Study: Obesity slows progress against cancer deaths
2021-05-13
Cancer death rates have fallen dramatically in the United States, but factor in obesity, as researchers did at the University of North Carolina Gillings School of Global Public Health, and the picture changes.
In a study published May 10 in JAMA Network Open, researchers showed that obesity-related cancer deaths are improving, but at a slowing pace.
Based on mortality data for 50 million people, deaths from cancers not associated with obesity -- that's lung cancer and skin cancer, among others - are declining at a rate almost three times faster than cancers linked to obesity, such as stomach, colorectal, uterine, thyroid and postmenopausal breast cancer.
"These are cancers where we could see even larger mortality improvements with creative and practical tools to combat ...
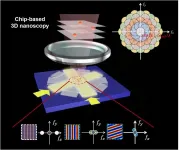
Can the diffraction limit overcome in the linear imaging system?
2021-05-13
Compared with the superresolution microscopy that bases on squeezing the point spread function in the spatial domain, the superresolution microscopy that broadens the detection range in the spatial frequency domain through the spatial-frequency-shift (SFS) effect shows intriguing advantages including large field of view, high speed, and good modularity, owing to its wide-field picture acquisition process and universal implementation without using special fluorophores labeling.
To enable spatial-frequency-shift microscopy with a superresolution at the subwavelength scale, it is essential to use the near-field evanescent wave with a larger wave vector than the far-field propagation wave for illumination, which can be built on the integrated photonics, paving the way for compact ...
A new polarized fluorescent probe for revealing architectural dynamics of living cells
2021-05-13
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU), collaborating with scientists from the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) and RIKEN, develop a novel technique for live-cell fluorescent imaging which leads them to discover a new actin structure in starfish early embryos.
Tokyo, Japan - Monitoring alignments of the building blocks of cells is important to understand how the cells are built. By collaborating with imaging scientists at the MBL, researchers from Japan have developed a new probe which they call POLArIS, allowing real-time imaging of molecular orientations in live cells.
A fluorophore emits polarized light as it glows. The orientation of polarized fluorescence ...
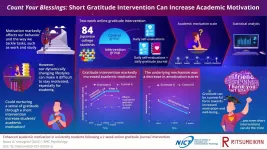
Count your blessings: Short gratitude intervention can increase academic motivation
2021-05-13
It is difficult for us to succeed in whatever we set out to do if we lack motivation. We usually need it as a driving force to achieve both short- and long-term goals, from household chores to getting a degree. However, because of the ongoing pandemic, our lifestyles have been subjected to drastic and dynamic changes, and many work- and study-related activities are now carried out online exclusively. This, among other complex factors, have made it difficult for some people to stay focused and motivated, and psychology researchers are trying to find effective and widely applicable solutions to address such problems.
In a END ...
Dental procedures during pandemic are no riskier than a drink of water
2021-05-13
COLUMBUS, Ohio - A new study's findings dispel the misconception that patients and providers are at high risk of catching COVID-19 at the dentist's office.
SARS-CoV-2 spreads mainly through respiratory droplets, and dental procedures are known to produce an abundance of aerosols - leading to fears that flying saliva during a cleaning or a restorative procedure could make the dentist's chair a high-transmission location.
Ohio State University researchers set out to determine whether saliva is the main source of the spray, collecting samples from personnel, equipment and other surfaces reached by aerosols during a range ...
Health effects of prenatal exposure to 1994 genocide against the Tutsi in Rwanda
2021-05-13
Twenty-seven years ago, more than 1 million Rwandans were killed during the genocide against the Tutsi in Rwanda from April 7 to July 4, 1994. It is estimated that 100,000 to 250,000 women were raped during the 100-day genocide, and that 10,000 children were born as a result. A new study finds that Rwandans who were conceived by mothers who survived the 1994 genocide against the Tutsi have poorer adult health outcomes than those who were conceived by Rwandan mothers living outside the country at that time. In addition, those who were conceived through genocidal rape have poorer adult health ...
Obesity during adolescence linked to increased risk of stroke as an adult
2021-05-13
DALLAS, May 13, 2021 -- Higher body mass index (BMI) in adolescence is associated with a significantly higher risk of first ischemic stroke in adults under age 50 regardless of whether they had Type 2 diabetes, according to new research published today in Stroke, a journal of the American Stroke Association, a division of the American Heart Association.
While rates of adolescent obesity and stroke among adults under the age of 50 years continue to rise around the world, the precise link between the two conditions is still not fully understood.
"Adults who survive stroke earlier in life face poor functional outcomes, which can lead to unemployment, depression and anxiety," said study co-author Gilad Twig, M.D., M.P.H., Ph.D., an ...
Largest-ever study of artificial insemination in sharks--and the occasional 'virgin birth'
2021-05-13
It's a tough time to be a shark. Pollution, industrialized fishing, and climate change threaten marine life, and the populations of many top ocean predators have declined in recent years. In addition to studying sharks in the wild, scientists working to save sharks rely on ones living in zoos and aquariums so that they can help build breeding programs and learn more about the conditions sharks need to thrive. One important way the scientists do that is by playing matchmakers to the sharks, pairing up individuals in ways that increase genetic diversity. In a new study in Scientific Reports, scientists undertook the largest-ever effort to artificially inseminate sharks.Their work resulted in 97 new baby sharks, ...
