No difference in outcomes between light exercise and rest for patients with mild TBI
2021-05-24
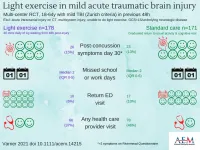
Des Plaines, IL - For acute mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI), there were no differences in recovery or health care utilization outcomes with prescribed early light exercise compared to standard care. These are the results of a study titled A randomized trial comparing prescribed light exercise to standard management for emergency department patients with acute mild traumatic brain injury, to be published in the May issue of Academic Emergency Medicine (AEM) journal, a peer-reviewed journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM).
Findings of the study suggest that early light exercise may be encouraged as tolerated at emergency department discharge following mTBI, but this guidance is not sufficient ...
MD Anderson researchers present new findings in targeted and combination therapies at 2021 ASCO Annual Meeting
2021-05-24
HOUSTON ? Several Phase II clinical trials conducted by researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center show promising results for patients with melanoma, breast cancer, HER2-positive tumors and ovarian cancer. The results of these studies, which will be presented at the virtual 2021 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, highlight new advances in drug therapy research to improve patient outcomes.
Combination therapy of nivolumab and relatlimab before and after surgery is effective against melanoma (Abstract #9502)
In a Phase II study, MD Anderson researchers showed that a regimen of neoadjuvant and ...
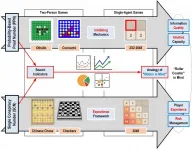
Games, computing, and the mind: How search algorithms reflect game playing
2021-05-24
Iahikawa, Japan - Humans benefit from playing games more than some might realize. Games can be a relaxed approach to learning or honing our problem-solving skills while relieving stress. However, game playing generally carries a considerable amount of decision-making, involving mathematical and statistical considerations that we make to decide on what we think is the best move. Thus, games showcase many of the impressive faculties and inner workings of the human brain, which in turns makes them a great testbed and playground for research on artificial intelligence (AI).
One aspect common to many games is decision making based on uncertain information about current and potential ...
Good news: Mild COVID-19 induces lasting antibody protection
2021-05-24
Months after recovering from mild cases of COVID-19, people still have immune cells in their body pumping out antibodies against the virus that causes COVID-19, according to a study from researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. Such cells could persist for a lifetime, churning out antibodies all the while.
The findings, published May 24 in the journal Nature, suggest that mild cases of COVID-19 leave those infected with lasting antibody protection and that repeated bouts of illness are likely to be uncommon.
"Last fall, there were reports that antibodies wane quickly after infection with the virus that causes COVID-19, and mainstream media interpreted that to mean that immunity was not long-lived," said senior author Ali Ellebedy, PhD, an associate professor ...
Virus infection cycle revealed in dynamic detail
2021-05-24
A critical process in the infection cycle of viruses has been revealed for the first time in dynamic detail using pioneering plant-based technology.
Evidence about the process of virus maturation revealed in the research could help us develop new methods for treating viral infections.
Maturation plays a critical role for all animal and bacterial viruses and is required to produce infectious virions or particles. Though the outlines of the process have been determined for many groups of viruses, detailed mechanistic studies have not been reported.
To provide the first detailed mechanistic study of maturation, Roger Castells-Graells, ...
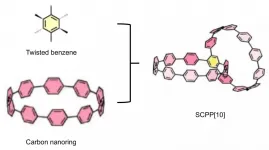
Researchers first synthesize conjoined bismacrocycle with all phenylene units
2021-05-24
The research team led by Prof. DU Pingwu from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) first successfully synthesized an all-phenylene bismacrocycle (bis- means two) with Siamese-twin structure and used fullerene as guest molecules to assemble a peanut-shaped supramolecular complex. This study was published in Angewandte Chemie.
As a new type of carbon material, carbon nanotubes (CNTs) have attracted widespread attention because of their outstanding mechanical and photophysical properties. However, the synthesis of CNTs or CNTs fragments with selective simple structure is still a challenge.
