(Press-News.org) ITHACA, N.Y. - We've all seen them: political ads on television that promise doom gloom if Candidate X is elected, and how all your problems will be solved if you choose Candidate Y. And Candidate Y, of course, approves this message.
Beyond attempting to move a large swath of the population to vote one way or another, the seemingly constant bombardment of negativity in the name of our democratic process is anxiety-inducing, researchers have found.
"Many of my friends and family members wind up quite stressed out, for lack of a better word, during each election season," said Jeff Niederdeppe, professor in the Department of Communication in the College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, "and I've seen this pattern repeat itself across the last several election cycles."
Niederdeppe is lead author of "Exposure to Televised Political Campaign Advertisements Aired in the United States 2015-2016 Election Cycle and Psychological Distress," which published April 3 in Social Science & Medicine.
Also contributing was Rosemary Avery, professor of policy analysis and management in the College of Human Ecology, and Jiawei Liu, a postdoctoral researcher in the Department of Communication, along with colleagues from the University of Minnesota School of Public Health, Wesleyan University and the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
Their research, Niederdeppe said, uncovered evidence that exposure to one form of political messaging - televised campaign ads - was associated with increased odds of a person being diagnosed with anxiety by a doctor.
For the study, Niederdeppe's team purchased and conducted secondary analysis on two large national datasets:
Kantar/CMAG's database on TV airings for campaign ads appearing between Jan. 1, 2015 and Election Day 2016; and
data from five waves of the Simmons National Consumer Survey on TV viewing patterns and consumer behavior completed between Nov. 10, 2015, and March 7, 2017.
The latter survey, used to gauge consumer preferences, also included a detailed section on health ailments and engagement with doctors about those concerns.
The Simmons survey asked respondents, "Have you been told by a doctor or other health care professional in the past year that you have ..." followed by a series of conditions that respondents could check as applicable - anxiety, depression and insomnia, as well as a negative control condition (cancer), in an attempt to clearly illustrate ad exposure's link to mental wellness.
The study found consistent positive association between the volume of campaign advertising exposure and a reported diagnosis of anxiety among U.S. adults, suggesting that elections themselves may contribute to individual-level mental health issues.
One of the aims of the study was assessing whether associations between campaign ad exposure and mental health outcomes varied by political party of the respondent, the party of the candidate featured in the ad, or the office under consideration.
The nature of the 2016 presidential campaign made that particularly relevant, Niederdeppe said.
"We included that analysis [of the presidential vs. non-presidential ads] as a check, essentially, to say, 'Is this a Trump vs. Clinton effect?'" he said. "Donald Trump and Hillary Clinton had a uniquely divisive rhetoric and campaign and so one possible explanation would say, 'Hey, is this just an outlier, because it's 2016?'"
Political ads in general have gotten increasingly negative, Niederdeppe said, because research has shown that people pay attention to and remember those types of ads more than positive messages.
Political ads also tend to catch people "in environments where they're not looking for them - a commercial break embedded within other programming," he said. "You don't watch 'Jeopardy!' with the purpose of seeking out political information. But there it is."
Niederdeppe hopes this research can be part of a larger conversation on the effect of campaign advertising on public health.
"If these results play out in future election cycles, there's an immediate sort of public health readiness kind of element to this," he said. "If you know that these political ads are going to potentially increase the number of people who need treatment for anxiety, say, then you can prepare as a sort of public health infrastructure by offering by broadening treatment or having treatment plans ready for how you might deal with this particular form of anxiety."
He said it could also inform the existence and tone of campaign ads themselves.
"I would never say you have to ban all political ads," he said. "But should you consider the broader health implications of political messaging? When you're considering the right way to go about regulating this in the future, I think the answer is yes, that should be one factor."
INFORMATION:
Emmett Tabor '19, Nathaniel Lee '19 and Brendan Welch '21, undergraduates from the Department of Policy Analysis and Management, also contributed to the paper.
This research was supported by a grant from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation.
With 'Eyecam' they now present the prototype of a webcam that not only looks like a human eye, but imitates its movements realistically. "The goal of our project is not to develop a 'better' design for cameras, but to spark a discussion. We want to draw attention to the fact that we are surrounded by sensing devices every day. That raises the question of how that affects us," says Marc Teyssier. In 2020, the French scientist completed his doctorate on the topic of anthropomorphic design in Paris. Now he is a postdoctoral researcher in the Human-Computer Interaction Lab at Saarland University in Germany.
The research team at Saarland Informatics Campus has developed ...
Human non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a little-understood condition that significantly increases the risk of inflammation, fibrosis and liver cancer and ultimately requires liver transplant.
