NIST, collaborators develop new method to better study microscopic plastics in the ocean
2021-05-21
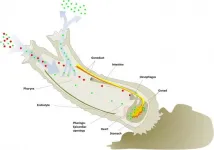
If you've been to your local beach, you may have noticed the wind tossing around litter such as an empty potato chip bag or a plastic straw. These plastics often make their way into the ocean, affecting not only marine life and the environment but also threatening food safety and human health.
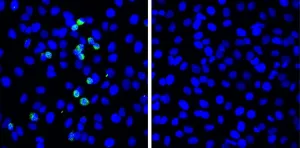
Eventually, many of these plastics break down into microscopic sizes, making it hard for scientists to quantify and measure them. Researchers call these incredibly small fragments "nanoplastics" and "microplastics" because they are not visible to the naked eye. Now, in a multiorganizational effort led by the National Institute of Standards and ...
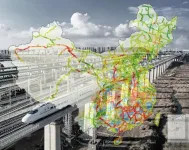
Railway infrastructure susceptible to greater damages from climate change
2021-05-21
Just half a degree Celsius less warming would save economic losses of Chinese railway infrastructure by approximately $0.63 billion per year, according to a new paper published by a collaborative research team based in Beijing Normal University and the Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China.
The study, which appears in Transportation Research Part D recently, found that the rainfall-induced disaster risk of railway infrastructure has increased with increasing extreme rainfall days during the decades 1981-2016. Limiting global ...
Legitimation strategies for coal exits in Germany and Canada
2021-05-21
Ending our dependence on coal is essential for effective climate protection. Nevertheless, efforts to phase out coal trigger anxiety and resistance, particularly in mining regions. The governments of both Canada and Germany have involved various stakeholders to develop recommendations aimed at delivering just transitions and guiding structural change. In a new study, researchers at the Institute for Advanced Sustainability Studies (IASS) compare the stakeholder commissions convened by the two countries, drawing on expert interviews with their members, and examine how governments use commissions to legitimize their transition policies.
In the study, the researchers identify similarities and ...
3D visualization of oxytocin and vasopressin circuits with unprecedented resolution
2021-05-21
The work, carried out by Pilar Madrigal and Sandra Jurado, from the UMH-CSIC Neurosciences Institute in Alicante, a joint center of the Spanish National Research Council and Miguel Hernández University, has been published in Communications Biology, a Nature group´s journal.
"Our in-depth analysis of the oxytocin-vasopressin circuit in the mouse brain has revealed that these two molecules have distinct dynamics throughout embryonic development. It is likely that these adaptations modulate the functional properties of different brain regions according to their developmental stage, contributing to the refinement ...
Device for detection of signs of sudden cardiac death developed at TPU
2021-05-21
Scientists of Tomsk Polytechnic University have developed a nanosensor-based hardware and software complex for measurement of cardiac micropotential energies without filtering and averaging-out cardiac cycles in real time. The device allows registering early abnormalities in the function of cardiac muscle cells, which otherwise can be recorded only during open-heart surgery or by inserting an electrode in a cardiac cavity through a vein. Such changes can lead to sudden cardiac death (SCD). Nowadays, there are no alternatives to the Tomsk device for a number of key characteristics in Russia and the world. The research findings of four-year measurement of cardiac micropotential energies using this device ...
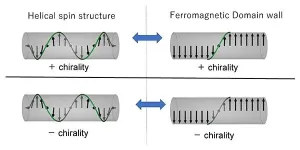
Chirality memory effect of ferromagnetic domain walls
2021-05-21
Using magnets, a collaborative group have furthered our understanding of chirality.
Their research was published in the journal Physical Review Letters on April 28, 2021.
Chirality is the lack of symmetry in matter. Human hands, for example, express chirality. A mirror image of your right hand differs from your left, giving it two distinguishable chiral states.
Chirality is an important issue in a myriad of scientific fields, ranging from high-energy physics to biology.
Within our bodies, some molecules, such as amino acids, show only one chiral state. In other words, they are homo-chiral. It is crucial to understand how this information is transferred and ...
