INFORMATION:
The project was funded by the Strategic Environmental Research and Development Program of the U.S. Department of Defense. In addition to Kostarelos, co-authors on the publication include Pushpesh Sharma of UH; and Emerson Christie, Thomas Wanzek and Jennifer Field, all of Oregon State University.
New clues help explain why PFAS chemicals resist remediation
Work suggests new avenues for cleaning up these 'forever chemicals'
2021-01-19
(Press-News.org) The synthetic chemicals known as PFAS, short for perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances, are found in soil and groundwater where they have accumulated, posing risks to human health ranging from respiratory problems to cancer.
New research from the University of Houston and Oregon State University published in Environmental Science and Technology Letters suggests why these "forever chemicals" - so called because they can persist in the environment for decades - are so difficult to permanently remove and offers new avenues for better remediation practices.
The work focused on the interactions sparked when firefighters use firefighting foam, which contains PFAS, to combat fires involving jet fuel, diesel or other hydrocarbon-based fuels. Firefighter training sites are well-documented sources of PFAS pollution.
Konstantinos Kostarelos, a researcher with UH Energy and corresponding author for the work, said the interactions form a viscous water-in-oil microemulsion, which chemical analysis determined retains a high level of the PFAS.
Unlike many emulsions of oil and liquid, which separate into their component parts over time, these microemulsions - comprised of liquids from the firefighting foam and the hydrocarbon-based fuel - retain their composition, Kostarelos said. "It behaves like a separate phase: the water phase, oil phase and the microemulsion phase. And the microemulsion phase encapsulates these PFAS."
Experimental trials that simulate the subsurface determined about 80% of PFAS were retained in the microemulsions when they flow through the soil, he said. "If they passed through easily, they wouldn't have been so persistent over the course of decades."
Produced during the post-World War II chemical boom, PFAS are found in consumer products ranging from anti-stain treatments to Teflon and microwave popcorn bags, in addition to firefighting foam. They were prized because they resist heat, oil and water - traditional methods of removing or breaking down chemicals - as a result of the strong bond between the carbon and fluorine atoms that make up PFAS molecules.
They have been the target of lawsuits and regulatory actions, and new chemical formulations have shortened their half-life.
In the meantime, the toxic legacy of the older formulations continues to resist permanent remediation. Kostarelos said the new understanding of microemulsion formation will help investigators better identify the source of the contamination, as well as stimulate new methods for clean-up efforts.
"It's very viscous," he said. "That's very useful information for designing a way to recover the microemulsion."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fatty acid may help combat multiple sclerosis
2021-01-19
The abnormal immune system response that causes multiple sclerosis (MS) by attacking and damaging the central nervous system can be triggered by the lack of a specific fatty acid in fat tissue, according to a new Yale study. The finding suggests that dietary change might help treat some people with the autoimmune disease.
The study was published Jan. 19 in The Journal of Clinical Investigation.
Fat tissue in patients diagnosed with MS lack normal levels of oleic acid, a monounsaturated fatty acid found at high levels in, for instance, cooking oils, meats (beef, chicken, and pork), cheese, nuts, sunflower seeds, eggs, pasta, ...
Researchers discover mechanism behind most severe cases of a common blood disorder
2021-01-19
With a name like glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, one would think it is a rare and obscure medical condition, but that's far from the truth. Roughly 400 million people worldwide live with potential of blood disorders due to the enzyme deficiency. While some people are asymptomatic, others suffer from jaundice, ruptured red blood cells and, in the worst cases, kidney failure.
Now, a team led by researchers at the Department of Energy's SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory have uncovered the elusive mechanism behind the most severe cases of the ...
Eggs reveal what may happen to brain on impact
2021-01-19
WASHINGTON, January 19, 2021 -- What causes brain concussions? Is it direct translational or rotational impact? This is one of the research areas currently being explored by Qianhong Wu's lab at Villanova University.
Our brains consist of soft matter bathed in watery cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside a hard skull. An impact on the hard skull is transmitted through the thin layer of CSF within the subarachnoid space to the soft brain matter.
In Physics of Fluids, from AIP Publishing, Wu and co-authors Ji Lang and Rungun Nathan describe studying another system with the same features, an egg, to search for answers. An egg resembles the brain, because its soft yolk is bathed within a liquid egg white inside a hard shell.
Considering that in most concussive brain injuries, the skull does ...
