Researchers estimate COVID-19-positive rate in Stockholm during first year of pandemic
2021-05-19
By the end of the first year of the pandemic in metropolitan Stockholm, investigators estimate that one-fifth of adults in the region previously had COVID-19. The findings, which are published in the Journal of Internal Medicine, come from analyses of anti-viral antibody responses in healthy blood donors and pregnant women.
For the study, researchers examined blood from 2,600 blood donors and 2,500 pregnant women taken between March 14th 2020 and February 28th 2021. Blood donors and pregnant women had a similar rate of past infection, approaching 19% of the study group by the end of February 2021, shortly ...
New antimicrobial surface reduces bacteria build-up on medical instruments
2021-05-19
Monash University researchers have engineered new antimicrobial surfaces that can significantly reduce the formation of bacteria on medical instruments, such as urinary catheters, and reduce the risk of patient infection while in hospital.
This world-first study demonstrates the potential for 3D engineered surfaces in preventing the initial formation of microcolonies of Escherichiacoli (E.coli), Klebsiellapneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa - the three most common urinary tract bacterial infections (UTIs) associated with catheters.
The study team, led by Dr Victor Cadarso, from Monash University's Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering and the ...
Study of Utah cancer care-at-home model demonstrates lower costs, better outcomes
2021-05-19
SALT LAKE CITY - A new study published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology reports findings on Huntsman at Home™, a cancer hospital-at-home model operated by Huntsman Cancer Institute (HCI) at the University of Utah (U of U). The study analyzed aspects of Huntsman at Home acute care--meaning a level of care that is generally provided in an inpatient hospital setting.
In the 30 days after study entry, Huntsman at Home participants had 55% fewer hospitalizations, 45% fewer emergency department visits, and shorter hospital stays by one day. They also had 47% lower health care costs during the same 30-day period ...
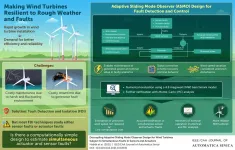
Getting "wind" of the future: Making wind turbines low-maintenance and more resilient
2021-05-19
A key driver of energy research is the ever-growing demand for energy. Traditional fossil-fuel-based energy sources currently meet these demands and do it well, but they're non-renewable and cause major environmental pollution. In a world with looming climate and resource crises threats, researchers have turned to renewable sources of energy as sustainable alternatives. Among renewables, wind energy, in particular, has gained considerable attention due to its low cost. As Dr. Afef Fekih, Computer Engineer at the University of Louisiana, USA, with a specialization in wind turbine design, notes, "Wind energy has been described as 'the world's fastest-growing renewable energy source', seeing a 30% annual growth on ...
Adolescents' well-being and learning during COVID-19 linked to psychological needs
2021-05-19
A new survey study suggests that, for adolescents who received unplanned distance education due to the COVID-19 pandemic, experiencing one's own competence was linked to positive emotion, self-motivation to learn, and pro-learning behaviors. Feeling connected to others was also linked to positive emotion. Julia Holzer of the University of Vienna, Austria, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE.
The new research draws on a psychological theory known as self-determination theory, which outlines three basic psychological needs for well-being: autonomy, connection to others, and experiencing one's own competence. Previous research has provided much ...
Americans who get news from traditional sources more likely to accept COVID-19 vaccine
2021-05-19
Americans who get their news from traditional sources (e.g.: TV, newspapers) are more likely to accept the COVID-19 vaccine than those who rely on social media.
INFORMATION:
Article Title: Examining the effect of information channel on COVID-19 vaccine acceptance
Funding: This research was with funding support from Jigsaw, Google. RPL, ES, JK, BH, and CMI received funding from Jigsaw to conduct this research. BG and TV are employed by Jigsaw/Google. Google, Inc. provided support in the form of salaries for authors, BG TV, but did not have any additional role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. The specific roles of these authors are articulated in the 'author contribution'. The data ...
Almost 1 in 4 COVID-19 patients have another infection simultaneously or subsequently
2021-05-19
Almost 1 in 4 COVID-19 patients have another bacterial, viral or fungal infection simultaneously or subsequently, with such patients experiencing worse disease outcomes.
INFORMATION:
Article Title: Prevalence and outcomes of co-infection and superinfection with SARS-CoV-2 and other pathogens: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Funding: NS received research support for this work from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases of the National Institutes of Health under Award Number DP2AI144244. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily ...
Maintaining self-control -- The careful balance of the immune system
2021-05-19
Tsukuba, Japan - Autoimmune diseases occur when an individual's immune system fights their own body as if it was a foreign invader. However, in healthy people, these responses are prevented by a process known as immune tolerance. Many complex biological mechanisms maintain the necessary balance between immune activation and suppression to ensure immune tolerance does not prevent the body from effectively fighting pathogens.
In a new study published in PNAS, a group of researchers from the University of Tsukuba uncovered how the relationship between two receptors called DNAM-1 and TIGIT helps preserve the balance for optimal immune function. Both of these molecules have previously been studied ...
