Study reveals huge pressures on anaesthesia and critical care workforce and hospitals during winter wave of COVID-19 pandemic, and devastating drop in surgical activity
2021-05-19
New research published in Anaesthesia (a journal of the Association of Anaesthetists) shows the huge pressure that anaesthesia and critical care staff in the UK have been under throughout the winter wave of COVID-19, as the number of newly admitted infected patients surged and most planned surgeries, including a substantial number of critical cancer operations, were cancelled.
"These findings have important implications for understanding what has happened during the COVID-19 pandemic, planning recovery and building a system that will better respond ...
Doctor and mother recounts COVID-19 experience that saw her placed on special ECMO respiratory support and remain in hospital for 150 days
2021-05-19
A general practitioner, wife and mother has recounted her experience with COVID-19 which saw her stay in hospital 150 days and become one of the first patients to be treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), special equipment that completely takes over the function of the lungs and is a last resort option.
The self-written case report, which appears in the journal Anaesthesia Reports (a journal of the Association of Anaesthetists) is by Dr Anushua Gupta, who works as a general practitioner in Stockport, Greater Manchester, UK. It is thought to be the first patient-written account of ECMO to treat COVID-19 to appear in the medical literature.
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation was introduced as ...
Saving the eastern monarch butterfly: SFU research
2021-05-18
Simon Fraser University researchers are playing a key role in guiding conservation efforts to protect a declining butterfly population. The eastern monarch butterfly, an important pollinating species known for its distinct yellow-orange and black colour, is diminishing due to the loss of the milkweed plant--its primary food source.
Researchers analyzed current conservation strategies and recommended changes to how and where declining milkweed can be restored, based on assessments of climate and butterfly migration. Their study is published today in Frontiers in Environmental ...
Researchers develop framework incorporating renewables and flexible carbon capture
2021-05-18
As the global energy demand continues to grow along with atmospheric levels of carbon dioxide (CO2), there has been a major push to adopt more sustainable and more carbon-neutral energy sources. Solar/wind power and CO2 capture - the process of capturing waste CO2 so it is not introduced into the atmosphere - are two promising pathways for decarbonization, but both have significant drawbacks.
Solar and wind power is intermittent and cannot be deployed everywhere; CO2 capture processes are incredibly energy-intensive. Both of these pathways have benefits, but each ...
Making mindfulness meditation more helpful starts with understanding how it can be harmful
2021-05-18
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- Mindfulness-based meditation programs have emerged as a promising treatment for conditions ranging from stress to sleeplessness to depression. In some cases, they're even offered to people -- schoolkids or employees, for example -- who aren't actively seeking help or who haven't been screened for suitability. Yet most research and discourse about these programs focuses only on their benefits, with little investigation of the risks or the potential for adverse effects.
A recent review of nearly 7,000 studies of meditation practices found that less than 1% of them measured adverse effects. Willoughby Britton, an associate professor of psychiatry and human behavior at Brown University, said that this is largely because ...
Strengthening interpersonal relationships helps medical patients live longer
2021-05-18
New research from BYU published in PLOS Medicine found that providing medical patients with social support leads to an increased chance of survival and elongation of life. Such findings come at a critical time as doctors and healthcare professionals seek new ways to improve care and decrease mortality.
"The premise of the research is that everyone is strongly influenced by their social context," said BYU counseling psychology professor Timothy B. Smith, lead author of the study. "Relationships influence our behavior and our physical health. We now know that it is possible to prolong ...
Grape genetics research reveals what makes the perfect flower
2021-05-18
ITHACA, N.Y. - Wines and table grapes exist thanks to a genetic exchange so rare that it's only happened twice in nature in the last 6 million years. And since the domestication of the grapevine 8,000 years ago, breeding has continued to be a gamble.
When today's growers cultivate new varieties - trying to produce better-tasting and more disease-resistant grapes - it takes two to four years for breeders to learn whether they have the genetic ingredients for the perfect flower.
Females set fruit, but produce sterile pollen. Males have stamens for pollen, but lack fruit. The perfect flower, however, carries both sex genes and can self-pollinate. These hermaphroditic varieties generally yield bigger and better-tasting berry ...
Rising energy demand for cooling
2021-05-18
Due to climate change, the average global temperature will rise in the coming decades. This should also significantly increase the number of so-called cooling degree days. These measure the number of hours, in which the ambient temperature is above a certain threshold, at which a building must be cooled to keep the indoor temperature at a comfortable level. The rising values may lead to an increased installation of AC systems in households. This could lead to a higher energy demand for cooling buildings, which is already expected to increase due to climate change and population growth.
Nip-and-tuck ...
Did Earth's early rise in oxygen help multicellular life evolve?
2021-05-18
Scientists have long thought that there was a direct connection between the rise in atmospheric oxygen, which started with the Great Oxygenation Event 2.5 billion years ago, and the rise of large, complex multicellular organisms.
