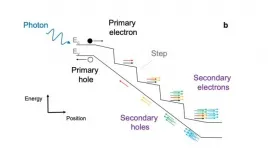
Gender-affirming hormone therapy may not increase CVD risk for transgender adolescents
2021-05-20
DALLAS, May 20, 2021 — Transgender adolescents are more likely to have at least one cardiovascular disease risk factor compared to cisgender (same gender as at birth) adolescents, according to preliminary research to be presented at the American Heart Association’s Epidemiology, Prevention, Lifestyle & Cardiometabolic Health Conference 2021. The meeting is virtual, May 20-21 and offers the latest science on population-based health and wellness and implications for lifestyle.
The United States has a growing population of transgender adolescents ages 12-21 who seek medical transition gender-affirming hormone therapy. Gender-affirming hormone therapy involves taking estrogen or testosterone ...
Moderate-to-high TV viewing in midlife linked to later cognitive and brain health decline
2021-05-20
DALLAS, May 20, 2021 — Spending moderate to high amounts of time watching television throughout midlife was linked to greater cognitive decline and lower gray matter volumes in the brain later in life, according to preliminary research from three studies (P149, MP24 and MP67) to be presented at the American Heart Association’s Epidemiology, Prevention, Lifestyle & Cardiometabolic Health Conference 2021 (EPI). The meeting is virtual, May 20-21, and offers the latest science on population-based health and wellness and implications for lifestyle.
“While studies have shown the benefits of exercise to support brain health, less is known about the potential consequences of prolonged sedentary behavior such as television viewing ...
2016 US presidential election skewed BP, heart rhythms in those with existing conditions
2021-05-20
DALLAS, May 20, 2021 -- Notable for high levels of stress and anger, the 2016 U.S. presidential campaign and election may have increased the risk of potentially life-threatening heart rhythms and worsened high blood pressure in people with underlying cardiovascular disease who already had a history of these conditions, according to a new study published today in the Journal of the American Heart Association and in a separate preliminary study to be presented at the American Heart Association's Epidemiology, Prevention, Lifestyle & Cardiometabolic Health Conference 2021. The meeting is virtual, May 20-21, and offers the latest science on population-based health and wellness and implications ...
Palaeontology: Ancient turtle from Texas yields evolutionary insights
2021-05-20
The discovery of the oldest known North American species of side-necked turtle -- turtles that withdraw their necks sideways into their shells when threatened -- is reported in Scientific Reports this week. The findings suggest that side-necked turtles may have migrated to North America during the Cenomanian age (100 to 94 million years ago).
Brent Adrian and colleagues have named the species Pleurochayah appalachius from the Greek word Pleuro (side), the Caddo word Cha'yah (turtle) and the North American Appalachian region. The fossilised remains of P. appalachius, which were discovered at the Arlington Archosaur Site of the Woodbine Group in Texas, USA, date back to the lower middle Cenomanian. They predate remains of Paiutemys tibert, a side-necked turtle species from Utah that ...
Overcoming long-term trauma can be facilitated
2021-05-20
How the brain deals with trauma is complex, and it's intuitive to say that we, as humans, get over trauma differently depending on if it happened a long time ago or if it was recent. But what scientific evidence do we have about the way the brain deals with short-term versus long-term traumatic memories?
EPFL scientists have identified the specific regions in the brains of mice responsible for reprograming traumatic experiences towards safety, and the brain regions are indeed different and depend on whether the trauma happened recently or a long time ago. They found that they could facilitate the extinction of long-lasting traumatic memories by enhancing the activity of a primitive region of the brain called the nucleus reuniens. The results are published today in Nature ...
A brand new cocktail to fight HIV
2021-05-20
Montréal, May 20, 2021--Researchers at the University of Montreal Hospital Research Centre (CRCHUM) and Yale University have succeeded in reducing the size of the HIV reservoir in humanized mice by using a "molecular can opener" and a combination of antibodies found in the blood of infected individuals.