Type 2 diabetes medication shown to benefit asthma patients
2021-05-21
Type 2 diabetes patients who also have asthma are benefitting from a diabetes medication, typically given to help the pancreas produce more insulin, that also improves asthma symptoms and may reduce lung and airway inflammation.
These types of medication -- GLP-1 receptor agonists -- are a newer class of FDA-approved therapeutics that are generally used in addition to metformin for control of blood sugar or to induce weight loss in patients with obesity.
Researchers from Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School and University Hospital Zurich in Switzerland used electronic health record (EHR) data of patients with asthma and type 2 diabetes who initiated treatment with GLP-1R agonists, finding lower rates of asthma exacerbations ...
Face masks effectively limit SARS-CoV-2 transmission
2021-05-21
'Don't forget the mask' - although most people nowadays follow this advice, professionals express different opinions about the effectiveness of face masks. An international team led by researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Chemistry in Mainz, Germany, has now used observational data and model calculations to answer open questions. The study shows under which conditions and in which way masks actually reduce individual and population-average risks of being infected with COVID-19 and help mitigate the corona pandemic. In most environments and situations, ...
Penn doubles the percentage of Black participants in cancer clinical trials
2021-05-21
PHILADELPHIA--A five-year community outreach and engagement effort by the Abramson Cancer Center at the University of Pennsylvania (ACC) to increase enrollment of Black patients into cancer clinical trials more than doubled the percentage of participants, improving access and treatment for a group with historically low representation in cancer research. The percentage of patients enrolled into a treatment clinical trial, for example, increased from 12 to 24 percent. A significant increase was also observed in non-therapeutic interventional and non-interventional trials.
The findings were published today in an abstract to be presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting on June 5. (Abstract #100). [ADD ...
In utero exposure to tiny air pollution particles is linked to asthma in preschoolers
2021-05-21
New York, NY (May 21, 2021) --Women who were highly exposed to ultra-fine particles in air pollution during their pregnancy were more likely to have children who developed asthma, according to a study published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine in May. This is the first time asthma has been linked with prenatal exposure to this type of air pollution, which is named for its tiny size and which is not regulated or routinely monitored in the United States.
Slightly more than 18 percent of the children born to these mothers developed asthma in their preschool years, compared ...
A novel defense mechanism for SARS-CoV-2 discovered
2021-05-21
Scientists from Hokkaido University have discovered a novel defensive response to SARS-CoV-2 that involves the viral pattern recognition receptor RIG-I. Upregulating expression of this protein could strengthen the immune response in COPD patients.
In the 18 months since the first report of COVID-19 and the spread of the pandemic, there has been a large amount of research into understanding it and developing menas to treat it. COVID-19 does not affect all infected individuals equally. Many individuals are asymptomatic; of those who are symptomatic, the large majority have mild symptoms, and only a small number have severe cases. The reasons for this are not fully understood and are an important area of ongoing research.
A team of scientists ...
A tripartite-chromosome E. coli strain allows the chromosome isolation and implantation
2021-05-21
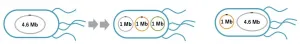
The issue of concern was that the Escherichia coli (E. coli) genome, consisting of 4.6 million base pairs of a single circular DNA, is too large to manipulate following the extraction and transfer to other bacteria.
In the present study, a group of Rikkyo University researchers led by Assistant Professor Takahito Mukai and Professor Masayuki Su'etsugu has succeeded in splitting the E.coli genome into tripartite-genome of 1 million base pairs per genome (split-genome) using the smallest E. coli genome strain established so far. In addition, they successfully extracted the split-genome from bacteria and installed it in other E. ...
Telling up from down: How marine flatworms learn to sense gravity
2021-05-21
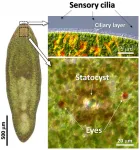
All living organisms are equipped with sensory organs to detect changes in their surrounding environment. It may not immediately strike us as obvious but, similar to how we can sense heat, cold, light, and darkness, we are also extremely adept at sensing gravity. In our case, it is our inner ear that does this job, helping us maintain balance, posture, and orientation in space. But, what about other organisms, for instance invertebrates that lack a backbone?
The gravity sensing organ in some aquatic invertebrates, known as a "statocyst," is, in fact, rather fascinating. The statocyst is essentially a fluid-filled sac with sensory cells lining its inner wall and a small, mineralized ...