That theory, the "Oxygen Control Hypothesis," suggests that the size of these early multicellular organisms was limited by the depth to which oxygen could diffuse into their bodies. The hypothesis makes a simple prediction that has been highly influential within both evolutionary biology and geosciences: Greater atmospheric oxygen should always increase the size to which multicellular organisms can grow. ...
A new theory for what's happening in the brain when something looks familiar
2021-05-18
When a person views a familiar image, even having seen it just once before for a few seconds, something unique happens in the human brain.
Until recently, neuroscientists believed that vigorous activity in a visual part of the brain called the inferotemporal (IT) cortex meant the person was looking at something novel, like the face of a stranger or a never-before-seen painting. Less IT cortex activity, on the other hand, indicated familiarity.
But something about that theory, called repetition suppression, didn't hold up for University of Pennsylvania neuroscientist Nicole Rust. "Different images produce different amounts of activation even when they are all novel," says ...
A gentler strategy for avoiding childhood dental decay
2021-05-18
The combination of a carb-heavy diet and poor oral hygiene can leave children with early childhood caries (ECC), a severe form of dental decay that can have a lasting impact on their oral and overall health.
A few years ago, scientists from Penn's School of Dental Medicine found that the dental plaque that gives rise to ECC is composed of both a bacterial species, Streptococcus mutans, and a fungus, Candida albicans. The two form a sticky symbiosis, known scientifically as a biofilm, that becomes extremely virulent and difficult to displace from the tooth surface.
Now, a new study from the group offers a strategy for disrupting this biofilm by targeting the yeast-bacterial interactions ...
WVU researchers find disparities for COVID-19 testing and positivity rates
2021-05-18
In studying COVID-19 testing and positivity rates in West Virginia between March and September 2020, West Virginia University researchers found disparities among Black residents and residents experiencing food insecurity.
Specifically, the researchers found communities with a higher Black population had testing rates six times lower than the state average, which they argue could potentially obscure prevalence estimates. They also found that areas associated with food insecurity had higher levels of testing and a higher rate of positivity.
"This could mean that public health officials are targeting predominately rural areas to keep tabs on how the pandemic will unfold in isolated communities within higher food insecurity," said Brian Hendricks, a research assistant professor with ...
Ancient Australian Aboriginal memory tool superior to 'memory palace' learning
2021-05-18
Australian scientists have compared an ancient Greek technique of memorising data to an even older technique from Aboriginal culture, using students in a rural medical school.
The study found that students using a technique called memory palace in which students memorised facts by placinthem into a memory blueprint of the childhood home, allowing them to revisit certain rooms to recapture that data. Another group of students were taught a technique developed by Australian Aboriginal people over more than 50,000 years of living in a custodial relationship with the Australian land.
The ...
Bone marrow disorder nearly 10-times more common in those with venom allergy
2021-05-18
Researchers at Michigan Medicine found that people with venom allergies are much more likely to suffer mastocytosis, a bone marrow disorder that causes higher risk of fatal reactions.
The team of allergists examined approximately 27 million United States patients through an insurance database - easily becoming the nation's largest study of allergies to bee and wasp stings, or hymenoptera venom. The results, published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, revealed mastocytosis in fewer than 0.1% of venom allergy patients - still near 10 times higher than those without allergies.
"Even though there is mounting interest, mast cell diseases are quite understudied; ...
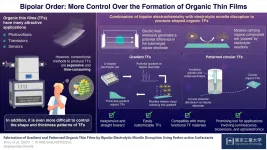
Bipolar order: A straightforward technique to have more control over organic thin films
2021-05-18
Modern and emerging applications in various fields have found creative uses for organic thin films (TFs); some prominent examples include sensors, photovoltaic systems, transistors, and optoelectronics. However, the methods currently available for producing TFs, such as chemical vapor deposition, are expensive and time-consuming, and often require highly controlled conditions. As one would expect, making TFs with specific shapes or thickness distributions is even more challenging. Because unlocking this customizability could spur advances in many sophisticated applications, researchers are actively exploring new approaches for ...
What happens in the brain when we imagine the future?
2021-05-18
In quiet moments, the brain likes to wander—to the events of tomorrow, an unpaid bill, an upcoming vacation.
Despite little external stimulation in these instances, a part of the brain called the default mode network (DMN) is hard at work. "These regions seem to be active when people aren't asked to do anything in particular, as opposed to being asked to do something cognitively," says Penn neuroscientist Joseph Kable.
Though the field has long suspected that this neural network plays a role in imagining the future, precisely how it works hadn't been fully understood. Now, research from Kable and two former graduate students in his lab, Trishala Parthasarathi, associate director of scientific services at OrtleyBio, and Sangil Lee, a postdoc at University of California, ...
San Diego Zoo Wildlife Alliance study finds topography is key factor in where Andean bears mothers make their dens
2021-05-18
SAN DIEGO (May TK, 2021) - Compared to most other bear species, very little is known about how female Andean bears choose where they give birth to cubs. As a critical component of the reproductive cycle, birthing dens are essential to the survival of South America's only bear species, listed as Vulnerable on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species.