New study identifies plasticity disparities between patients with brain malformation
2021-05-19
Recently published in the scientific journal Brain Communications, a new study distinguished structural patterns between individuals with corpus callosum dysgenesis (CCD), a congenital condition that consists of the absence or incomplete development in the connecting structure between the two brain hemispheres. The research was carried out by the D'Or Institute for Research and Education (IDOR), the University of Pittsburgh, Oswaldo Cruz Foundation (Fiocruz), and the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ).
Investigating CCD is an arduous task for doctors and neuroscientists. There aren't many patients available for research, and the anatomical variability of brains with CCD creates a broad ...
Childhood disadvantage affects brain connectivity
2021-05-19
Philadelphia, May 18, 2021 - Many socioeconomically disadvantaged children face poor cognitive and mental health outcomes, and researchers are working to determine the specific factors that link childhood conditions to those poor outcomes, including how they might shape brain circuitry. In a new study, researchers have examined how "neighborhood disadvantage" can affect the developing brain, including the brain's connectivity between regions.
The study appears in Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging, published by Elsevier.
Sarah Whittle, PhD, and Divyangana Rakesh, lead authors of the study, studied existing brain scans from 7,618 children aged 9-10 collected as part of the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development ...
Oregon researchers find cell division machinery that makes brain cells
2021-05-19
EUGENE, Ore. -- May 19, 2021 -- High-resolution imaging of fruit flies at the University of Oregon has captured mechanical motions that stem cells use to make neurons, the cells that make up the brain.
These motions coordinate cell division with differentiation, where newly born cells become neurons. Differentiation is essential for building the brain circuitry in complex organisms that underlies human cognition and emotions, said Ken Prehoda, a professor in the UO's Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry.
Prehoda was principal investigator of a project published online May 18 in the journal ...
New insights into androgen's action could boost battle against prostate cancer
2021-05-19
Researchers at UVA Cancer Center have unveiled important new insights into how hormones known as androgens act on our cells - and the discovery could boost efforts to develop better treatments for prostate, ovarian and breast cancers.
The findings shed light on how androgens interact with their receptors inside cells to affect gene activity. This process is important in both healthy cells and certain cancers. Hormone therapy for prostate cancer, for example, aims to reduce the amount of androgen in the body, or to stop it from fueling the cancer cells. However, ...
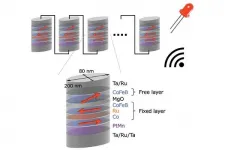
Wireless and battery-free spintronic energy harvester
2021-05-19
Researchers at the National University of Singapore (NUS) and Tohoku University have demonstrated that an array of electrically connected spintronic devices can harvest a 2.4 GHz wireless signal, which can be used to power and charge small electronic devices and sensors.
The researchers from NUS and Tohoku University have successfully synchronized the four electrically connected magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ), for the signal transmission at 2.4 GHz. Furthermore, the eight MTJs array was integrated with the conventional battery-free electronics to harvest a wireless signal of 2.4 GHz to a DC signal, which is used to power light emitting ...
Scientists take a bite out of solar efficiency challenge with sandwich model
2021-05-19
In a world hungry for cheaper, more efficient renewable energy, Australian researchers have served up a treat.
Work led by the ARC Centre of Excellence in Exciton Science has shown that the two-dimensional (2D) thin films used in some perovskite solar cells closely resemble a sandwich. Perovskite is an exciting material at the forefront of solar energy research and design.
Previously, scientists thought these 2D perovskite films had a 'gradient' structure, in which certain components were found deep in the material, with other complementary elements only located nearer to the surface, like topping on a cracker.
However, in a paper published ...
'No level of smoke exposure is safe'
2021-05-19
Nearly a quarter of pregnant women say they've been around secondhand smoke - in their homes, at work, around a friend or relative - which, according to new research, is linked to epigenetic changes - meaning changes to how genes are regulated rather than changes to the genetic code itself - in babies that could raise the risk of developmental disorders and cancer.
The study, published today in Environmental Health Perspectives by researchers at Virginia Commonwealth University Massey Cancer Center, is the first to connect secondhand smoke during pregnancy with epigenetic modifications to disease-related genes, measured at birth, which supports the idea that many adult ...
Children's sleep and adenotonsillectomy
2021-05-19
While a pint-sized snorer may seem adorable tucked up in bed, studies shows that children with sleep disordered breathing are likely to show aggressive and hyperactive behaviours during the day.
The recommended treatment is an adenotonsillectomy - the removal of adenoid and tonsils - not only to fix the snore, but also the behaviour.
Yet according to new research from the University of South Australia, while the surgery can cure a child's snoring it doesn't change their behaviour, despite common misconceptions by parents and doctors alike.
Conducted in partnership with the University ...
Same nerve cell -- Different influence on food intake
2021-05-19
The nerve cells, also called neurons, in our brain control all the basic processes of our body. For this reason, there are different types of neurons distributed over specific regions of the brain. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Metabolic Research and the CECAD Cluster of Excellence in Aging Research of the University of Cologne have developed an approach that allows them to show that neurons that are supposedly the same are actually very different: they not only sense different hormones for the body's energy state, but also have a different influence on food intake. This can have a direct effect on our metabolism, for example by differentially restraining our appetite.