This study reported a conjugated highly strained all-phenylene Siamese-twin bismacrocycle, SCPP[10]. Two phenylene nanorings, [10]CPP, conjoined ...
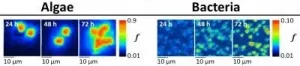
New study shows never before seen nutrient exchanges between algae and bacteria
2021-05-24
Research co-led by Newcastle University has shed new light on important microscopic scale interactions between algae and bacteria predicated on the mutually beneficial exchange of nutrients.
The research was carried out at the University of Cambridge and the Nordsim laboratory at the Swedish Museum of Natural History in Stockholm by Dr Hannah Laeverenz Schlogelhofer, now at the University of Exeter, and a team led by Dr Ottavio Croze, of Newcastle University's School of Mathematics, Statistics and Physics.
They have used an advanced high-spatial resolution isotope mapping technique called 'SIMS' (secondary ion mass spectrometry) to chart for the first time how long it takes for labelled carbon produced by microalgae to be transferred ...
Supersensitive connection causes hatred of noises
2021-05-24
A supersensitised brain connection has been identified in people who suffer from misophonia, an extreme reaction to "trigger" sounds.
For the first time, researchers led by Newcastle University, have discovered increased connectivity in the brain between the auditory cortex and the motor control areas related to the face, mouth and throat.
Publishing today, in the Journal of Neuroscience, lead author Dr Sukhbinder Kumar, Newcastle University Research Fellow in the Biosciences Institute said: "Our findings indicate that for people with misophonia there is abnormal communication between the auditory and motor ...
Posts to Reddit forum "SuicideWatch" spike in the early hours of Monday morning
2021-05-24
Posts to Reddit forum "SuicideWatch" spike in the early hours of Monday morning
New research from the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN) at King's College London has found that people on a social media suicide support forum are most likely to post to the site during the early hours of Monday morning.
The study, which has been published in BMC Psychiatry, suggests that there is a clear variation in behaviour throughout the week and throughout the day. The researchers hope that this means that targeted support to at risk populations can be made more readily available to those most in need.
The researchers looked at the timings at which users of the Reddit ...
Link between local oxygen depletion in the brain and Alzheimer's disease
2021-05-24
The study, published in the journal Nature Aging and led by the laboratories of Dr. Alberto Pascual (CSIC), from the Neuronal Maintenance Mechanisms Group, and Prof. Javier Vitorica (University of Seville/CIBERNED) of the Physiopathology of Alzheimer's Disease Group at IBiS, demonstrates for the first time that low oxygen levels in the so-called senile plaques in the brain reduces the immune system's defensive capacity against the disease.
The study also suggests that this lack of oxygen in the brain enhances the action of disorders associated with Alzheimer's disease that are characterised by low systemic oxygen levels, such as atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases.
What happens ...
Forensic archaeologists begin to recover Spanish Civil War missing bodies
2021-05-24
Forensic archaeologists and anthropologists from Cranfield University have started to recover the bodies of victims executed by the Franco regime at the end of the Spanish Civil War during an excavation in the Ciudad Real region of Spain.
The team from Cranfield is working with partners from the University Complutense of Madrid (UCM) and social anthropologists from Mapas de Memoria (Maps of Memory) to search for, exhume and identify those executed and buried in the civil cemetery at Almagro between 1939 and 1940.
Several bodies with gunshot wounds to the head, personal effects and parts of clothing ...
Obesity protects against death in severe bacterial infection
2021-05-24
For many diseases, overweight and obesity are risk factors. But now a study shows that a higher BMI may be linked to higher survival rates in patients hospitalized for severe bacterial infections.
Scientists at Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, and Skaraborg Hospital in Skövde carried out the research, and their study has now been published in the journal PLOS ONE. The data were collected before the COVID-19 pandemic.
The population-based study involved observations, over a nine-month period, of all 2,196 individual adults receiving care for suspected severe bacterial ...