Integrated cyber attack analysis platform "NIRVANA Kai" supports IPv6
2021-05-21
[Highlights]
- Integrated cyber attack analysis platform "NIRVANA Kai" newly supports IPv6 and enhances its functions.
- Observation of IPv6 communications, collection of IPv6-related alerts, and real-time visualization of IPv6 networks.
- Expected to simplify security operations in IPv6 networks.
[Abstract]
The Cybersecurity Laboratory of the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT, President: TOKUDA Hideyuki, Ph.D.) has enhanced its cyber attack integrated analysis platform "NIRVANA Kai" to support the Internet Protocol version ...
China's PM2.5 pathways under carbon neutrality goals
2021-05-21
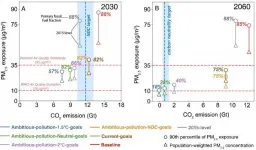
China's clean air policies have substantially reduced PM2.5 air pollution in recent years. Yet >99% of Chinese population is still exposed to PM2.5 concentrations in excess of the World Health Organization (WHO) Air Quality Guidelines of 10 μg/m3. Climate actions targeting to reduce fossil fuel consumption also have substantial air quality benefits. The announcement of ambitious climate commitment to achieve carbon neutrality by 2060 may fuel the power to long-term air quality improvement in China.
Combining Global/China's climate mitigation pathways (i.e. global 2°C- and 1.5°C-pathways, NDC pledges, and carbon neutrality goals) and local clean ...
New mechanism to control tomato ripening discovered
2021-05-21
An international research group involving the Institute of Molecular and Cellular Biology of Plants (IBMCP), a joint centre of the Universitat Politècnica de València (UPV) and the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC), has discovered that a genetic mechanism, called CHLORAD, which is involved in the ageing of plant leaves, also plays a decisive role in the tomato ripening process. Thus, tomatoes with an activated CHLORAD system turn red more quickly, and accumulate more lycopene, a compound beneficial to health. The results, which have been published in the latest issue of the journal Nature Plants, will lead to better quality tomatoes.
The ripening of most fleshy fruits gives them attractive colours and smells, which is a trick of the plant to spread its seeds ...
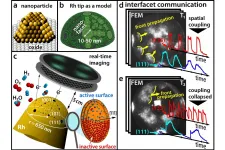
Nanoparticles: The complex rhythm of chemistry
2021-05-21
Most of commercial chemicals are produced using catalysts. Usually, these catalysts consist of tiny metal nanoparticles that are placed on an oxidic support. Similar to a cut diamond, whose surface consists of different facets oriented in different directions, a catalytic nanoparticle also possesses crystallographically different facets - and these facets can have different chemical properties.
Until now, these differences have often remained unconsidered in catalysis research because it is very difficult to simultaneously obtain information about the chemical reaction itself and about the surface structure of the catalyst. At TU Wien (Vienna), this has now been achieved by combining different microscopic methods: with ...
Scientists discover gene signature for plaque-eating microglia in Alzheimer's Disease
2021-05-21
SINGAPORE, 21 May 2021 - Alzheimer's Disease is the most common form of dementia and is characterised by the build-up of amyloid plaques in the brain. Microglia, the immune sentinels of the brain, are not only responsible for eliminating foreign invaders, but also maintaining brain homeostasis by clearing toxic waste such as the amyloid plaques.
However, the role of microglia in Alzheimer's Disease and its relationship to amyloid plaque accumulation remain unclear. Now, a team of scientists from Duke-NUS Medical School and Monash University have found the gene expression signatures underlying microglia associated ...
Pu particles from nuclear testing more complex than previously thought
2021-05-21
More than 100 kg of highly toxic uranium (U) and plutonium (Pu) was dispersed in the form of tiny 'hot' radioactive particles after the British detonated nine atomic bombs in remote areas of South Australia, including Maralinga.
Scientists say that these radioactive particles persist in soils to this day, more than 60 years after the detonations. Previously, we had limited understanding of how Pu was released from these "hot" particles into the environment for uptake by wildlife around Maralinga.