Orangutan finding highlights need to protect habitat
2021-05-13
Wild orangutans are known for their ability to survive food shortages, but scientists have made a surprising finding that highlights the need to protect the habitat of these critically endangered primates, which face rapid habitat destruction and threats linked to climate change.
Scientists found that the muscle mass of orangutans on the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia was significantly lower when less fruit was available. That's remarkable because orangutans are thought to be especially good at storing and using fat for energy, according a Rutgers-led study in the journal Scientific Reports.
The findings highlight ...
Life may have become cellular by using unusual molecules
2021-05-13
All modern life is composed of cells, from single-celled bacteria to more complex organisms such as humans, which may contain billions or even trillions of cells, but how life came to be cellular remains uncertain. New research led by specially appointed assistant professor Tony Z. Jia at the Earth-Life Science Institute (ELSI) at Tokyo Institute of Technology, along with colleagues from around the world (Japan, Malaysia, France, Czech Republic, India and the USA), shows that simple chemical compounds known as hydroxy acids, which were likely common on primitive Earth, spontaneously link together ...
Scientists find molecular patterns that may help identify extraterrestrial life
2021-05-13
Scientists have begun the search for extraterrestrial life in the Solar System in earnest, but such life may be subtly or profoundly different from Earth-life, and methods based on detecting particular molecules as biosignatures may not apply to life with a different evolutionary history. A new study by a joint Japan/US-based team, led by researchers at the Earth-Life Science Institute (ELSI) at the Tokyo Institute of Technology, has developed a machine learning technique which assesses complex organic mixtures using mass spectrometry to reliably classify them as biological or abiological.
In season 1, episode 29 ("Operation: Annihilate!") of Star Trek, which aired in 1966, the human-Vulcan hybrid character ...
Congestion pricing could shrink car size
2021-05-13
PULLMAN, Wash. - Rush hour will likely return when pandemic lockdowns lift, but a new study suggests that congestion pricing--policies that charge tolls for driving during peak hours--could not only cure traffic jams but also convince motorists it is safe to buy smaller, more efficient cars.
Researchers from Washington State University and the Brookings Institution studied a sample of nearly 300 households in the Seattle area over a six-year period, finding that the more congested their commutes, the more likely they would buy bigger cars which they perceive as safer and more ...
Study finds that obesity drug semaglutide supresses appetite, food cravings and energy intake
2021-05-13
New research presented at this year's European Congress on Obesity (held online, 10-13 May) shows that the obesity drug semaglutide reduces appetite, food cravings and energy intake in people given a meal where they could eat as much as they liked. The study is by Dr Dorthe Skovgaard, Novo Nordisk A/S (the manufacturer of the drug), Søborg, Denmark, and colleagues.
Semaglutide, in the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogue drug class, is currently available at the dose of 1.0 mg injected once weekly for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and is under development for chronic weight management at the dose ...
New experimental drug cagrilintide (AM833), when combined with emaglutide, shows potential for treatment of obesity (The Lancet)
2021-05-13
An early study of a new experimental drug to treat obesity known as cagrilintide shows that, when combined with semaglutide 2.4 mg, the combination leads to more weight loss than semaglutide 2.4 mg alone and is well tolerated. This phase 1 study, which was recently published in The Lancet will be presented at this year's European Congress on Obesity (held online, 10-13 May) by Dr Lone Enebo, Novo Nordisk A/S, Denmark, on behalf of her colleagues. Novo Nordisk A/S is the manufacturer of both drugs in this study.
Combining medications with different modes of action may provide more effective treatment options for people with obesity. Weekly injections of cagrilintide, ...
Two-thirds of California prison residents offered COVID vaccine accepted at least one dose
2021-05-13
Two-thirds of California prisoners who were offered a COVID-19 vaccine accepted at least one dose, according to a new study by researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine.
"We found that many incarcerated people in California prisons were willing to be vaccinated for COVID-19," said Elizabeth Chin, the lead author of the study and a PhD candidate in biomedical data science. "This is an encouraging sign for other states at an early stage of rolling out vaccination programs in their prisons and jails."
The researchers also found that nearly half of those who initially turned down a COVID-19 vaccine accepted it when it was offered to them again. The finding is an important indication that vaccine hesitancy is not necessarily fixed.
Two-thirds ...
Previously unknown letter reveals Einstein's thinking on bees, birds and physics
2021-05-13
The 1949 letter by the physicist and Nobel laureate discusses bees, birds and whether new physics principles could come from studying animal senses.
It's a position still being realised within physics to this day, with a growing body of research and understanding of how animals such as birds and bees find their way around.
Now a study led by RMIT University in Melbourne, Australia, discusses how recent discoveries in migratory birds back up Einstein's thinking 72 years ago.
