(Press-News.org) People's fear of 5G technology is rational. Such technology does emit radiation, even if it's at low levels. But 5G isn't all that different from 4G, and it certainly doesn't cause COVID-19 despite such rumors having spread rapidly across the globe.
Researchers need to better understand how misinformation like this spreads in order to hone their intervention efforts and prevent misinformed perspectives from taking root. In society's virtual world, preventing technological misinformation, in particular, is important now more than ever.
A research team led by Elaine Nsoesie, a Hariri Institute Faculty Fellow, investigated how COVID-19 misinformation proliferated using the same epidemiological techniques for modeling disease transmission. Nsoesie, along with Nina Cesare, a postdoctoral associate at the BU School of Public Health, and other scientists from Harvard Medical School and École Polytechnique Fédérale recently published their findings in the Journal of Medical Internet Research.
The team examined the spread of COVID-19 misinformation across eight English-speaking countries, including the United States, using Google Trends. The researchers focused on myths that the World Health Organization (WHO) "busted" on its website including the relationships between COVID-19 and alcohol, ginger root, the sun, 5G, and hydroxychloroquine.
What Nsoesie and colleagues found was that some COVID-19 misinformation spread exponentially across the countries, much like the coronavirus itself.
This rapid proliferation isn't surprising. Most people were scrambling for any sort of information on the mysterious virus in the early months of 2020. "There was such a rapid proliferation of any information at the onset of the pandemic that misinformation had a golden opportunity to enter the public conscience," said Cesare.
Thankfully, debunking myths online seems effective in stopping their spread. As soon as public health officials at WHO responded to COVID-19 misinformation on the WHO website, the number of Google searches for that misinformation dropped significantly.
But, the team was surprised that there seems to be a consistent, global misunderstanding of 5G technology. The myth of "COVID-19 and 5G" spread faster than any of the other rumors they investigated. "I didn't expect 5G to stand out among the misinformation as much as it did," said Nsoesie.
What makes this even more surprising is that 5G technology isn't brand new. Rather, it's a continued development, based on international standards, of the communication technologies preceding it, like 4G.
"5G is the new standard for communication technology. It allows for faster communication by using different frequencies and multiple antennas," said David Starobinski, a professor in Boston University's Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. "It is an evolution of communication technology rather than a revolution," he said.
Even though 5G technology isn't entirely new, there are a few reasons why people might have believed it causes COVID-19.
For one, there is very little transparency from researchers in communication technologies that leads to institutional distrust. "I think the belief has something to do with a certain distrust in government and the ability to tie this narrative about 5G technology into conversations around government surveillance," said Cesare. This distrust is a concern even now, as myths around microchips being put into vaccines explode on Facebook.
Another explanation for why folks might associate 5G with COVID-19 is that such technology emits invisible electromagnetic waves that people fear could impact their health. "People are much more worried about things [like radiation] that they cannot see," said Starobinski.
While exposure to high-power radiation can be harmful to health, Starobinski assures that there have been safety guidelines on the radiation from communication technologies and 5G should be safe to use. "People have been using smartphones for years and we don't see evidence that this radiation has caused noticeable increase in diseases or hospitalizations due to usage," he said. He also noted that "regulators have set limits on the radiation power of 5G devices, though additional safety studies may still be warranted."
And, such radiation can't cause COVID-19. COVID-19 is a viral disease that comes from the coronavirus known as SARS-CoV-2.
To stop the spread of similar myths in the future, experts need to consistently and clearly correct common misconceptions. And better transparency from both government bodies and researchers could prevent misinformation from ever taking root.
"We [researchers] need to humanize the conversations around misinformation and continue to share true information so that misinformation becomes less prevalent in the media," said Nsoesie.
INFORMATION:
A new study out of the University of Chicago and Stanford University on pairs of twins with and without food allergies has identified potential microbial players in this condition. The results were published on Jan. 19 in the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
The study grew out of prior research in the Nagler laboratory at UChicago on the fecal microbiota in infants. By transplanting fecal microbes from healthy and food-allergic infants to germ-free mice (who do not possess a microbiome), investigators found that the healthy infant microbiota was protective against the development ...
The synthetic chemicals known as PFAS, short for perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances, are found in soil and groundwater where they have accumulated, posing risks to human health ranging from respiratory problems to cancer.
New research from the University of Houston and Oregon State University published in Environmental Science and Technology Letters suggests why these "forever chemicals" - so called because they can persist in the environment for decades - are so difficult to permanently remove and offers new avenues for better remediation practices.
