Temperature explains why aquatic life more diverse near equator
2021-05-06
The bulging, equator-belted midsection of Earth currently teems with a greater diversity of life than anywhere else -- a biodiversity that generally wanes when moving from the tropics to the mid-latitudes and the mid-latitudes to the poles.
As well-accepted as that gradient is, though, ecologists continue to grapple with the primary reasons for it. New research from the University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Yale University and Stanford University suggests that temperature can largely explain why the greatest variety of aquatic life resides in the tropics -- but also why it has not ...
Discovery of genetic drivers linked to progression in Parkinson's disease
2021-05-06
A key driver of patients' well-being and clinical trials for Parkinson's disease (PD) is the course the disease takes over time. However, nearly all that is known about the genetics of PD is related to susceptibility -- a person's risk for developing the disease in the future. A new study by investigators from Brigham and Women's Hospital published in Nature Genetics uncovers the genetic architecture of progression and prognosis, identifying five genetic locations (loci) associated with progression. The team also developed the first risk score for predicting ...
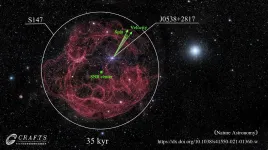
FAST detects 3D spin-velocity alignment in a pulsar
2021-05-06
Pulsars - another name for fast-spinning neutron stars - originate from the imploded cores of massive dying stars through supernova explosion.
Now, more than 50 years after the discovery of pulsars and confirmation of their association with supernova explosions, the origin of the initial spin and velocity of pulsars is finally beginning to be understood.
Based on observations from the Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST), Dr. YAO Jumei, member of a team led by Dr. LI Di from National Astronomical Observatories of Chinese Academy of Sciences (NAOC), found the first evidence for three-dimensional (3D) spin-velocity alignment in pulsars.
The study was published in Nature Astronomy on May 6. It also marks the beginning of in-depth pulsar research with FAST.
For decades, ...
UChicago Medicine's ED maintains HIV screening despite pandemic interruptions
2021-05-06
While other medical systems across the country failed to maintain HIV screening volumes throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, the University of Chicago Medicine maintained screening volumes by including universal HIV screening alongside COVID-19 testing in its busy emergency department, according to a new report published April 12 in JAMA Internal Medicine. Through targeted efforts to maintain infrastructure and enthusiasm for HIV screening, the number of HIV tests remained at pre-pandemic levels while the rate of acute HIV diagnoses actually increased.
Widespread screening to diagnose individuals newly infected with HIV is a key part of Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's (CDC) plan to ...
The origin of reproductive organs
2021-05-06
Early in human development, during the first trimester of gestation, a fetus may have XX or XY chromosomes that indicate its sex. Yet at this stage a mass of cells known as the bipotential gonad that ultimately develops into either ovaries or testes has yet to commit to its final destiny.
While researchers had studied the steps that go into the later stages of this process, little has been known about the precursors of the bipotential gonad. In a new study published in Cell Reports and co-led by Kotaro Sasaki of Penn's School of Veterinary Medicine, an international team lays ...
Not so wicked after all?
2021-05-06
Although the fairy tale of the wicked stepmother is a tale as old as time, the effects of blending children with their new stepfamilies may not be as grim as once thought.
In fact, new research shows that stepparents are not at a disadvantage compared to their peers from single-parent households and actually experience better outcomes than their halfsiblings -- good news for the more than 113 million Americans that are part of a steprelationship.
Led by East Carolina University anthropologist Ryan Schacht and researchers from the University of Utah, the study, "Was Cinderella just a fairy tale? Survival differences between stepchildren and their half-siblings," is available in the May edition of the Philosophical Transactions ...
In the Alps, climate change affects biodiversity
2021-05-06
The European Alps is certainly one of the most scrutinized mountain range in the world, as it forms a true open-air laboratory showing how climate change affects biodiversity. Although many studies have independently demonstrated the impact of climate change in the Alps on either the seasonal activity (i.e. phenology) or the migration of plants and animals, no systematic analysis has been carried out on both consequences simultaneously. A European team of ecologists1, including Jonathan Lenoir, CNRS Researcher in the research unit Écologie et Dynamique des Systèmes Anthropisés (CNRS/University of Picardie Jules Verne), has just published a review that ...
Archaeal enzyme that produces membrane lipids is spectacularly promiscuous
2021-05-06
Cells of all life forms are surrounded by a membrane that is made of phospholipids. One of these are the cardiolipins, which form a separate class due to their unique structure. When studying the enzyme that is responsible for producing cardiolipins in archaea (single-cell organisms that constitute a separate domain of life), biochemists at the University of Groningen made a surprising discovery. A single archaeal enzyme can produce a spectacular range of natural and non-natural cardiolipins, as well as other phospholipids. The results, which show potential for biotechnological applications, ...
India's polio vaccination provides valuable insights for mass vaccination campaigns
2021-05-06
Lessons Learned from India's Polio Vaccination Program Provide Valuable Insights for Future Mass Vaccination Initiatives.
Toronto - As India urgently scales up its vaccination campaign for the COVID-19 virus, a new study which examined the country's successful program to eliminate polio provides guidance on how this and future mass immunization campaigns can be successful, especially in vaccinating hard to reach groups.
The study, conducted by students and faculty with the Reach Alliance, a research initiative based at the University of Toronto's Munk School of Global Affairs & