Teachers' gender, sexuality, and age affect perceptions of sexual misconduct of students
2021-05-14
The United States has witnessed a steep rise in reports, arrests, and media coverage of teachers' sexual misconduct with students. A new study investigated the impact of perpetrators' gender, sexuality, and age on perceptions of teacher sexual misconduct. The study found that
responses to teachers' misconduct varied according to certain characteristics, which can influence whether victims report the misconduct.
The study, by researchers at Prairie View A&M University and the University of Nevada, Reno, appears in Feminist Criminology.
"Because sexual abuse of a child or adolescent in any context has substantial psychological, emotional, and physical consequences for the victim, teachers' sexual misconduct is a serious public health ...
You're so vein: Scientists discover faster way to manufacture vascular materials
2021-05-14
Developing self-healing materials is nothing new for Nancy Sottos, lead of the Autonomous Materials Systems Group at the END ...
U-M researchers trace path of light in photosynthesis
2021-05-14
Three billion years ago, light first zipped through chlorophyll within tiny reaction centers, the first step plants and photosynthetic bacteria take to convert light into food.
Heliobacteria, a type of bacteria that uses photosynthesis to generate energy, has reaction centers thought to be similar to those of the common ancestors for all photosynthetic organisms. Now, a University of Michigan team has determined the first steps in converting light into energy for this bacterium.
"Our study highlights the different ways in which nature has made use of the basic reaction ...
Most pediatric spinal fractures related to not wearing seatbelts
2021-05-14
May 14, 2021 - Two thirds of all pediatric spinal fractures, especially in the adolescent population, occur in motor vehicle accidents (MVAs) where seatbelts are not utilized, reports a study in Spine. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Over 60 percent of pediatric spinal fractures occur in children ages 15 to 17, coinciding with the beginning of legal driving," according to the new research by Dr. Vishal Sarwahi, MD, of Cohen Children's Medical Center, New Hyde Park, NY, and colleagues. They emphasize the need for measures to increase seatbelt usage, particularly by younger drivers, and outline the potential trauma that can be avoided through proper seatbelt use.
Seatbelts save lives... and ...
New benefit increases Veterans' access to urgent care in the community
2021-05-14
May 14, 2021 - Two years ago, the Veterans Affairs healthcare system (VA) began rolling out a new benefit, enabling Veterans to receive urgent care from a network of community providers - rather than visiting a VA emergency department or clinic. Progress toward expanding community care services for Veterans is the focus of a special supplement to the May issue of Medical Care. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
The urgent care benefit "provides a new way to deliver unscheduled, low-acuity acute care to Veterans," according to the ...
New pre-clinical model could hold the key to better HIV treatments
2021-05-14
A team led by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and Children's National Hospital has developed a unique pre-clinical model that enables the study of long-term HIV infection, and the testing of new therapies aimed at curing the disease.
Ordinary mice cannot be infected with HIV, so previous HIV mouse models have used mice that carry human stem cells or CD4 T cells, a type of immune cell that can be infected with HIV. But these models tend to have limited utility because the human cells soon perceive the tissues of their mouse hosts as "foreign," ...
Our dreams' weirdness might be why we have them, argues new AI-inspired theory of dreaming
2021-05-14
The question of why we dream is a divisive topic within the scientific community: it's hard to prove concretely why dreams occur and the neuroscience field is saturated with hypotheses. Inspired by techniques used to train deep neural networks, Erik Hoel (@erikphoel), a research assistant professor of neuroscience at Tufts University, argues for a new theory of dreams: the overfitted brain hypothesis. The hypothesis, described May 14 in a review in the journal Patterns, suggests that the strangeness of our dreams serves to help our brains better generalize our day-to-day experiences.
"There's obviously an incredible number of theories of why we dream," says Hoel. "But I wanted to bring to ...
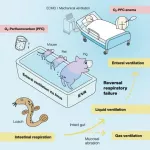
Mammals can use their intestines to breathe
2021-05-14
Rodents and pigs share with certain aquatic organisms the ability to use their intestines for respiration, finds a study publishing May 14th in the journal Med. The researchers demonstrated that the delivery of oxygen gas or oxygenated liquid through the rectum provided vital rescue to two mammalian models of respiratory failure.
"Artificial respiratory support plays a vital role in the clinical management of respiratory failure due to severe illnesses such as pneumonia or acute respiratory distress syndrome," says senior study author Takanori Takebe (@TakebeLab) of the Tokyo Medical and Dental University and the Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center. "Although the side effects and safety need to be thoroughly ...
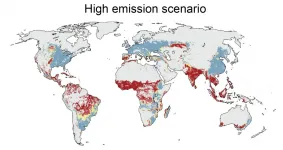
Climate change threatens one-third of global food production
2021-05-14
Climate change is known to negatively affect agriculture and livestock, but there has been little scientific knowledge on which regions of the planet would be touched or what the biggest risks may be. New research led by Aalto University assesses just how global food production will be affected if greenhouse gas emissions are left uncut. The study is published in the prestigious journal One Earth on Friday 14 May.