The brain processes our sensory perceptions, controls our behaviour and stores ...
Study led by NTU Singapore finds that microbes work as a network in causing lung infection
2021-05-19
Traditionally, an infection is thought to happen when microbes - bacteria, fungi, or viruses - enter and multiply in the body, and its severity is associated with how prevalent the microbes are in the body.
Now, an international research team led by Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) has proposed a new way of understanding infections. Their study of close to 400 respiratory samples from patients with bronchiectasis, a chronic lung condition, has shown that microbes in the body exist as a network, and that an infection's severity could be a result of interactions between these microbes.
Through statistical modelling ...
We've got the dirt on soil protists
2021-05-19
Among the large cast of microbiome players, bacteria have long been hogging the spotlight. But the single-celled organisms known as protists are finally getting the starring role they deserve.
A group of scientists who study the interactions between plants and microbes have released a new study detailing the dynamic relationships between soil-dwelling protists and developing plants, demonstrating that soil protists respond to plant signals much like bacteria do.
An enormous variety and diversity of microbes live in soil, and studying how these organisms interact with each ...
Plant consumers play unexpectedly large role in the evolution of seedling success
2021-05-19
For young plants, timing is just about everything. Now, scientists have found that herbivores, animals that consume plants, have a lot to say about evolution at this vulnerable life stage.
Once a plant seedling breaches the soil surface and begins to grow, a broad range of factors will determine whether it thrives or perishes.
Scientists have long perceived that natural selection favors early rising seeds. Seedlings that emerge early in the growing season should have a competitive advantage in monopolizing precious soil resources. Early growth also should mean more access to light, since early growers can block sunlight for seedlings that emerge later in the season.
Despite plenty of proof that germinating early is highly advantageous, many plants germinate ...
Tumor marker may help overcome endocrine treatment-resistant breast cancer
2021-05-19
LA JOLLA, CALIF. - May 19, 2021 - A study led by scientists at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute has identified a tumor marker that may be used to predict which breast cancer patients will experience resistance to endocrine therapy. The research offers a new approach to selecting patients for therapy that targets HER2, a protein that promotes the growth of cancer cells, to help avoid disease relapse or progression of endocrine-sensitive disease.
The study was published in the journal Nature Communications.
Nearly 80% of breast tumors are estrogen receptor (ER)-positive. For decades, ...
Parental consumption shapes how teens think about and use cannabis
2021-05-19
Turns out the old adage, "monkey see, monkey do," does ring true -- even when it comes to cannabis use. However, when cannabis use involves youth it's see, think, then do, says a team of UBC Okanagan researchers.
The team found that kids who grow up in homes where parents consume cannabis will more than likely use it themselves. Parental influence on the use of cannabis is important to study as it can help with the development of effective prevention programs, explains Maya Pilin, a doctoral psychology student in the Irving K. Barber Faculty of Arts and Social Sciences.
"Adolescence is a critical period in which drug and alcohol experimentation takes place and when cannabis use is often initiated," says Pilin. "Parents are perhaps the most influential socializing agent for ...
Why bipolar patients don't take their meds
2021-05-19
People with bipolar disorder may not take their medication because of side effects, fear of addiction and a preference for alternative treatment - according to research from Norfolk and Suffolk NHS Foundation Trust (NSFT) and the University of East Anglia (UEA).
Nearly half of people with bipolar disorder do not take their medication as prescribed leading to relapse, hospitalisation, and increased risk of suicide.
A new study, published today, reveals six key factors that stop people taking their medication as prescribed.
These include whether they are experiencing side effects, difficulties in remembering to take medication and a lack of support from family, friends and healthcare ...
A protein modification of MECP2 can convey neuroprotection under inflammation
2021-05-19
Researchers at the University of Eastern Finland have found a potential neuroprotective effect of a protein modification that could be a therapeutic target in early Alzheimer's disease. The new study investigated the role of MECP2, a regulator of gene expression, in Alzheimer's disease related processes in brain cells. The study found that phosphorylation of MECP2 protein at a specific amino acid decreases in the brain as Alzheimer's disease is progressing. Abolishing this phosphorylation of MECP2 in cultured mouse neurons upon inflammatory stimulation enhanced their viability and ...
Pancreatic cancer: Mechanisms of metastasis
2021-05-19
A study led by MedUni Vienna (Institute of Cancer Research and Comprehensive Cancer Center Vienna) sheds light on the mechanisms that lead to extremely aggressive metastasis in a particular type of pancreatic cancer, the basal subtype of ductal adenocarcinoma. The results contribute to a better understanding of the disease. The study has recently been published in the leading journal "Gut".
The most prevalent form of pancreatic cancer, Pancreatic Ductal AdenoCarcinoma (PDAC) is usually divided into two subtypes, a classical subtype and a basal subtype. The latter is highly aggressive and tends towards early metastasis. One of the distinguishing features between the two subtypes is that the classical subtype exhibits the protein GATA6. This is no longer present ...
[1] ... [2302]
[2303]
[2304]
[2305]
[2306]
[2307]
[2308]
[2309]
2310
[2311]
[2312]
[2313]
[2314]
[2315]
[2316]
[2317]
[2318]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.