(Press-News.org) In a large-scale study of electronic health records, Vanderbilt University Medical Center investigators have determined the prevalence of functional seizures and characterized comorbidities associated with them.
Functional seizures are sudden attacks or spasms that look like epileptic seizures but do not have the aberrant brain electrical patterns of epilepsy.
The research team, headed by Lea Davis, PhD, associate professor of Medicine and an investigator in the Vanderbilt Genetics Institute, confirmed associations between functional seizures and psychiatric disorders including posttraumatic stress disorder, anxiety and depression as well as sexual assault trauma. They also discovered a novel association between functional seizures and cerebrovascular disease, including stroke.
The findings were reported in the journal JAMA Network Open.
Also known as psychogenic nonepileptic seizures, functional seizures have been historically understudied. Patients often experience a long delay -- on average seven years -- before they receive an accurate diagnosis.
About 80% of patients experiencing functional seizures are initially misdiagnosed with epilepsy and treated with anti-epileptic drugs, said Slavina Goleva, a graduate student in Molecular Physiology and Biophysics and first author of the study. An accurate diagnosis requires assessment with video electroencephalogram (EEG).
Davis got interested in functional seizures after hearing an NPR story several years ago.
"The story gave the patient perspective on these seizures -- the stigma that patients felt and the difficulties they experienced in the medical system," Davis recalled. "I felt like studies within electronic health records could potentially be really impactful for this community."
Working with Kevin Haas, MD, PhD, associate professor of Neurology, the researchers developed an algorithm to identify people with functional seizures in the VUMC-EHR system.
"We initially recognized that finding these patients within the EHR would be a challenge because the ICD (International Classification of Diseases) codes are not as specific as they are for a lot of diseases," Goleva said. In addition to ICD codes, the researchers included Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes and used natural language processing to search within the records for a list of keywords.
Goleva and Haas manually reviewed charts to confirm that the algorithm correctly identified patients with functional seizures.
The study included more than 2.3 million patients 18 or older in the VUMC-EHR system from 1989 to 2018. The researchers identified 3,341 patients with functional seizures, 74% of whom were women. They calculated a prevalence of 0.14% (140 cases per 100,000 people); previous estimates ranged from 2 to 33 cases per 100,000 people.
"Our report is the first direct calculation of the prevalence of functional seizures," Goleva said. She noted that the epilepsy monitoring unit at VUMC may result in a higher prevalence of functional seizures in patients in the VUMC-EHR compared to the general population.
Among the patients with functional seizures, the researchers validated comorbidities including psychiatric disorders and sexual assault trauma and discovered a novel association with cerebrovascular disease. They also found that sexual assault trauma explained about a quarter of the increased rate of functional seizures among women, Goleva said.
"Functional seizures are not occurring in isolation; patients who are experiencing these seizures are also experiencing a higher burden of additional health care issues," Davis said.
"If there is a suspicion that someone presenting with seizures could have functional seizures rather than epileptic seizures, it's critical to refer those patients to an epilepsy monitoring unit for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment," Haas said. "Historically, even once diagnosed, care of these patients has often fallen through the cracks between neurology and psychiatry, but we are now actively developing a more integrated approach to care for this patient population."
The researchers recommended that patients experiencing seizures who have psychiatric comorbidities or a history of sexual assault trauma be referred for video-EEG assessment. Patients who develop seizures after a stroke and do not initially respond to treatment with medications should also be considered for early video-EEG assessment.
Up to 30% of patients referred for video-EEG are eventually diagnosed with functional seizures, they noted.
"It's frustrating that there is no ICD code for functional seizures, given how common the diagnosis is and the fact that codes exist for strange things like alligator bite, second occurrence," Davis said. "It really emphasizes how little attention this population of patients has gotten."
The investigators are currently exploring the genetics of functional seizures using genome-wide association studies of biobanks including Vanderbilt's BioVU.
INFORMATION:
Other authors of the JAMA Network Open study included Allison Lake and Eric Torstenson. The research was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (MD010722, NS102371, MH113362, HG009086, HD098859, DC016977, NS105746, MH120736, HG010652, HG009034 and TR000445). Goleva was supported by a Graduate Research Fellowship from the National Science Foundation.
FINDINGS
A study led by researchers at the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center has found that magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI, frequently underestimates the size of prostate tumors, potentially leading to undertreatment.
The study authors found that such underestimation occurs most often when the MRI-measured tumor size is small and the PI-RADS score, which is used to classify lesions in prostate MRI analysis, is low.
For prostate tumor treatments to be successful, both the MRI size measurement and PI-RADS score must be accurate because they allow physicians to determine precisely ...
A University of Arizona-led research team has found bands and stripes on the brown dwarf closest to Earth, hinting at the processes churning the brown dwarf's atmosphere from within.