'Our research shows that rapid, out-of-control growth of greenhouse gas emissions may, by the end of the century, lead to more than a third of current global food production falling into conditions in which no food is produced today - that is, out of safe climatic space,' explains Matti Kummu, professor of global water and food issues at Aalto University.
According ...
Changes in filled opioid, naloxone prescriptions before, during COVID-19
2021-05-14
What The Study Did: Researchers analyzed changes in filled prescriptions for naloxone (medication to reverse opioid overdoses) during the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States and compared them with changes in opioid prescriptions and overall prescriptions.
Authors: Ashley L. O'Donoghue, Ph.D., of the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2021.0393)
Editor's Note: The ...
Transmission of COVID-19 in simulated nursing homes with frequent testing, immunity-based staffing
2021-05-14
What The Study Did: Associations of staffing and testing interventions with COVID-19 transmission in nursing homes are examined in this decision analytical modeling study.
Authors: Rebecca Kahn, Ph.D., of the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10071)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, ...
Crowdsourcing for university community engagement COVID-19 safety strategies
2021-05-14
What The Study Did: This is a qualitative study that evaluates a crowdsourcing open call to gather community input for engaging the university community in COVID-19 safety strategies.
Authors: Suzanne Day, Ph.D., of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10090)
Editor's Note: This article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media ...
Availability of US hospital price data
2021-05-14
What The Study Did: Researchers evaluated the compliance of hospitals with a Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services ruling mandating that a list of charges for services, procedures and items be publicly available and in a machine-readable file.
Authors: David Hsiehchen, M.D., of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10109)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, ...
Ventilating the rectum to support respiration
2021-05-14
Tokyo, Japan - Oxygen is crucial to many forms of life. Its delivery to the organs and tissues of the body through the process of respiration is vital for most biological processes. Now, researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have shown that oxygen can be delivered through the wall of the intestine to compensate for the reduced availability of oxygen within the body that occurs in lung diseases that cause respiratory failure.
To breathe is to live; for higher animals, respiration involves absorbing oxygen and excreting carbon dioxide at gills or in the lungs. However, some animals have evolved alternative ventilatory mechanisms: loaches, catfish, sea cucumbers and orb-weaving spiders can absorb oxygen through their hindgut to ...
Researchers suggest pathway for improving stability of next-generation solar cells
2021-05-14
Scientists have uncovered the exact mechanism that causes new solar cells to break down, and suggest a potential solution.
Solar cells harness energy from the Sun and provide an alternative to non-renewable energy sources like fossil fuels. However, they face challenges from costly manufacturing processes and poor efficiency - the amount of sunlight converted to useable energy.
Perovskites are materials developed for next-generation solar cells. Although perovskites are more flexible cheaper to make than traditional silicon-based solar panels and deliver similar efficiency, perovskites ...
Researchers pinpoint possible way to prevent permanent hearing loss caused by cancer drug
2021-05-14
University of Alberta scientists have identified a receptor in cells that could be key to preventing permanent hearing loss in childhood cancer survivors who are being treated with the drug cisplatin. The researchers believe by inhibiting the receptor, they may be able to eliminate toxic side-effects from the drug that cause the hearing loss.
Cisplatin is an incredibly effective chemotherapeutic when it comes to treating solid tumours in children, contributing to an 80 per cent overall survival rate over five years, according to U of A researcher Amit Bhavsar, an assistant professor in the Department of Medical Microbiology & Immunology. The problem ...
Access to overdose-reversing drugs declined during pandemic, researchers find
2021-05-14
Boston - While overall emergency department visits have decreased during the pandemic, nonfatal opioid overdose visits have more than doubled. However, few patients who overdosed on opioids had received a prescription for naloxone, a medication designed to block the effects of opioids on the brain and rapidly reverse opioid overdose.
In a new study, clinician-researchers at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) analyzed naloxone prescription trends during the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States and compared them to trends in opioid prescriptions and to overall prescriptions. The team's findings, published in the journal JAMA Health Forum, suggest patents with opioid misuse disorders may be experiencing a dangerous decrease in access to the overdose-reversing ...
New research optimizes body's own immune system to fight cancer
2021-05-14
A groundbreaking study led by engineering and medical researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how engineered immune cells used in new cancer therapies can overcome physical barriers to allow a patient's own immune system to fight tumors. The research could improve cancer therapies in the future for millions of people worldwide.
The research is published in Nature Communications, a peer-reviewed, open access, scientific journal published by Nature Research.
Instead of using chemicals or radiation, immunotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that helps the patient's immune system fight cancer. T cells are a type of white ...