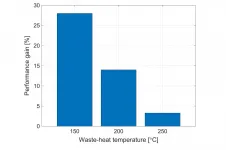
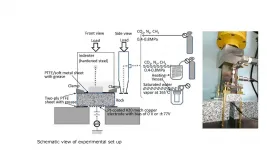
Using waste heat to power an environmentally sustainable future
2021-05-24
In his most recent published research, appearing in Applied Thermal Engineering, City, University of London's Dr Martin White explores a novel organic Rankine cycle system, based on a two-phase expansion through numerical simulations of the system.
His paper, Cycle and turbine optimisation for an ORC operating with two-phase expansion, considers the use of modern fluids whose properties could help to mitigate concerns around turbine damage, whilst allowing the benefits of two-phase expansion to be realised.
Waste heat from a range of industries, ranging from iron and steel to food and drink, ...
Electromagnetic anomalies that occur before an earthquake
2021-05-24
It has been documented over hundreds of years that various electromagnetic anomalies occur during a few weeks before the occurrence of a large earthquake. These electromagnetic anomalies are variations that appear in telluric current, geomagnetism, electromagnetic waves etc. before the earthquake.
Although there are various models to explain the mechanism, the large current generated at the source was not fully explained. For example, many researchers thought that the stress applied to the fault produced an electric current, but the stress applied to the fault takes place over hundreds or thousands of years before the occurrence of the earthquake. It is a common belief among seismologists ...
Telomere length, a longevity measure, may be determined early in life
2021-05-24
Telomeres are protective caps on DNA that shorten as we grow older. Now, one of the first studies to examine telomere length (TL) in childhood finds that the initial setting of TL during prenatal development and in the first years of life may determine one's TL throughout childhood and potentially even into adulthood or older age. The study also finds that TL decreases most rapidly from birth to age 3, followed by a period of maintenance into the pre-puberty period, although it was sometimes seen to lengthen.
The study, which followed children from birth to age 9, was led by researchers ...
New fishing tech may pose risks to fisheries, says study co-authored by UMass researcher
2021-05-24
AMHERST, Mass. - New developments in recreational fishing technology--from the use of aerial drones and social media scouting reports to advances in hook design--are creating challenges for fisheries management and effective policy making, according to a new study co-authored by University of Massachusetts Amherst researcher Andy Danylchuk.
With the opening of the spring fishing season, millions of recreational fishing aficionados across North America are dusting off their tackleboxes, fitting together their rods, and heading to the bait and tackle shop to purchase the latest ...
Researchers use artificial intelligence to determine extent of damage in kidney disease
2021-05-24
(Boston)--Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is caused by diabetes and hypertension. In 2017, the global prevalence of CKD was 9.1 percent, which is approximately 700 million cases. Chronic kidney damage is assessed by scoring the amount of interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy (IFTA) in a renal biopsy sample. Although image digitization and morphometric (measuring external shapes and dimensions) techniques can better quantify the extent of histologic damage, a more widely applicable way to stratify kidney disease severity is needed.
Now, researchers from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) have developed a novel Artificial Intelligence (AI) tool to predict the grade of IFTA, a known structural ...
Researchers discover oligodendrocyte loss and subtype alteration in CTE brains
2021-05-24
(Boston)--Since 2008, researchers at Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) and VA Boston Healthcare System have studied Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE), a progressive brain disease associated with repetitive head impacts that has been diagnosed after death in the brains of American football players and other contact sport athletes as well as members of the armed services. Clinically, impulsivity, explosivity, depression, memory impairment and executive dysfunction have been reported to occur in the disease.
While many of the scientific studies to date ...
Moderate use of hair relaxers does not increase breast cancer risk among black women
2021-05-24
New study fills an important knowledge gap about the potential health effects of hair relaxers commonly used by Black women.
(Boston)--The lifetime risk of breast cancer is similar among Black and white women in the U.S., but Black women are disproportionately affected by aggressive breast cancer subtypes such as estrogen receptor (ER) negative tumors, which are diagnosed at a younger age and have a higher mortality rate. While certain hair care products, including relaxers (straighteners) and leave-in conditioners, used more commonly by Black than white women may contain compounds with estrogens or endocrine-disrupting chemicals, few epidemiologic studies have assessed the relationship of hair relaxer use to breast cancer risk.