A new study led by Russ Van Horn, Ph.D., published April in the journal Ursus, takes the most detailed look yet at the dens of this species. Van Horn, a population sustainability scientist, leads San Diego Zoo Wildlife Alliance's Andean bear conservation program. He was joined by colleagues from the University of British Columbia's Department of Forest ...
Study shows racial differences in personal care product use, may lead to health inequities
2021-05-18
A large survey of women in California shows significant racial and ethnic differences in the types of personal care products women use on a daily basis. Because many personal care products contain endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) like parabens and phthalates that interfere with the body's hormones, the findings could shed light on how different products influence women's exposures to harmful chemicals that contribute to health inequities.
The study appears in the Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology as part of a special issue focused on health equity. ...
New model for infectious disease could better predict future pandemics
2021-05-18
In the midst of a devastating global pandemic of wildlife origin and with future spillovers imminent as humans continue to come into closer contact with wildlife, infectious-disease models that consider the full ecological and anthropological contexts of disease transmission are critical to the health of all life. Existing models are limited in their ability to predict disease emergence, since they rarely consider the dynamics of the hosts and ecosystems from which pandemics emerge.
Published May 17 in Nature Ecology and Evolution, Smithsonian scientists and partners provide a framework for a new approach to modeling infectious diseases. It adapts established methods developed to study the planet's natural systems, including ...
Salk scientists reveal role of genetic switch in pigmentation and melanoma
2021-05-18
LA JOLLA--(MAY 18, 2021) Despite only accounting for about 1 percent of skin cancers, melanoma causes the majority of skin cancer-related deaths. While treatments for this serious disease do exist, these drugs can vary in effectiveness depending on the individual.
A Salk study published on May 18, 2021, in the journal Cell Reports reveals new insights about a protein called CRTC3, a genetic switch that could potentially be targeted to develop new treatments for melanoma by keeping the switch turned off.
"We've been able to correlate the activity of this genetic switch to melanin production and cancer," says Salk study ...
Study finds potential causality between blood clot factors and migraine with aura
2021-05-18
Nearly 15 percent of the U.S. population experiences migraine. One subtype of migraine that is not well understood is migraine with aura (MA). Individuals who experience MA often see flashing lights, blind spots, or jagged lines in their visual field prior to onset of their migraine headaches. Individuals who experience MA also face a heightened risk of stroke and cardiovascular disease, although scientists continue to explore why this correlation exists. In a new study from Brigham and Women's Hospital, researchers used a technique in genetic analysis termed Mendelian randomization to examine 12 coagulation measures, uncovering four that are associated ...
Novel simulation method predicts blood flow conditions behind von Willebrand disease
2021-05-18
For the first time, researchers can quantitatively predict blood flow conditions that likely cause pathological behavior of the human blood protein von Willebrand factor (vWF). Predictions from this new method of simulation, developed at Lehigh University, can be used to optimize the design of the mechanical pumps known as left ventricular assist devices used in heart failure patients. The method also has the potential to improve diagnosis and treatment of von Willebrand disease, the most common inherited bleeding disorder in the U.S., according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The article, "Predicting pathological von Willebrand factor unraveling in elongational flow," appears ...
Ancient horse DNA reveals gene flow between Eurasian and North American horses
2021-05-18
A new study of ancient DNA from horse fossils found in North America and Eurasia shows that horse populations on the two continents remained connected through the Bering Land Bridge, moving back and forth and interbreeding multiple times over hundreds of thousands of years.
The new findings demonstrate the genetic continuity between the horses that died out in North America at the end of the last ice age and the horses that were eventually domesticated in Eurasia and later reintroduced to North America by Europeans. The study has been accepted for publication in the journal Molecular Ecology and is currently available ...
Scientists discover five new species of listeria, improving food safety
2021-05-18
ITHACA, N.Y. - While examining the prevalence of listeria in agricultural soil throughout the U.S., Cornell University food scientists have stumbled upon five previously unknown and novel relatives of the bacteria.
The discovery, researchers said, will help food facilities identify potential growth niches that until now, may have been overlooked - thus improving food safety.
"This research increases the set of listeria species monitored in food production environments," said lead author Catharine R. Carlin, a doctoral student in food science. "Expanding the knowledge base to understand the diversity of listeria will save the commercial food world confusion and errors, as well as prevent ...
Embryo cryopreservation minimizes cryoinjuries, offers hope for would-be parents
2021-05-18
WASHINGTON, May 18, 2021 -- What are the most delicate and valuable things you have handled? How would you feel if your daily job involved handling human eggs and any mistakes would affect someone's life?
Typical egg collection requires a healthy woman to go through weeks of hormone therapy and then undergo an operation to retrieve eggs. These hard-earned and precious eggs are fertilized in vitro, and the best embryos are selected for future transfer.
But not all transfers succeed, which gives rise to the practice of freezing the extra embryos from an IVF cycle for future ...
[1] ... [2304]
[2305]
[2306]
[2307]
[2308]
[2309]
[2310]
[2311]
2312
[2313]
[2314]
[2315]
[2316]
[2317]
[2318]
[2319]
[2320]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.