All-purpose dinosaur opening reconstructed for first time
2021-01-19
For the first time ever, a team of scientists, led by the University of Bristol, have described in detail a dinosaur's cloacal or vent - the all-purpose opening used for defecation, urination and breeding.
Although most mammals may have different openings for these functions, most vertebrate animals possess a cloaca.
Although we know now much about dinosaurs and their appearance as feathered, scaly and horned creatures and even which colours they sported, we have not known anything about how the vent appears.
Dr Jakob Vinther from the University of Bristol's School of Earth Sciences, along with colleagues Robert Nicholls, a palaeoartist, and Dr Diane Kelly, ...
Obese, snoring mini pigs show how air flows through the throat during sleep apnea
2021-01-19
With a small snout, a short and curled tail, and a big, round stomach, mini pigs are the epitome of cute--and sometimes, they snore. Now, researchers think these snoring pigs can be used to study obstructive sleep apnea. A study appearing January 19 in the journal Heliyon found that obese Yucatan mini pigs do have naturally occurring sleep apnea and that MRI scans taken while they're in sedated sleep can be used to gain new insights into what happens in the airways during sleep apnea episodes via computational flow dynamic (CFD) analysis.
"These are very fat pigs," says first author Zi-Jun Liu, a research professor and principal investigator in the Department of Orthodontics ...
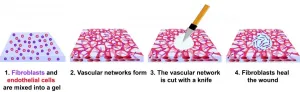
New insights into wound healing process
2021-01-19
WASHINGTON, January 19, 2021 -- Biomedical engineers developed a technique to observe wound healing in real time, discovering a central role for cells known as fibroblasts. The work, reported in APL Bioengineering, by AIP Publishing, is the first demonstration of a wound closure model within human vascularized tissue in a petri dish.
Prior investigations of wound healing have used animal models, but healing in humans does not occur the same way. One difference is that wounds in mice and rats, for example, can heal without granulation tissue, a type of tissue critical to the healing of human wounds.
Granulation tissue forms after blood coagulates, and the wound scabs over. Coagulation creates a fibrin network that serves as a temporary matrix. Granulation tissue then takes over, ...
DNA origami enables fabricating superconducting nanowires
2021-01-19
WASHINGTON, January 19, 2021 -- The quest for ever-smaller electronic components led an international group of researchers to explore using molecular building blocks to create them. DNA is able to self-assemble into arbitrary structures, but the challenge with using these structures for nanoelectronic circuits is the DNA strands must be converted into highly conductive wires.
Inspired by previous works using the DNA molecule as a template for superconducting nanowires, the group took advantage of a recent bioengineering advance known as DNA origami to fold DNA into arbitrary shapes.
In AIP ...
Youths with mood disorders who use marijuana at higher risk of death, self-harm
2021-01-19
Youths with mood disorders who use and abuse cannabis (marijuana) have a higher risk for self-harm, death by all causes and death by unintentional overdose and homicide, according to research led by The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and The Ohio State University College of Medicine.
Study findings are published in the JAMA Pediatrics.
"Marijuana use and addiction is common among youth and young adults with mood disorders, but the association of this behavior with self-harm, suicide and overall mortality risk is poorly understood in this already vulnerable population. These findings ...
Appreciating a flower's texture, color, and shape leads to better drone landings
2021-01-19
If you ever saw a honeybee hopping elegantly from flower to flower or avoiding you as you passed by, you may have wondered how such a tiny insect has such perfect navigation skills. These flying insects' skills are partially explained by the concept of optical flow: they perceive the speed with which objects move through their field of view. Robotics researchers have tried to mimic these strategies on flying robots, but with limited success. A team of TU Delft and the Westphalian University of Applied Sciences researchers therefore present an optical flow-based learning process that allows robots to estimate distances through the visual appearance (shape, color, texture) of the objects ...
NAD+ can restore age-related muscle deterioration
2021-01-19
The older we grow, the weaker our muscles get, riddling old age with frailty and physical disability. But this doesn't only affect the individual, it also creates a significant burden on public healthcare. And yet, research efforts into the biological processes and biomarkers that define muscle aging have not yet defined the underlying causes.
Now, a team of scientists from lab of Johan Auwerx at EPFL's School of Life Sciences looked at the issue through a different angle: the similarities between muscle aging and degenerative muscle diseases. They have discovered protein aggregates that deposit in skeletal muscles during natural aging, and that blocking this can prevent the detrimental features of muscle ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
[Press-News.org] New clues help explain why PFAS chemicals resist remediationWork suggests new avenues for cleaning up these 'forever chemicals'