The work focused on the interactions sparked when firefighters use ...
The abnormal immune system response that causes multiple sclerosis (MS) by attacking and damaging the central nervous system can be triggered by the lack of a specific fatty acid in fat tissue, according to a new Yale study. The finding suggests that dietary change might help treat some people with the autoimmune disease.
The study was published Jan. 19 in The Journal of Clinical Investigation.
Fat tissue in patients diagnosed with MS lack normal levels of oleic acid, a monounsaturated fatty acid found at high levels in, for instance, cooking oils, meats (beef, chicken, and pork), cheese, nuts, sunflower seeds, eggs, pasta, ...
With a name like glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, one would think it is a rare and obscure medical condition, but that's far from the truth. Roughly 400 million people worldwide live with potential of blood disorders due to the enzyme deficiency. While some people are asymptomatic, others suffer from jaundice, ruptured red blood cells and, in the worst cases, kidney failure.
Now, a team led by researchers at the Department of Energy's SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory have uncovered the elusive mechanism behind the most severe cases of the ...
WASHINGTON, January 19, 2021 -- What causes brain concussions? Is it direct translational or rotational impact? This is one of the research areas currently being explored by Qianhong Wu's lab at Villanova University.
Our brains consist of soft matter bathed in watery cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside a hard skull. An impact on the hard skull is transmitted through the thin layer of CSF within the subarachnoid space to the soft brain matter.
In Physics of Fluids, from AIP Publishing, Wu and co-authors Ji Lang and Rungun Nathan describe studying another system with the same features, an egg, to search for answers. An egg resembles the brain, because its soft yolk is bathed within a liquid egg white inside a hard shell.
Considering that in most concussive brain injuries, the skull does ...
For the first time ever, a team of scientists, led by the University of Bristol, have described in detail a dinosaur's cloacal or vent - the all-purpose opening used for defecation, urination and breeding.
Although most mammals may have different openings for these functions, most vertebrate animals possess a cloaca.
Although we know now much about dinosaurs and their appearance as feathered, scaly and horned creatures and even which colours they sported, we have not known anything about how the vent appears.
Dr Jakob Vinther from the University of Bristol's School of Earth Sciences, along with colleagues Robert Nicholls, a palaeoartist, and Dr Diane Kelly, ...
With a small snout, a short and curled tail, and a big, round stomach, mini pigs are the epitome of cute--and sometimes, they snore. Now, researchers think these snoring pigs can be used to study obstructive sleep apnea. A study appearing January 19 in the journal Heliyon found that obese Yucatan mini pigs do have naturally occurring sleep apnea and that MRI scans taken while they're in sedated sleep can be used to gain new insights into what happens in the airways during sleep apnea episodes via computational flow dynamic (CFD) analysis.
"These are very fat pigs," says first author Zi-Jun Liu, a research professor and principal investigator in the Department of Orthodontics ...
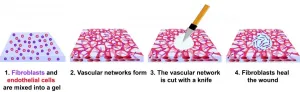
WASHINGTON, January 19, 2021 -- Biomedical engineers developed a technique to observe wound healing in real time, discovering a central role for cells known as fibroblasts. The work, reported in APL Bioengineering, by AIP Publishing, is the first demonstration of a wound closure model within human vascularized tissue in a petri dish.
Prior investigations of wound healing have used animal models, but healing in humans does not occur the same way. One difference is that wounds in mice and rats, for example, can heal without granulation tissue, a type of tissue critical to the healing of human wounds.
Granulation tissue forms after blood coagulates, and the wound scabs over. Coagulation creates a fibrin network that serves as a temporary matrix. Granulation tissue then takes over, ...
WASHINGTON, January 19, 2021 -- The quest for ever-smaller electronic components led an international group of researchers to explore using molecular building blocks to create them. DNA is able to self-assemble into arbitrary structures, but the challenge with using these structures for nanoelectronic circuits is the DNA strands must be converted into highly conductive wires.
Inspired by previous works using the DNA molecule as a template for superconducting nanowires, the group took advantage of a recent bioengineering advance known as DNA origami to fold DNA into arbitrary shapes.
In AIP ...
Youths with mood disorders who use and abuse cannabis (marijuana) have a higher risk for self-harm, death by all causes and death by unintentional overdose and homicide, according to research led by The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and The Ohio State University College of Medicine.
Study findings are published in the JAMA Pediatrics.
"Marijuana use and addiction is common among youth and young adults with mood disorders, but the association of this behavior with self-harm, suicide and overall mortality risk is poorly understood in this already vulnerable population. These findings ...