Researchers have now found no association ...
UH authors 'design for value' to improve patient and physician experience for referrals
2021-05-24
CLEVELAND -- A new paper in the June issue of New England Journal of Medicine Catalyst Innovations in Care Delivery describes how the University Hospitals (UH) system applied design-based thinking in a re-imagined process for referrals of patients from primary care physicians to psychiatrists in a value-based, high-reliability model.
"Referrals from primary care to specialty care represent a critical pathway in the patient journey to wellness. As we move toward value-based payment models, high-reliability referral pathways will be of increasing importance in achieving better outcomes at lower cost," said Patrick Runnels, MD, Chief Medical Officer of Population Health and Behavioral Health at UH, Vice Chair of Psychiatry at Case Western ...
How school board meetings could attract more diverse audiences and boost public trust
2021-05-24
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- Schools in the U.S. are set to receive $123 billion in federal pandemic relief funding. Across the country, parents and school administrators are engaging in spirited debates about whether to teach critical race theory. And Americans are bitterly divided in their opinions about how and when to resume in-person instruction following rising rates of vaccination against COVID-19.
One might expect that given all that's at stake, school board meetings across the U.S. would be hotbeds of discussion. But in many cases, they're the same staid, sparsely attended affairs that they can often be.
"We have more ...
Analyzing the impact of college gameday homes in the American south
2021-05-24
ATLANTA--Absentee property ownership in many small college football towns has a negative impact on permanent residents of those communities, according to a study by a Georgia State University geosciences researcher.
The research is the first known attempt to quantify and map local geographies of gameday home investments.
Each weekend in the fall tens of thousands of football fans flood into college towns to watch their favorite teams kick off against rival schools. Many of them stay in gameday homes, investment properties that sit vacant for much of the year. Taylor Shelton, assistant professor of geosciences and the study's author, examined data from more than a dozen college towns in the South where schools in the Southeastern Conference attract large ...
A community health worker intervention reduces hospital readmissions
2021-05-24
BOSTON - A clinical trial pairing community health workers (CHWs) with patients admitted to Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) has found that fewer intervention group participants were readmitted within 30 days than were control group participants. The effect was significant for those discharged to short-term rehabilitation but not for those discharged home. The study, one of few of its kind, has been published in JAMA Network Open.
"These results indicate that CHW interventions may help reduce hospital readmissions and improve preventive care among some clinically complex patients ...
Study finds women with osteoporosis and low bone density are at increased risk of hearing loss
2021-05-24
BOSTON -- Hearing loss is the third most common chronic health condition in the United States. Previous studies of people with hearing loss have uncovered higher prevalence of osteoporosis -- a disease in which the bones become weak and brittle -- and low bone density (LBD). But research on whether these conditions may influence risk of hearing loss over time is scarce. It is also unknown whether hearing loss can be avoided by taking bisphosphonates, the primary medication used to prevent fractures in people with reduced bone density. As part of the Conservation of Hearing Study ...
Young teens should only use recreational internet and video games one hour daily
2021-05-24
Middle-school aged children who use the internet, social media or video games recreationally for more than an hour each day during the school week have significantly lower grades and test scores, according to a study from the Center for Gambling Studies at Rutgers University-New Brunswick.
The findings appear in the journal Computers in Human Behavior.
Researchers say the findings give parents and children a moderate threshold for using entertainment-related technology -- no more than one hour daily on school days and four hours a day on weekends.
"Interactive technology is widely used to promote children's educational access and achievement," said lead author Vivien (Wen Li) Anthony, an assistant professor at ...
[1] ... [2287]
[2288]
[2289]
[2290]
[2291]
[2292]
[2293]
[2294]
2295
[2296]
[2297]
[2298]
[2299]
[2300]
[2301]
[2302]
[2303]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.