Petting therapy dogs enhances thinking skills of stressed college students
2021-05-12
For college students under pressure, a dog may be the best stress fighter around.
Programs exclusively focused on petting therapy dogs improved stressed-out students' thinking and planning skills more effectively than programs that included traditional stress-management information, according to new Washington State University research.
The study was published today in the journal AERA Open, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research Association. The paper demonstrated that stressed students still exhibited these cognitive skills improvements up to six weeks after completion of the four-week-long program.
"It's a really powerful finding," said Patricia Pendry, associate professor in WSU's Department of ...
How social media and AI enable companies to track brand reputations in real-time
2021-05-12
Researchers from University of Maryland, North Carolina State University, National Taiwan University, Oxford University, Kings College London, and Perceptronics Solutions, Inc. published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that examines how artificial intelligence (AI)-based text analysis of social media can monitor the extent to which brand reputation rises and falls over time.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Real-Time Brand Reputation Tracking using Social Media" and is authored by Roland Rust, William Rand, Ming-Hui Huang, Andrew Stephen, Gillian Brooks, ...
Eliminating bias from healthcare AI critical to improve health equity
2021-05-12
INDIANAPOLIS -- Artificial intelligence (AI)-driven healthcare has the potential to transform medical decision-making and treatment, but these algorithms must be thoroughly tested and continuously monitored to avoid unintended consequences to patients.
In a JAMA Network Open Invited Commentary, Regenstrief Institute President and Chief Executive Officer and Indiana University School of Medicine Associate Dean for Informatics and Health Services Research Peter Embí, M.D., M.S., strongly stated the importance of algorithmovigilance to address inherent biases in healthcare algorithms and their deployment. ...
Defining climate-smart pathways towards tree crop yield intensification
2021-05-12
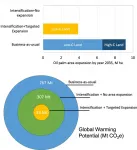
A global team of researchers recently released the results of a 'data-rich' modeling approach designed to illustrate a range of what-if scenarios for future oil palm plantation development in Indonesia. The study provides new insight into crop production strategies available to an industry facing increasing scrutiny.
Oil palm production is challenged by global and domestic concerns related to how it operates within its tropical rainforest environment, which is highly valued for its contribution to climate change mitigation potential and biodiversity protection. The study sheds new light on the future implications of maintaining business-as-usual ...
Fatigue, mood disorders associated with post-COVID-19 syndrome
2021-05-12
ROCHESTER, Minn. ­­­-- Patients diagnosed with post-COVID-19 syndrome, also known as "PCS," "COVID-19 long-haul syndrome" and "Post-Acute Sequelae of SARS COV-2," experience symptoms such as mood disorders, fatigue and perceived cognitive impairment that can negatively affect returning to work and resuming normal activities, according to a Mayo Clinic study published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
The study reports on the first 100 patients to participate in Mayo Clinic's COVID-19 Activity Rehabilitation program (CARP), one of the first multidisciplinary programs established to evaluate ...
NTU study of ancient corals in Indonesia reveals slowest earthquake ever recorded
2021-05-12
A 'slow-motion' earthquake lasting 32 years - the slowest ever recorded - eventually led to the catastrophic 1861 Sumatra earthquake, researchers at the Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) have found.
The NTU research team says their study highlights potential missing factors or mismodelling in global earthquake risk assessments today.
'Slow motion' earthquakes or 'slow slip events' refer to a type of long, drawn-out stress release phenomenon in which the Earth's tectonic plates slide against one another without causing major ground shaking or destruction. They typically involve movements of between ...
New findings linking brain immune system to psychosis
2021-05-12
New research at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden suggests a link between psychosis and a genetic change that affects the brain's immune system. The study published in Molecular Psychiatry may impact the development of modern medicines for bipolar disorder or schizophrenia.
Psychosis affects approximately 2-3 per cent of the population and is characterized by a change in the perception of reality, often with elements of hallucinations and paranoid reactions.
Most of the people affected are patients with schizophrenia, but people with bipolar disorder may also experience psychotic symptoms.
The antipsychotics available today often have insufficient efficacy, and for patients, ...
Southern African dinosaur had irregular growth
2021-05-12
Anyone who's raised a child or a pet will know just how fast and how steady their growth seems to be. You leave for a few days on a work trip and when you come home the child seems to have grown 10cm! That's all well and good for the modern household, but how did dinosaurs grow up? Did they, too, surprise their parents with their non-stop growth?
A new study lead by Dr Kimberley Chapelle of the American Museum of Natural History in New York City and Honorary Research Fellow at the University of the Witwatersrand suggests NOT. At least for one iconic southern African dinosaur species. By looking at the fossil ...
How to thermally cloak an object
2021-05-12
Can you feel the heat? To a thermal camera, which measures infrared radiation, the heat that we can feel is visible, like the heat of a traveler in an airport with a fever or the cold of a leaky window or door in the winter.
In a paper published in Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, an international group of applied mathematicians and physicists, including Fernando Guevara Vasquez and Trent DeGiovanni from the University of Utah, report a theoretical way of mimicking thermal objects or making objects invisible to thermal measurements. And it doesn't ...
