ORIENT-12 Study demonstrates adding sintilimab to gemcitabine/platinum has clinical benefit
2021-05-25
(10 a.m. EDT May 25, 2021 Denver)-- Adding sintilimab to a regimen of gemcitabine and platinum demonstrates clinical benefit over gemcitabine and platinum alone as first-line therapy in patients with locally advanced or metastatic squamous cell non-small cell lung cancer, according to a study published in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology, the official journal of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer.
The standard chemotherapy for squamous NSCLC (sqNSCLC), includes platinum plus gemcitabine. sintilimab, an anti-PD-1 antibody, plus platinum/gemcitabine, has shown encouraging efficacy as first-line therapy for sqNSCLC in the phase III study ECOG 1594. Platinum/gemcitabine is another standard regimen of chemotherapy for sqNSCLC and is commonly used in ...
China makes remarkable gains in maternal and child survival rates
2021-05-25
China has made remarkable gains in reducing the number of women who die during childbirth and boosting child survival rates over the past 70 years, according to new review.
The Lancet report brought together China's health research institutions alongside its international colleagues from Australia, the UK and the US to review the country's progress in maternal, newborn, child and adolescent health and nutrition since 1949.
Murdoch Children's Research Institute (MCRI) Professor George Patton, one of the international researchers, said over the past 70 years China had made a remarkable transition from where the survival of women and children was the priority to one where children ...
AI spots neurons better than human experts
2021-05-25
DURHAM, N.C. -- A new combination of optical coherence tomography (OCT), adaptive optics and deep neural networks should enable better diagnosis and monitoring for neuron-damaging eye and brain diseases like glaucoma.
Biomedical engineers at Duke University led a multi-institution consortium to develop the process, which easily and precisely tracks changes in the number and shape of retinal ganglion cells in the eye.
This work appears in a paper published on May 3 in the journal Optica.
The retina of the eye is an extension of the central nervous system. Ganglion cells are one of the primary neurons in the eye that process and send visual information to the brain. In many neurodegenerative ...
Can TV shows help teens navigate bullying, depression and other mental health issues?
2021-05-25
Popular television shows and movies can bolster teenagers' mental health and help them cope with bullying, sexual assault, suicidal thoughts, substance abuse and depression when these issues are depicted with empathy and appropriate resources are provided, a report published by UCLA's Center for Scholars and Storytellers shows.
And the need is great. Recent research has shown that children between the ages of 11 and 17 are more likely than any other age group to report moderate to severe anxiety and depression, said Yalda Uhls, founder and executive director of the center and an adjunct assistant professor of psychology.
Even before the pandemic, teen suicide rates were rising, along with reported symptoms of anxiety and depression, she noted. At the same time, nearly half ...
Synchrotron X-ray experiment reveals a small nudge with big consequences
2021-05-25
QUT researchers have used experimental x-ray techniques at the Australian Synchrotron to gain fundamental insights into how gypsum dehydrates under pressure and the processes that create earthquakes.
In the study published in the Nature Research journal Communications Materials, QUT researchers Dr Christoph Schrank, Dr Oliver Gaede, from the School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences, and Master of Science graduate Katherine Gioseffi teamed up with the Australian Synchrotron and colleagues from the University of New South Wales and the University of Warsaw to study how gypsum dehydrates much faster under pressure.
"Dehydration is a process in which minerals shed the water bound in their crystal lattices due to heating," Dr Schrank ...
Newly discovered enzymes are not heavy metal fans
2021-05-25
Tsukuba, Japan - Carbonic anhydrases are essential enzymes that are present in virtually all living things; all eight classes of carbonic anhydrases that have been identified to date need a metal ion to function. But now, researchers from Japan have discovered that metal is not crucial for all carbonic anhydrases.
In a study published this month in BMC Biology, researchers from the Faculty of Life and Environmental Sciences at the University of Tsukuba have described two members of the COG4337 protein family that are the first known examples of carbonic anhydrase enzymes that do not require a metal ion to function.
Carbonic anhydrases ...
Food scraps get a bold new life
2021-05-25
Tokyo, Japan - Most people don't think much about the food scraps they throw away; however, investigators from the Institute of Industrial Science at The University of Tokyo have developed a new method to reduce food waste by recycling discarded fruit and vegetable scraps into robust construction materials.
Worldwide industrial and household food waste amounts to hundreds of billions of pounds per year, a large proportion of which comprises edible scraps, like fruit and vegetable peels. This unsustainable practice is both costly and environmentally unfriendly, so researchers have been searching for new ways to recycle these organic ...
New technique breaks the mould for 3D printing medical implants
2021-05-25
Researchers have flipped traditional 3D printing to create some of the most intricate biomedical structures yet, advancing the development of new technologies for regrowing bones and tissue.
The emerging field of tissue engineering aims to harness the human body's natural ability to heal itself, to rebuild bone and muscle lost to tumours or injuries.
A key focus for biomedical engineers has been the design and development of 3D printed scaffolds that can be implanted in the body to support cell regrowth.
But making these structures small and complex enough for cells to thrive remains a significant challenge.