In their study published in Cell Host & Microbe, the team of scientists, in collaboration with their colleagues at the University of Pennsylvania and Harvard Medical School, show that they were also able to significantly delay the return of the virus after stopping antiretroviral therapy in this animal model.
Humanized mice are generated from immunodeficient mice that don't have their own ...
Ultra-sensitive light detector gives self-driving tech a jolt
2021-05-20
Realizing the potential of self-driving cars hinges on technology that can quickly sense and react to obstacles and other vehicles in real time. Engineers from The University of Texas at Austin and the University of Virginia created a new first-of-its-kind light detecting device that can more accurately amplify weak signals bouncing off of faraway objects than current technology allows, giving autonomous vehicles a fuller picture of what's happening on the road.
The new device is more sensitive than other light detectors in that it also eliminates inconsistency, or noise, associated with the detection process. Such noise can cause systems to miss signals and put autonomous vehicle passengers at risk.
"Autonomous ...
Radar tracking uncovers mystery of where honeybee drones have sex
2021-05-20
Scientists from Queen Mary University of London and Rothamsted Research have used radar technology to track male honeybees, called drones, and reveal the secrets of their mating behaviours.
The study suggests that male bees swarm together in specific aerial locations to find and attempt to mate with queens. The researchers found that drones also move between different congregation areas during a single flight.
Drones have one main purpose in life, to mate with queens in mid-air. Beekeepers and some scientists have long believed that drones gather in huge numbers of up to 10,000 in locations known as 'drone congregation areas'. Previous research has used pheromone lures to attract drones, raising concerns ...
Preliminary analysis of association between COVID-19 vaccination, sudden hearing loss
2021-05-20
What The Study Did: These preliminary findings using U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System data in the early phase of societal COVID-19 vaccination using two messenger RNA vaccines suggest that no association exists between inoculation with a SARS-CoV-2 messenger RNA vaccine and incident sudden hearing loss.
Authors: Eric J. Formeister, M.D., M.S., of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2021.0869)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, ...
Timing of exposure to secondhand smoke, ADHD symptoms in children
2021-05-20
What The Study Did: Researchers assessed associations between prenatal, early postnatal or current exposure to secondhand smoke and symptoms of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) among school-age children in China.
Authors: Li-Wen Hu, M.D., Ph.D., and Guang-Hui Dong, M.D., Ph.D., of Sun Yat-sen University in Guangzhou, China, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10931)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
Colorectal cancer screening past age 75 lowers cancer death risk for most
2021-05-20
BOSTON - Screening for colorectal cancer - the second most common cause of cancer-related death in the United States - can save lives by detecting both pre-cancerous lesions that can be removed during the screening procedure, and colorectal cancer in its early stages, when it is highly curable.
Screening is most commonly performed with endoscopy: visualization of the entire colon and rectum using a long flexible optical tube (colonoscopy), or of the lower part of the colon and rectum with a shorter flexible tube (sigmoidoscopy).
This week, the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) lowered the recommended beginning age for screening from 50 to 45 for persons without a family history of colorectal ...
New 96 million-year-old fossil represents oldest side-necked turtle in north america
2021-05-20
The discovery of a new species of ancient turtle is shedding light on hard-to-track reptile migrations about 100 million years ago. Pleurochayah appalachius, a bothremydid turtle adapted for coastal life, is described in a new paper published by a multi-institution research group in the journal Scientific Reports.
P. appalachius was discovered at the Arlington Archosaur Site (AAS) of Texas, which preserves the remnants of an ancient Late Cretaceous river delta that once existed in the Dallas-Fort Worth area and is also known for discoveries of fossil crocodyliformes and dinosaurs. P. appalachius belonged to an extinct lineage of pleurodiran (side-necked) ...
Solving a natural riddle of water filtration
2021-05-20
For many engineers and scientists, nature is the world's greatest muse. They seek to better understand natural processes that have evolved over millions of years, mimic them in ways that can benefit society and sometimes even improve on them.
An international, interdisciplinary team of researchers that includes engineers from The University of Austin has found a way to replicate a natural process that moves water between cells, with a goal of improving how we filter out salt and other elements and molecules to create clean water while consuming less energy.