The previously unpublished letter was shared with researchers by Judith Davys - Einstein had addressed ...
COVID-19 is not influenza, but it offers lessons on beating it, say Concordia researchers
2021-05-12
If you did not catch the flu this year -- and there is an overwhelming chance that you did not -- you have COVID-19 to thank.
It's a small consolation, given the enormously disruptive scope of the pandemic. But it's the focus of a new paper published in the journal Frontiers in Public Health by two Concordia researchers and their colleagues that studies the 2020 influenza figures from Canada, the United States, Australia and Brazil. The authors show there is a clear relationship between the implementation of COVID-mitigation measures such as hand-washing, masking and social distancing and the spread of the annual flu.
They write that these preventive measures all but eliminated ...
Breakthrough could lead to early detection of pregnancy complications
2021-05-12
The quest to create safer, more successful pregnancies is one of the top goals of modern science. While pregnancy is better understood today than ever before, with improvements in technology helping to lower the risk of negative outcomes, there is much researchers still don't know about a vital part of the pregnancy process: uterine fluid.
Secreted by glands in the uterus during pregnancy, uterine fluid is believed to play an important role in supporting a developing embryo by sending information from the uterus to the embryo, along with a host ...
Backyard chickens, rabbits, soybeans can meet household protein demand
2021-05-12
In 2020, stores sold out of garden seed, coops and rabbit cages. Now, we have an idea how much protein people can grow in their backyards.
The 2020 meat shortages led many to wonder what to eat for protein when supply chains are disrupted. Some people turned to gathering eggs, raising animals and growing their own food. A team from Michigan Technological University and the University of Alaska Fairbanks found that the work is well worth it. In a new study published in Sustainability, the researchers looked at how a typical household with a typical backyard can raise chickens, rabbits or soybeans to meet its protein needs.
People eat a lot of protein in the U.S. and the average person needs 51 grams of ...
University of Minnesota Medical School researchers identify target for senolytic drugs
2021-05-12
MINNEAPOLIS/ST.PAUL (05/12/2021) -- In a study recently published in END ...
UNH research estimates 1.4 million children have yearly violence-related medical visits
2021-05-12
DURHAM, N.H.-- A national report from the University of New Hampshire shows close to one and a half million children each year visit a doctor, emergency room or medical facility as a result of an assault, abuse, crime or other form of violence. This is four times higher than previous estimates based only on data from U.S. emergency rooms for violence-related treatment.
In their END ...
A PROMPT, low-cost platform speeds up gonorrhea testing and spots antibiotic resistance
2021-05-12
A portable, rapid testing platform can detect gonorrhea infections in patient samples in under 15 minutes, far faster than standard-of-care tests that can take hours or days. The platform accurately detected infections and determined resistance to a common antibiotic in 217 patient samples from sexual health clinics in Baltimore and Uganda. The technology's speed and low cost could empower quicker and more affordable gonorrhea testing in low-resource regions, as well as help combat the spread of drug-resistant strains. Rates of gonorrhea and other sexually transmitted ...
Measuring brain blood flow and activity with light
2021-05-12
A new, noninvasive method for measuring brain blood flow with light has been developed by biomedical engineers and neurologists at the University of California, Davis, and used to detect brain activation. The new method, functional interferometric diffusing wave spectroscopy, or fiDWS, promises to be cheaper than existing technology and could be used for assessing brain injuries, or in neuroscience research. The work is published May 12 in Science Advances.
"Now we can assess how well the brain regulates blood flow, and even detect brain activation noninvasively in adult humans, using principles similar to functional ...
Research reveals ancient people had more diverse gut microorganisms
2021-05-12
MISSOULA - Only an anthropologist would treasure millennia-old human feces found in dry caves.
Just ask Dr. Meradeth Snow, a University of Montana researcher and co-chair of UM's Department of Anthropology. She is part of an international team, led by the Harvard Medical School-affiliated Joslin Diabetes Center, that used human "paleofeces" to discover that ancient people had far different microorganisms living in their guts than we do in modern times.
Snow said studying the gut microbes found in the ancient fecal material may offer clues to combat diseases like diabetes that afflict people living in today's industrialized societies.
"We ...
Scientists use genetic engineering to explore mechanisms involved in psychiatric disorders
2021-05-12
Researchers used genetic engineering tools to create a virus that can enter specific neurons and insert into the prefrontal cortex a new genetic code that induces the production of modified proteins. In tests with mice, the alteration of these proteins was sufficient to modify brain activity, indicating a potential biomarker for the diagnosis of psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia and autism.
Sometimes referred to as the "executive brain", the prefrontal cortex is the region that governs higher-level cognitive functions and decision making. Studies of tissue from this brain region in patients with schizophrenia have detected alterations in two proteins: BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor) and trkB (tyrosine receptor kinase B).
The relationship ...
[1] ... [2317]
[2318]
[2319]
[2320]
[2321]
[2322]
[2323]
[2324]
2325
[2326]
[2327]
[2328]
[2329]
[2330]
[2331]
[2332]
[2333]
... [8812]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.