Brown dwarfs are mysterious celestial objects that are not quite stars and not quite planets. They are about the size of Jupiter but typically dozens of times more massive. Still, they are less massive than the smallest stars, so their cores do not have enough pressure to fuse atoms the way stars do. They are hot when they form and gradually cool, glowing faintly and dimming slowly throughout their lives, making them hard to find. No telescope can clearly ...
People taking immunosuppressive drugs to prevent organ transplant rejection or to treat inflammatory or autoimmune diseases do not fare worse than others on average when they are hospitalized with COVID-19, according to a study from researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
Estimates suggest that there are approximately 10 million immunocompromised people in the U.S. alone. Suppression of the immune system has been considered a potentially major risk factor for severe and fatal COVID-19 because it could allow the SARS-CoV-2 ...
PHILADELPHIA -- (Jan. 7, 2021) -- Scientists at The Wistar Institute characterized an inhibitor that targets acetate metabolism in cancer cells. Cancer cells use acetate metabolism to support tumor growth in conditions of low nutrient and oxygen availability. This molecule caused tumor growth inhibition and regression in preclinical studies, demonstrating the promise of this approach as a novel therapeutic strategy for solid tumors. Study results were published today in Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
Highly proliferating cancer cells within a tumor ...
Scientists who publish in Cell Press research journals (e.g., Cell, Joule, Current Biology, etc.) will now have the option to include a short statement that highlights elements of the study design and/or author characteristics that are relevant to inclusion and diversity. The statement is generated based on information provided on a dedicated inclusion and diversity form that study authors complete as part of the acceptance process. This pilot initiative will also allow Cell Press to better collect, analyze, and share back data about research teams' general inclusion and diversity efforts.
"In an ideal world, science would cover and be ...
In the early decades of televised news, Americans turned to the stern faces of newsmen like Walter Cronkite, Tom Brokaw, and Dan Rather as trusted sources for news of the important events in America and around the world, delivered with gravitas and measured voices. The rise of comedy-news programs, helmed by the likes of Jon Stewart, Stephen Colbert, John Oliver, Trevor Noah, and Samantha Bee, raised concerns over the blending of entertainment and news. But could the merging of humor and news actually help inform the public?
In fact, new research suggests that humor may help ...
A study led by Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health researchers examines attitudes toward long-acting injectable (LAI) HIV therapies, among women with a history of injection--including medical purposes and substance use. The findings appear in the journal AIDS Patient Care and STDs.
Currently, most HIV therapies for treatment and prevention (pre-exposure prophylaxis, PrEP) necessitate daily pills, which pose barriers to adherence. Recently, however, LAI for HIV has emerged as an alternative with the potential to boost adherence, although little research has been done on how people with a history of injection feel about these new forms of injectable HIV therapy. There 258,000 women in the United States living with HIV.
The study involved interviews with 89 women across ...
HOUSTON - (Jan. 7, 2021) - Rice University and Baylor College of Medicine researchers have found a way to mimic conditions in intestines, giving them a mechanical model for the real-time growth of bacterial infections.
In a new study, they demonstrate a lab tool that simplifies simulations of the human intestine, making it more practical to find treatments for diseases like infectious diarrhea.
The team led by bioengineer Jane Grande-Allen of Rice's Brown School of Engineering developed transparent millifluidic perfusion cassettes (mPCs) that are easy to fabricate and operate and compatible with common microscopic and biochemical analysis.
The cassettes allow even non-bioengineers to perform the kind of studies ...
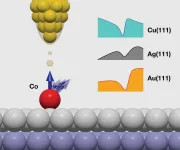
Jülich, Germany, 7 January 2021. The Kondo effect influences the electrical resistance of metals at low temperatures and generates complex electronic and magnetic orders. Novel concepts for data storage and processing, such as using quantum dots, are based on this. In 1998, researchers from the United States published spectroscopic studies on the Kondo effect using scanning tunnelling microscopy, which are considered ground-breaking and have triggered countless others of a similar kind. Many of these studies may have to be re-examined now that Jülich researchers have shown that the Kondo effect cannot be proven beyond doubt ...
As the first doses of COVID-19 vaccines are being rolled out, it is still unclear whether enough Americans are willing to be vaccinated to allow the nation to return to normalcy. Many believe a key part of the equation lies in how effective vaccine communication teams are at convincing the public to get vaccinated. And the key to effective communication tactics in promoting the vaccines may lie in demonstrated behavioral economics and consumer behavior theory, experts say.
"The country has made an incredible investment in fast-tracking SARS-CoV-2 vaccines from conception to market, which would make it even more tragic if we fail to curtail the virus simply because Americans ...