In a new paper published today in Nature Nanotechnology, researchers created a molecule-sized water transport channel that can carry water between cells while excluding protons ...
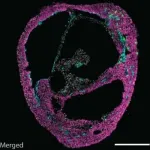
Cardioids -- heartbeat, heartbreak and recovery in a dish
2021-05-20
Self-organizing heart organoids developed at IMBA - Institute of Molecular Biotechnology of the Austrian Academy of Sciences - are also effective injury- and in vitro congenital disease models. These "cardioids" may revolutionize research into cardiovascular disorders and malformations of the heart. The results are published in the journal Cell.
About 18 million people die each year from cardiovascular diseases, making them the leading cause of fatalities globally. Moreover, the most prevalent birth defects in children pertain to the heart. Currently, a major bottleneck in understanding human heart malformations and developing regenerative therapies are missing human physiological models of the heart.
The research group of Sasha Mendjan established cardioids ...
New single-cell analysis tool links immune cells to kidney cancer recurrence
2021-05-20
NEW YORK, NY (May 20, 2021)--The immune nature of kidney cancer stands out when compared to other cancers: More immune cells infiltrate kidney cancers than most other solid tumors, and kidney cancer is one of the most responsive malignancies to today's immunotherapy regimens.
But despite treatment, many patients with clear cell renal carcinoma--the most common type of kidney cancer--eventually relapse and develop incurable metastatic disease.
A new study shows that the presence of a rare and previously unknown type of immune cell in kidney tumors can predict which patients are likely to have cancer recur after surgery. These cells could even ...
Condensing by turning toward the crowd
2021-05-20
We observe water vapor condensing into liquid droplets on a daily basis, be it as dew drops on leaves or as droplets on the lid of a cooking pot. Since the work of Dutch physicist J.D. van der Waals in the 19th century, condensation has been understood to result from attractive forces between the molecules of a fluid.
Now, an international team of researchers has discovered a new mechanism of condensation: Even if they don't attract each other, self-propelled particles can condense by turning toward dense regions, where they accumulate. The study was published in Nature Physics.
"It's like if cars steered toward crowded areas and made the crowd even bigger," explained Steve Granick, director of the IBS Center for Soft and Living ...
Molecule enlists patient's immune system to combat HIV
2021-05-20
Antiretroviral therapy, the common approach in the treatment of HIV, halts replication of the virus and has saved the lives of millions of people. However, for patients the drug cocktail becomes a lifetime necessity because they continue to harbor latent HIV in a small number of immune system cells. In the absence of treatment, HIV can again replicate and rebound into full blown AIDs.
A new study, however, suggests that addition of a single small molecule can rip away the cloak that shields those cells containing HIV and make them susceptible the patient's own antibodies that otherwise are not normally of much use against HIV.
For the study, a team of researchers ...
New AI-based tool can find rare cell populations in large single-cell datasets
2021-05-20
HOUSTON - Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have developed a first-of-its-kind artificial intelligence (AI)-based tool that can accurately identify rare groups of biologically important cells from single-cell datasets, which often contain gene or protein expression data from thousands of cells. The research was published today in Nature Computational Science.
This computational tool, called SCMER (Single-Cell Manifold presERving feature selection), can help researchers sort through the noise of complex datasets to study cells that would likely not be identifiable otherwise.
SCMER may be used broadly for many applications in oncology and beyond, explained senior author Ken Chen, Ph.D., associate professor of Bioinformatics ...
Nearly 3% of Americans take immune-weakening drugs that may limit COVID vaccine response
2021-05-20
A national study from researchers at Michigan Medicine found that nearly 3% of insured U.S. adults under 65 take medications that weaken their immune systems.
The findings, published in JAMA Network Open, are based on data from over 3 million patients with private insurance. They focus on patients' use of immunosuppressive drugs, including chemotherapy medications and steroids such as prednisone.
The analysis reveals nearly 90,000 people met the study criteria for drug-induced immunosuppression that may elevate risk for severe COVID-19 symptoms and hospitalization ...