But now, a new study published today in Scientific Reports and led by Monash University researchers warns that the particles are actually more ...
Biodiversity devastation: Human-driven decline requires millions of years of recovery
2021-05-21
A new study shows that the current rate of biodiversity decline in freshwater ecosystems outcompetes that at the end-Cretaceous extinction that killed the dinosaurs: damage now being done in decades to centuries may take millions of years to undo.
The current biodiversity crisis, often called the 6th mass extinction, is one of the critical challenges we face in the 21st century. Numerous species are threatened with extinction, mostly as a direct or indirect consequence of human impact. Habitat destruction, climate change, overexploitation, pollution and invasive species are among the main causes for Earth's biota to decline rapidly.
To investigate the tempo of extinction and predict recovery times, an international team of evolutionary biologists, paleontologists, geologists and modelers ...
New nondestructive broadband imager is the next step towards advanced technology
2021-05-21
One of the key aspects of academic and industrial research today is non-destructive imaging, a technique in which an object or sample is imaged (using light) without causing any damage to it. Often, such imaging techniques are crucial to ensuring safety and quality of industrial products, subsequently leading to growing demands for high-performance imaging of objects with arbitrary structures and locations.
On one hand, there has been tremendous advancements in the scope of non-destructive imaging regarding the region of electromagnetic (EM) spectrum it can access, which now ranges from visible light to as far as millimeter waves! On the other, imaging devices have become flexible and wearable, enabling stereoscopic (3D) visualization ...
Green light on gold atoms
2021-05-21
Because individual atoms or molecules are 100 to 1000 times smaller than the wavelength of visible light, it is notoriously difficult to collect information about their dynamics, especially when they are embedded within larger structures.
In an effort to circumvent this limitation, researchers are engineering metallic nano-antennas that concentrate light into a tiny volume to dramatically enhance any signal coming from the same nanoscale region. Nano-antennas are the backbone of nanoplasmonics, a field that is profoundly impacting biosensing, photochemistry, solar energy harvesting, and photonics.
Now, researchers at EPFL led by Professor Christophe Galland at the School of Basic Sciences ...
Study on intermittency in gang membership underscores value of preventing youth from rejoining gangs
2021-05-21
Research has shown that joining a gang is associated with increased criminal behavior. A new study examined whether the intermittent nature of gang membership affects offending. Researchers sought to determine whether the association with increased offending was a consistent attribute or, since people enter and exit and re-enter gangs, whether the intermittent nature of membership affected members' likelihood of offending. The study found that first-time membership was associated with increases in criminal behavior from when gang members were not in gangs, and that joining for a second ...
First-of-its-kind flower smells like dead insects to imprison 'coffin flies'
2021-05-21
The plant Aristolochia microstoma uses a unique trick: its flowers emit a fetid-musty scent that seems to mimic the smell of decomposing insects. Flies from the genus Megaselia (family Phoridae) likely get attracted to this smell while searching for insect corpses to mate over and lay their eggs in. When they enter a flower, they are imprisoned and first pollinate the female organs, before being covered with pollen by the male organs. The flower then releases them unharmed.
"Here we show that the flowers of A. microstoma emit an unusual mix of volatiles that includes alkylpyrazines, which are otherwise rarely produced by flowering plants. Our results suggest that this is the first known case of a flower that tricks pollinators by smelling like dead and rotting insects rather than vertebrate ...
Doctors have nothing to fear from a central register of interests, say experts
2021-05-21
UK doctors have nothing to fear from the introduction of a central register listing money or benefits they receive in addition to their NHS salary, say experts today ahead of a public meeting on the issue hosted by the All-Party Parliamentary Group for First Do No Harm and The BMJ.
Last year the Independent Medicines and Medical Devices Safety Review, chaired by Baroness Julia Cumberlege, investigated harmful side effects caused by the hormone pregnancy test Primodos, the anti-epileptic drug sodium valproate, and pelvic mesh.
During the review, she heard from patients who were concerned that clinicians ...
[1] ... [2292]
[2293]
[2294]
[2295]
[2296]
[2297]
[2298]
[2299]
2300
[2301]
[2302]
[2303]
[2304]
[2305]
[2306]
[2307]
[2308]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.