2021--More than a year after COVID-19 appeared in the U.S., dentists continue to have a lower infection rate than other front-line health professionals, such as nurses and physicians, according to a study published online ahead of the June print issue in the Journal of the American Dental Association. The study, "COVID19 among Dentists in the U.S. and Associated Infection Control: a six-month longitudinal study," is based on data collected June 9 - Nov. 13, 2020.
According to the study, based on the number of dentists with confirmed or probable COVID-19 infections over more than six months, the cumulative infection rate for U.S. dentists is 2.6%. The monthly incidence ...
Simple diagnostic tool predicts individual risk of Alzheimer's
2021-05-24
Researchers at Lund University in Sweden have developed an algorithm that combines data from a simple blood test and brief memory tests, to predict with great accuracy who will develop Alzheimer's disease in the future. The findings are published in Nature Medicine.
Approximately 20-30% of patients with Alzheimer's disease are wrongly diagnosed within specialist healthcare, and diagnostic work-up is even more difficult in primary care. Accuracy can be significantly improved by measuring the proteins tau and beta-amyloid via a spinal fluid sample, or PET scan. However, those methods are expensive and only available at a relatively few specialized memory clinics worldwide. Early and accurate ...
To unpack colonial influence on ecology, researchers propose five strategies
2021-05-24
Ecology, the field of biology devoted to the study of organisms and their natural environments, needs to account for the historical legacy of colonialism that has shaped people and the natural world, researchers argued in a new perspective in the journal Nature Ecology & Evolution.
To make ecology more inclusive of the world's diverse people and cultures living in diverse ecosystems, researchers from University of Cape Town, North West University in South Africa and North Carolina State University proposed five strategies to untangle the impacts of colonialism on research and thinking in the field today.
"There are significant biases in our understanding ...
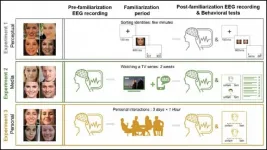
The brain learns faces fastest in person
2021-05-24
The neural representation of a familiar face strengthens faster when you see someone in person, according to a new study published in JNeurosci.
The brain loves faces -- there's even an interconnected network of brain areas dedicated to face-processing. Despite all the research on how the brain sees faces, little is known about how the neural representation of a face changes as it becomes familiar.
To track how familiarity brain signals change, Ambrus et al. measured participants' brain activity with EEG before and after getting to know different ...
Dental crowding: Ancient baleen whales had a mouthful
2021-05-24
A strange phenomenon happens with modern blue whales, humpback whales and gray whales: they have teeth in the womb but are born toothless. Replacing the teeth is baleen, a series of plates composed of thin, hair- and fingernail-like structures growing from the roof of their mouths that act as a sieve for filter feeding small fish and tiny shrimp-like krill.
The disappearing embryonic teeth are testament to an evolutionary history from ancient whales that had teeth and consumed larger prey. Modern baleen whales on the other hand use their fringed baleen to strain their miniscule prey from water, hence the term filter feeding.
A new study that utilized high-resolution computed tomography (CT) to ...
Researchers identify facilitators for rehabilitation care for people with spatial neglect
2021-05-24
East Hanover, NJ. May 24, 2021. A recent qualitative study of rehabilitation professionals caring for people with spatial neglect enabled researchers to identify interventions to improve rehabilitation outcomes. Experts reported that implementation of spatial neglect care depends on interventions involving family support and training, promotion of interdisciplinary collaboration, development of interprofessional vocabulary, and continuous treatment and follow-up assessment through care transitions.
The article, "Barriers and Facilitators to Rehabilitation Care of Individuals with Spatial ...
Step-closer to nasal spray drug delivery for Parkinson's disease
2021-05-24
Scientists at the University of York have made significant progress in the development of a nasal spray treatment for patients with Parkinson's disease.
Researchers have developed a new gel that can adhere to tissue inside the nose alongside the drug levodopa, helping deliver treatment directly to the brain.
Levodopa is converted to dopamine in the brain, which makes-up for the deficit of dopamine-producing cells in Parkinson's patients, and helps treat the symptoms of the disease. Over extended periods of time, however, levodopa becomes less effective, and increased doses are needed.
Professor David Smith, from the ...
Sustainable funding needed to provide nursery places
2021-05-24
Extra funding should be made available for early years care in the wake of the pandemic, researchers say.
Experts at the University of Leeds, University of Oxford and Oxford Brookes University have made the call after assessing the benefits of early childhood education and care (ECEC) for children under three during COVID-19.
They found children who attended childcare outside the home throughout the first UK lockdown made greater gains in language and thinking skills, particularly if they were from less advantaged backgrounds.
And now they are making several policy recommendations ...
New research shows ridesharing services reduce sexual assault
2021-05-24
Research Study Key Takeaways:
Ridesharing can reduce a passenger's risk of being a target of sexual assault by providing a more reliable and timely transportation option for traveling to a safer place.
The entry of Uber into a city contributes to a 6.3% reduction in rape incidents.
A 1% increase in Uber pickups in a neighborhood translates to a more than 3% decrease in the likelihood of sexual assaults.
CATONSVILLE, MD, May 24, 2021 - Contrary to portraits painted in popular media, new research involving ridesharing services shows they provide an additional level of protection for potential sexual assault victims, particularly ...
Regular physical activity linked to better organized preteen brains
2021-05-24
Regular physical activity has positive effects on children's developing brain circuits, finds a Boston Children's Hospital study using neuroimaging data from nearly 6,000 early adolescents. Physical activity of any kind was associated with more efficiently organized, flexible, and robust brain networks, the researchers found. The more physical activity, the more "fit" the brain.
Findings were published in Cerebral Cortex on May 14.
"It didn't matter what kind of physical activity children were involved in - it only mattered that they were active," says Caterina Stamoulis, PhD, principal ...
[1] ... [2285]
[2286]
[2287]
[2288]
[2289]
[2290]
[2291]
[2292]
2293
[2294]
[2295]
[2296]
[2297]
[2298]
[2299]
[2300]
[2301]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.