These cognitive exercises help young children boost their math skills, study shows
2021-05-20
Young children who practice visual working memory and reasoning tasks improve their math skills more than children who focus on spatial rotation exercises, according to a large study by researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden. The findings support the notion that training spatial cognition can enhance academic performance and that when it comes to math, the type of training matters. The study is published in the journal Nature Human Behaviour.
"In this large, randomized study we found that when it comes to enhancing mathematical learning in young children, the type of cognitive training performed plays a significant role," says corresponding author Torkel Klingberg, professor in the Department of Neuroscience, Karolinska Institutet. "It is an important finding because it provides ...
Immune cells promote proinflammatory fatty liver disease
2021-05-20
A particular type of dendritic cell is responsible for the tissue damage that occurs in non-alcoholic steatohepatits (NASH) in mice and humans. The dendritic cells cause aggressive, proinflammatory behavior in T cells, as now discovered by researchers from the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) in collaboration with colleagues from Israeli research institutes. Blocking these dendritic cells alleviates symptoms in mice. This type of approach might also prevent the development of serious liver damage in NASH patients.
Obesity is extremely widespread in the Western world, and 90 percent of those affected show signs of fatty degeneration of the liver. If they maintain an unhealthy lifestyle ...
Solar geoengineering may be effective in alleviating impacts of global warming on crops
2021-05-20
Solar geoengineering -- putting aerosols into the atmosphere to reflect sunlight and reduce global warming -- is not a fix-all for climate change but it could be one of several tools to manage climate risks. A growing body of research has explored the ability of solar geoengineering to reduce physical climate changes. But much less is known about how solar geoengineering could affect the ecosystem and, particularly, agriculture.
Now, research from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) finds that solar geoengineering may be surprisingly effective in alleviating some of the worst impacts of ...
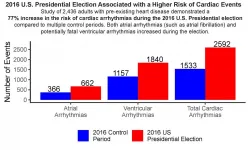
Stress from 2016 US presidential election associated with increase in cardiac events
2021-05-20
CHAPEL HILL, NC - American politics can be stressful and confrontational, which can lead to anger. The combination of intense stress and negative emotions can trigger potentially fatal cardiovascular events in people who are susceptible to these health issues. But the direct link between a stressful political election and an increase in cardiac events hadn't been established, until now. A new study in the Journal of the American Heart Association is the first to show that exposure to a stressful political election is strongly associated with an increase in potentially life-threatening cardiac events.
"This retrospective ...
Study finds evidence emotional support animals benefit those with chronic mental illness
2021-05-20
A team led by a social work researcher at The University of Toledo has published the first empirical evidence that emotional support animals can provide quantifiable benefits to individuals with serious mental illness who are experiencing depression, anxiety and loneliness.
The research brings credence to the many anecdotal reports of emotional support animals having positive impacts on chronic mental health issues.
"This is the first peer-reviewed, published scientific evidence that emotional support animals may benefit people's mental health," said Dr. Janet Hoy-Gerlach, a professor of social work and the lead investigator on the project. "My hope is that our pilot study catalyzes additional research in this area with more rigorous ...
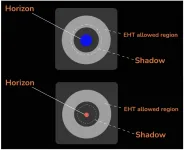
Not all theories can explain the black hole M87*
2021-05-20
FRANKFURT. As first pointed out by the German astronomer Karl Schwarzschild, black holes bend space-time to an extreme degree due to their extraordinary concentration of mass, and heat up the matter in their vicinity so that it begins to glow. New Zealand physicist Roy Kerr showed rotation can change the black hole's size and the geometry of its surroundings. The "edge" of a black hole is known as the event horizon, the boundary around the concentration of mass beyond which light and matter cannot escape and which makes the black hole "black". Black holes, theory predicts, can be described by a handful ...
[1] ... [2309]
[2310]
[2311]
[2312]
[2313]
[2314]
[2315]
[2316]
2317
[2318]
[2319]
[2320]
[2321]
[2322]
[2323]
[2324]
[2325]
... [8833]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.