The Lancet: More nurses lead to fewer patient deaths&readmissions, shorter hospital stays, and savings
2021-05-12
A study across 55 hospitals in Queensland, Australia suggests that a recent state policy to introduce a minimum ratio of one nurse to four patients for day shifts has successfully improved patient care, with a 7% drop in the chance of death and readmission, and 3% reduction in length of stay for every one less patient a nurse has on their workload.
The study of more than 400,000 patients and 17,000 nurses in 27 hospitals that implemented the policy and 28 comparison hospitals is published in The Lancet. It is the first prospective evaluation of the ...
COVID-19 vaccine does not damage the placenta in pregnancy
2021-05-12
CHICAGO --- A new Northwestern Medicine study of placentas from patients who received the COVID-19 vaccine during pregnancy found no evidence of injury, adding to the growing literature that COVID-19 vaccines are safe in pregnancy.
"The placenta is like the black box in an airplane. If something goes wrong with a pregnancy, we usually see changes in the placenta that can help us figure out what happened," said corresponding author Dr. Jeffery Goldstein, assistant professor of pathology at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine and a Northwestern Medicine pathologist. "From what we can tell, the COVID vaccine does not damage the placenta."
The study will be published May 11 in the journal Obstetrics ...
Discovery of new geologic process calls for changes to plate tectonic cycle
2021-05-11
TORONTO, ON - Geoscientists at the University of Toronto (U of T) and Istanbul Technical University have discovered a new process in plate tectonics which shows that tremendous damage occurs to areas of Earth's crust long before it should be geologically altered by known plate-boundary processes, highlighting the need to amend current understandings of the planet's tectonic cycle.
Plate tectonics, an accepted theory for over 60 years that explains the geologic processes occurring below the surface of Earth, holds that its outer shell is fragmented into continent-sized blocks of solid rock, called "plates," that slide over Earth's mantle, the rocky inner layer above ...
Phenomenon explains why patients who survive sepsis die sooner after hospital discharge
2021-05-11
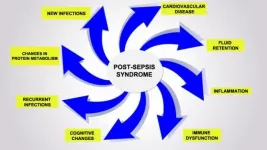
An article published in Frontiers in Immunology suggests that sepsis can cause alterations in the functioning of defense cells that persist even after the patient is discharged from hospital. This cellular reprogramming creates a disorder the authors call post-sepsis syndrome, whose symptoms include frequent reinfections, cardiovascular alterations, cognitive disabilities, declining physical functions, and poor quality of life. The phenomenon explains why so many patients who survive sepsis die sooner after hospital discharge than patients with other diseases or suffer from post-sepsis syndrome, immunosuppression ...
Understanding SARS-COV-2 proteins is key to improve therapeutic options for COVID-19
2021-05-11
COVID-19 has had a significant impact since the pandemic was declared by WHO in 2020, with over 3 million deaths and counting, Researchers and medical teams have been hard at work at developing strategies to control the spread of the infection, caused by SARS-COV-2 virus and treat affected patients. Of special interest to the global population is the developments of vaccines to boost human immunity against SARS-COV-2, which are based on our understanding of how the viral proteins work during the infection in host cells. Two vaccines, namely the Pfizer/BioINtech and Oxford/AZ vaccine rely on the use of delivering the gene that encodes the viral spike protein either as an mRNA or through an adenovirus vector to promote the production of relevant antibodies. The use of monoclonal ...
Improving smoking cessation counseling and blood pressure quality metrics in primary care
2021-05-11
In order to make meaningful gains in cardiovascular disease care, primary care medical practices should adopt a set of care improvements specific to their practice size and type, according to a new study from the national primary care quality improvement initiative EvidenceNOW. High blood pressure and smoking are among the biggest risk factors associated with cardiovascular disease. Primary care physicians help patients manage high blood pressure and provide smoking cessation interventions.
Researchers found that there is no one central playbook for all types of practices, but they did identify ...
Multiple factors influence family physicians' practice scope
2021-05-11
Although new family medicine graduates intend to provide a broader scope of practice than their senior counterparts, individual family physicians' scope of practice has been decreasing, with fewer family physicians providing basic primary care services, such pediatric and prenatal care. Russell et al conducted a study to explore family medicine graduates' attitudes and perspectives on modifiable and non-modifiable factors that influenced their scope of practice and career choices. The authors conducted five focus group discussions with 32 family physicians and explored their attitudes and perspectives on their desired and actual scope of practice. Using a conceptual framework ...
Gene editing expands to new types of immune cells
2021-05-11
In the decade since the advent of CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing, researchers have used the technology to delete or change genes in a growing number of cell types. Now, researchers at Gladstone Institutes and UC San Francisco (UCSF) have added human monocytes--white blood cells that play key roles in the immune system--to that list.
The team has adapted CRISPR-Cas9 for use in monocytes and shown the potential utility of the technology for understanding how the human immune system fights viruses and microbes. Their results were published online today in the journal Cell Reports.