Enter a RMIT University-led research team, collaborating with clinicians at St Vincent's Hospital Melbourne, Australia, who have overturned ...
Pain monitoring helps assess the effectiveness of opioid-sparing approaches during surgery
2021-05-25
A new study has shown that effective opioid-sparing anaesthesia with dexmedetomidine can be guided with NOL pain monitoring technology (Medasense, Israel). The study showed that the NOL monitor is able to detect the effect of dexmedetomidine on the patient's pain response and enable administration of less intraoperative opioids.
Patients undergoing anaesthesia for surgical procedures are traditionally treated with opioids (e.g., remifentanil) to manage intraoperative pain. But clinicians are progressively seeking to reduce opioid use by introducing multimodal analgesia, a technique that involves a combination of medications that often includes a central ...
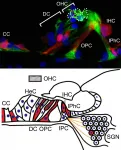
Superoxide produced in the cochlea of inner ears causes acquired hearing loss
2021-05-25
Professor UEYAMA Takehiko (Biosignal Research Center, Kobe University) and the inner ear research group (Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine) have identified the cell types in the inner ear cochlea (*1) responsible for the production of superoxide (Nox3*2-expressing cells). They achieved this by using genetically modified mice that they developed. The researchers discovered that these superoxide-producing cells increase in number in response to aging, noise damage, and ototoxic drugs, thus causing age-related, noise-induced and drug-induced hearing loss. In addition, they were able to suppress the onset of these three types of ...
Decreased testing could lead to surge in sexually transmitted infections
2021-05-25
HERSHEY, Pa. -- Screening and testing for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) decreased by 63% for men and 59% for women during the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a new study led by Penn State and Quest Diagnostics researchers. The researchers said this may be the result of restrictions placed on direct patient care and shifts to telehealth and could lead to a possible future surge in STI cases.
This is the first national study to explore the impact of the pandemic on STIs since the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention ...
Scientific software - Quality not always good
2021-05-25
Computational tools are indispensable in almost all scientific disciplines. Especially in cases where large amounts of research data are generated and need to be quickly processed, reliable, carefully developed software is crucial for analyzing and correctly interpreting such data. Nevertheless, scientific software can have quality quality deficiencies. To evaluate software quality in an automated way, computer scientists at Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) and Heidelberg Institute for Theoretical Studies (HITS) have designed the SoftWipe tool.
"Adherence to coding standards is rarely considered in scientific software, although it can even lead to incorrect scientific results," says ...
Wearable devices show that physical activity may lower atrial fibrillation and stroke risk
2021-05-25
BOSTON - Physical activity that conforms to medical and health association guidelines is associated with a lower risk of atrial fibrillation (Afib) and stroke, according to a study by researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), who analyzed nearly 100,000 individuals equipped with wrist-worn accelerometers to measure their movement. The researchers' findings suggest that data from wearables, including a new generation of devices with sensors that allow for Afib detection, could provide an opportunity for the public health community to promote moderate physical activity as an effective way to improve health outcomes. The study ...
New AI technology protects privacy
2021-05-25
Digital medicine is opening up entirely new possibilities. For example, it can detect tumors at an early stage. But the effectiveness of new AI algorithms depends on the quantity and quality of the data used to train them.
To maximize the data pool, it is customary to share patient data between clinics by sending copies of databases to the clinics where the algorithm is being trained. For data protection purposes, the material usually undergoes anonymization and pseudonymization processes - a procedure that has also come in for criticism. "These processes have often proven inadequate in terms of protecting patients' health data," says Daniel Rueckert, ...
Is deference to supernatural beings present in infancy?
2021-05-25
From shamans and mystics to cult leaders and divine kings, why have people throughout history accorded high status to people believed to have supernatural powers?
According to a study led by researchers from the University of Oxford, this tendency to attribute social dominance to such individuals is rooted in early development.
As part of the study, 48 infants aged 12 to 16 months watched a series of animated videos in which two characters competed for a reward. In each scenario, one character displayed physically counterintuitive methods of making ...
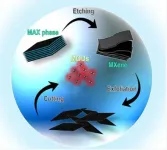
Light-emitting MXene quantum dots
2021-05-25
In a new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI https://doi.org/10.29026/oea.2021.200077, Researchers led by Professor Jeongyong Kim at the Department of Energy Science, Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon, Republic of Korea review light-emitting MXene quantum dots.
MXenes have found wide-ranging applications in energy storage devices, sensors, catalysis, etc. owing to their high electronic conductivity and wide range of optical absorption. However, the absence of semiconducting MXenes has limited their applications related to light emission.
Extensively reviewing current relevant research, the authors summarise recent advances in MXene quantum dot (MQD) research on the synthesis, optical properties and applications of MQDs as light emitting quantum materials. Research ...
Superflimsy graphene turned ultrastiff by optical forging
2021-05-25
Graphene is an ultrathin material characterized by its ultrasmall bending modulus, superflimsiness. Now the researchers at the Nanoscience Center of the University of Jyväskylä have demonstrated how an experimental technique called optical forging can make graphene ultrastiff, increase its stiffness by several orders of magnitude. The research was published in npj 2D Materials and Applications in May 2021.