"NAFLD has been difficult to study mainly because we had no good animal model," said corresponding author Dr. Karl-Dimiter Bissig, who was at Baylor during the development of this project and is now at Duke University.
The disease has both genetic and nutritional components, which have been hard to understand in human studies, and murine models ...
A new study verifies the age and origin of one of the oldest specimens of Homo erectus--a very successful early human who roamed the world for nearly 2 million years. In doing so, the researchers also found two new specimens at the site--likely the earliest pieces of the Homo erectus skeleton yet discovered. Details are published today in the journal Nature Communications.
"Homo erectus is the first hominin that we know about that has a body plan more like our own and seemed to be on its way to being more human-like," said Ashley Hammond, an assistant curator in the American Museum of Natural History's Division of Anthropology and the lead author of the new study. "It had longer lower limbs than upper limbs, a torso ...
ITHACA, N.Y. - The muon is a tiny particle, but it has the giant potential to upend our understanding of the subatomic world and reveal an undiscovered type of fundamental physics.
That possibility is looking more and more likely, according to the initial results of an international collaboration - hosted by the U.S. Department of Energy's Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory - that involved key contributions by a Cornell team led by Lawrence Gibbons, professor of physics in the College of Arts and Sciences.
The collaboration, which brought together 200 scientists from 35 institutions in seven countries, set out to confirm the findings of a 1998 experiment that startled physicists by indicating that muons' magnetic ...
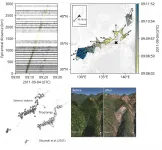
In the Cascadia subduction zone, medium and large-sized "intraslab" earthquakes, which take place at greater than crustal depths within the subducting plate, will likely produce only a few detectable aftershocks, according to a new study.
The findings could have implications for forecasting aftershock seismic hazard in the Pacific Northwest, say Joan Gomberg of the U.S. Geological Survey and Paul Bodin of the University of Washington in Seattle, in their paper published in the Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America.
Researchers now calculate aftershock forecasts in the region based in part on data from subduction zones around the world. ...
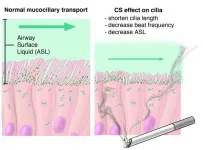
In a series of experiments that began with amoebas -- single-celled organisms that extend podlike appendages to move around -- Johns Hopkins Medicine scientists say they have identified a genetic pathway that could be activated to help sweep out mucus from the lungs of people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease a widespread lung ailment.
"Physician-scientists and fundamental biologists worked together to understand a problem at the root of a major human illness, and the problem, as often happens, relates to the core biology of cells," says Doug Robinson, Ph.D., professor of cell ...
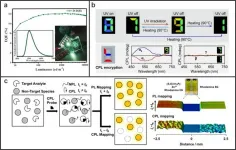
Circularly polarized light exhibits promising applications in future displays and photonic technologies. Traditionally, circularly polarized light is converted from unpolarized light by the linear polarizer and the quarter-wave plate. During this indirectly physical process, at least 50% of energy will be lost. Circularly polarized luminescence (CPL) from chiral luminophores provides an ideal approach to directly generate circularly polarized light, in which the energy loss induced by polarized filter can be reduced. Among various chiral luminophores, organic micro-/nano-structures have attracted increasing attention owing to the high quantum efficiency ...
Tsukuba, Japan - Tropical cyclones like typhoons may invoke imagery of violent winds and storm surges flooding coastal areas, but with the heavy rainfall these storms may bring, another major hazard they can cause is landslides--sometimes a whole series of landslides across an affected area over a short time. Detecting these landslides is often difficult during the hazardous weather conditions that trigger them. New methods to rapidly detect and respond to these events can help mitigate their harm, as well as better understand the physical processes themselves.
In a new study published in Geophysical Journal International, a research team led ...
Hokkaido University researchers have clarified different causes of past glacial river floods in the far north of Greenland, and what it means for the region's residents as the climate changes.
The river flowing from the Qaanaaq Glacier in northwest Greenland flooded in 2015 and 2016, washing out the only road connecting the small village of Qaanaaq and its 600 residents to the local airport. What caused the floods was unclear at the time. Now, by combining physical field measurements and meteorological data into a numerical model, researchers at Japan's Hokkaido ...
The semiconductor industry and pretty much all of electronics today are dominated by silicon. In transistors, computer chips, and solar cells, silicon has been a standard component for decades. But all this may change soon, with gallium nitride (GaN) emerging as a powerful, even superior, alternative. While not very heard of, GaN semiconductors have been in the electronics market since 1990s and are often employed in power electronic devices due to their relatively larger bandgap than silicon--an aspect that makes it a better candidate for high-voltage and high-temperature applications. Moreover, current travels quicker through GaN, which ensures fewer switching losses during switching applications.
Not everything about GaN is perfect, however. While impurities are usually desirable ...