"These experiments set the stage for many more studies on the interactions between major infectious diseases and human immune cells," says senior author Alex Marson, MD, PhD, director of the Gladstone-UCSF Institute ...
Pregnant women hospitalized for COVID-19 infection do not face increased risk of death
2021-05-11
Pregnant women who develop severe COVID-19 infections that require hospitalization for pneumonia and other complications may not be more likely to die from these infections than non-pregnant women. In fact, they may have significantly lower death rates than their non-pregnant counterparts. That is the finding of a new study published today in the Annals of Internal Medicine conducted by researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM).
The study examined medical records from nearly 1,100 pregnant women and more than 9,800 non-pregnant patients aged 15 to 45 who were hospitalized with COVID-19 and pneumonia. Slightly less than 1 percent of the pregnant patients died from COVID-19 compared to 3.5 percent of non-pregnant patients, according to the study findings.
There ...
Tiny, wireless, injectable chips use ultrasound to monitor body processes
2021-05-11
New York, NY--May 11, 2021--Widely used to monitor and map biological signals, to support and enhance physiological functions, and to treat diseases, implantable medical devices are transforming healthcare and improving the quality of life for millions of people. Researchers are increasingly interested in designing wireless, miniaturized implantable medical devices for in vivo and in situ physiological monitoring. These devices could be used to monitor physiological conditions, such as temperature, blood pressure, glucose, and respiration for both diagnostic and therapeutic ...
History of giants in the gene: Scientists use DNA to trace the origins of giant viruses
2021-05-11
2003 was a big year for virologists. The first giant virus was discovered in this year, which shook the virology scene, revising what was thought to be an established understanding of this elusive group and expanding the virus world from simple, small agents to forms that are as complex as some bacteria. Because of their link to disease and the difficulties in defining them--they are biological entities but do not fit comfortably in the existing tree of life--viruses incite the curiosity of many people.
Scientists have long been interested in how viruses evolved, especially when it comes to giant viruses that can produce new viruses with very little help from the host--in contrast to most small viruses, which utilize the host's machinery to replicate. ...
Greater presence of family docs, midwives may decrease rates of cesarean birth
2021-05-11
Surgical cesarean births can expose new mothers to a range of health complications, including infection, blood clots and hemorrhage. As part of Healthy People 2020 and other maternal health objectives, the state of California exerted pressure to reduce cesarean deliveries, and statewide organizations established quality initiatives in partnership with those goals. In this study, researchers from Stanford University and the University of Chicago examined unit culture and provider mix differences on hospital and delivery units to identify characteristics of units that successfully reduced their cesarean delivery rates. The mixed-methods study surveyed ...
Novel circuitry solves a myriad of computationally intensive problems with minimum energy
2021-05-11
From the branching pattern of leaf veins to the variety of interconnected pathways that spread the coronavirus, nature thrives on networks -- grids that link the different components of complex systems. Networks underlie such real-life problems as determining the most efficient route for a trucking company to deliver life-saving drugs and calculating the smallest number of mutations required to transform one string of DNA into another.
Instead of relying on software to tackle these computationally intensive puzzles, researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology ...
Combination of psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy more effective in treating depression
2021-05-11
Most patients with depression are treated in primary care, however, relatively few clinical trials for treating depression have focused on primary care. Researchers at the Vrije University Amsterdam examined the effects of the two major approaches to treating depression: psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy, as well as combined treatment and care-as-usual. The study integrated the results of 58 randomized controlled trials with a total of 9,301 patients. Results concluded that both psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy were significantly more effective than care-as-usual or waitlist control. However, they found no significant difference between psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy as stand-alone treatments. Combined treatment, particularly in studies that included ...
Newer class of fluoroquinolone antibiotics may present reduced risk of tendon ruptures
2021-05-11
It's widely understood that people taking a common class of antibiotics, like ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin, run the risk of tendonitis and tendon ruptures. However, a new analysis sheds light on newer, third-generation fluoroquinolones and suggests they may have a lower risk of Achilles tendon rupture. Researchers from Jichi Medical University in Tochigi, Japan, used health care administrative data to identify 504 patient cases of Achilles tendon ruptures with co-occurrence of antibiotics. They found that third-generation fluoroquinolones were not associated with an increase in Achilles tendon rupture. First- ...
Focus on outliers creates flawed snap judgments
2021-05-11
DURHAM, N.C. -- You enter a room and quickly scan the crowd to gain a sense of who's there - how many men versus women. How reliable is your estimate?
Not very, according to new research from Duke University.
In an experimental study, researchers found that participants consistently erred in estimating the proportion of men and women in a group. And participants erred in a particular way: They overestimated whichever group was in the minority.
"Our attention is drawn to outliers," said Mel W. Khaw, a postdoctoral research associate at Duke and the study's lead author. "We tend to overestimate people who stand out in a crowd."
For the study, which appears ...
[1] ... [2322]
[2323]
[2324]
[2325]
[2326]
[2327]
[2328]
[2329]
2330
[2331]
[2332]
[2333]
[2334]
[2335]
[2336]
[2337]
[2338]
... [8812]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.