Graphene is an atomically thin carbon material loaded with excellent properties, such as large charge carrier mobility, superb thermal conductivity, and high ...
Immune cells imperfect at distinguishing between friend and foe, study suggests
2021-05-25
When it comes to distinguishing a healthy cell from an infected one that needs to be destroyed, the immune system's killer T cells sometimes make mistakes.
This discovery, described today in eLife, upends a long-held belief among scientists that T cells were nearly perfect at discriminating friend from foe. The results may point to new ways to treat autoimmune diseases that cause the immune system to attack the body, or lead to improvements in cutting-edge cancer treatments.
It is widely believed that T cells can discriminate perfectly between infected cells and healthy ones based on how tightly they are able to bind to molecules called antigens ...
Study reveals new details on what happened in the first microsecond of Big Bang
2021-05-25
About 14 billion years ago, our universe changed from being a lot hotter and denser to expanding radically - a process that scientists have named 'The Big Bang'.
And even though we know that this fast expansion created particles, atoms, stars, galaxies and life as we know it today, the details of how it all happened are still unknown.
Now a new study performed by researchers from University of Copenhagen reveals insights on how it all began.
"We have studied a substance called Quark-Gluon Plasma that was the only matter, which existed during the first microsecond ...
Impaired dopamine transporters contribute to Parkinson's disease-like symptoms
2021-05-25
A rare mutation that causes Parkinson's disease-like symptoms interrupts the flow of dopamine in the brain, suggests a study in fruit flies published today in eLife.
The findings provide more detailed insights about why young children with this mutation develop these symptoms. This new information, as well as previous evidence that therapies helping to improve dopamine balance in the brain can alleviate some symptoms in the flies, suggests that this could be a beneficial new treatment strategy.
Parkinson's disease causes progressive degeneration of the brain that leads to impaired movement and coordination. Current treatments focus on replacing or increasing the levels of dopamine to help reduce movement-related symptoms. But these drugs can have side ...
"Bite" defects in bottom-up graphene nanoribbons
2021-05-25
Graphene nanoribbons (GNRs), narrow strips of single-layer graphene, have interesting physical, electrical, thermal, and optical properties because of the interplay between their crystal and electronic structures. These novel characteristics have pushed them to the forefront in the search for ways to advance next-generation nanotechnologies.
While bottom-up fabrication techniques now allow the synthesis of a broad range of graphene nanoribbons that feature well-defined edge geometries, widths, and heteroatom incorporations, the question of whether or not structural disorder is present in these atomically precise GNRs, and to what extent, is still subject to debate. The answer to this ...
States' developmental disability services lacking for adults with autism and their families
2021-05-25
In the latest National Autism Indicators Report, researchers from Drexel University’s A.J. Drexel Autism Institute examined surveys of family members of autistic adults who use Developmental Disability services, and found needs for additional supports like respite care and assistance to plan for crisis and emergencies, especially among families whose adult lived with them.
Data from the surveys showed over one quarter of families with autistic adults who use Developmental Disability services and live with family do not have enough services or supports for themselves, according to the report. And over half of these families ...
New international research provides tips for entrepreneurs to beat the grind
2021-05-25
Staying up all night, working nonstop, eating on the run and skipping meals are often telltale signs of starting a new business. But research shows this constant hustle - which is often glorified as the key to success - can have a negative impact not only on an entrepreneur's health and well-being but also his or her business.
New research led by UCF assistant professor of management Jeff Gish suggests that engaging in recovery may help entrepreneurs reduce the negative impact of stress.
"Entrepreneurs who work really hard and grind on their business and who most ...
Researchers seek deeper understanding on how cells in the body operate
2021-05-25
Cells sense and respond to the mechanical properties of the cellular microenvironment in the body. Changes in these properties, which occur in a number of human pathologies, including cancer, can elicit abnormal responses from cells. How the cells adapt to such changes in the mechanical microenvironment is not well understood.
A team of researchers at Texas A&M University are working to understand cellular mechanosensing -- the ability to sense and respond to the mechanical properties of the microenvironment -- in a unique way. Dr. Tanmay Lele, Unocal Professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering, Department of Chemical Engineering and the Department of Translational Medical Sciences, partnered with Dr. Charles Baer, an evolutionary biologist at the University of Florida. ...
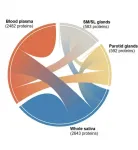
New wiki on salivary proteins may transform diagnostic testing and personalized medicine
2021-05-25
BUFFALO, N.Y. - To improve the development of new saliva-based diagnostic tests and personalized medicine, the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR) has supported the development of the Human Salivary Proteome Wiki, the first public platform that catalogs and curates data on each of the thousands of proteins within our saliva.
Detailed in an article published on Tuesday, May 25 in the Journal of Dental Research, the wiki provides researchers and clinicians with rich, unbiased evidence from multiple independent studies to help explore the dynamic and complex nature of saliva, as well as analytical tools to search for data by tissue type, disease and more.
"This ...
[1] ... [2296]
[2297]
[2298]
[2299]
[2300]
[2301]
[2302]
[2303]
2304
[2305]
[2306]
[2307]
[2308]
[2309]
[2310]
[2311]
[2312]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.