Sensors developed at URI can identify threats at the molecular level
2021-05-14
KINGSTON, R.I. - May 14, 2021 - We are frequently reminded of how vulnerable our health and safety are to threats from nature or those who wish to harm us.
New sensors developed by Professor Otto Gregory, of the College of Engineering at the University of Rhode Island, and chemical engineering doctoral student Peter Ricci, are so powerful that they can detect threats at the molecular level, whether it's explosive materials, particles from a potentially deadly virus or illegal drugs entering the country.
"This is potentially life-saving technology," said Gregory. "We have detected ...
Artificial intelligence identifies the tiger mosquito from photos in the Mosquito Alert
2021-05-14
Researchers from Mosquito Alert (who belong to CEAB-CSIC, CREAF and UPF) together with researchers from the University of Budapest have shown that an artificial intelligence algorithm is capable of recognizing the tiger mosquito (Aedes albopictus) in the photos sent by Mosquito Alert users.
The results of the study published in Scientific Reports have been obtained by applying deep learning technology or deep learning, an aspect of artificial intelligence that seeks to emulate the way of learning of humans and that has previously been used in the health field to interpret ...
Few realistic scenarios left to limit global warming to 1.5°C
2021-05-14
Of the over 400 climate scenarios assessed in the 1.5°C report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), only around 50 scenarios avoid significantly overshooting 1.5°C. Of those only around 20 make realistic assumptions on mitigation options, for instance the rate and scale of carbon removal from the atmosphere or extent of tree planting, a new study shows. All 20 scenarios need to pull at least one mitigation lever at "challenging" rather than "reasonable" levels, according to the analysis. Hence the world faces a high degree of risk of overstepping the 1.5°C limit. The realistic window for meeting the 1.5°C target is very rapidly closing.
If all climate mitigation levers are pulled, it may still be possible ...
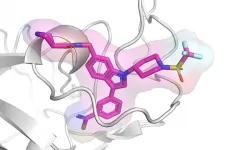
Researchers develop first-in-class inhibitors against key leukemia protein
2021-05-14
The protein made by the ASH1L gene plays a key role in the development of acute leukemia, along with other diseases. The ASH1L protein, however, has been challenging to target therapeutically.
Now a team of researchers led by Jolanta Grembecka, Ph.D., and Tomasz Cierpicki, Ph.D., from the University of Michigan has developed first-in-class small molecules to inhibit ASH1L's SET domain -- preventing critical molecular interactions in the development and progression of leukemia.
The team's findings, which used fragment-based screening, followed by medicinal chemistry and a structure-based design, appear in Nature Communications.
In mouse models of mixed lineage leukemia, the lead compound, known as AS-99, successfully reduced leukemia progression.
"This ...
Emergence of a new heteronanostructure library
2021-05-14
Organizing functional objects in a complex, sophisticated architecture at the nanoscale can yield hybrid materials that tremendously outperform their solo objects, offering exciting routes towards a spectrum of applications. The development in synthetic chemistry over past decades has enabled a library of hybrid nanostructures, such as core-shell, patchy, dimer, and hierarchical/branched ones.
Nevertheless, the material combinations of these non-van der Waals solids are largely limited by the rule of lattice-matched epitaxy.
A research team led by professor YU Shuhong at the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) has reported a new class of heteronanostructures they ...
The mechanism of action of genes with high mutation frequency in cancer
2021-05-14
After the p53 tumour suppressor gene, the genes most frequently found mutated in cancer are those encoding two proteins of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodelling complex. This complex's function is to "accommodate" the histones that cover the DNA of the chromosomes so that the processes of transcription, DNA repair and replication or chromosome segregation can occur, as appropriate. A group from the University of Seville has demonstrated at CABIMER that the inactivation of BRG1, the factor responsible for the enzymatic activity of the SWI/SNF complexes, leads to high genetic instability, a characteristic common to the vast majority of tumours.
This study's most important contribution is that it deciphers the mechanism by which this occurs. The SWI/SNF complex ...
Yoga and breathing exercises aid children with ADHD to focus
2021-05-14
Yoga and breathing exercises have a positive effect on children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). After special classes, children improve their attention, decrease hyperactivity, they do not get tired longer, they can engage in complex activities longer. This is the conclusion reached by psychologists at Ural Federal University who studied the effect of exercise on functions associated with voluntary regulation and control in 16 children with ADHD aged six to seven years. The results of the study are published in the journal Biological Psychiatry.
"For children with ADHD, as a rule, the part of the brain that is responsible ...
[1] ... [2310]
[2311]
[2312]
[2313]
[2314]
[2315]
[2316]
[2317]
2318
[2319]
[2320]
[2321]
[2322]
[2323]
[2324]
[2325]
[2326]
... [8812]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.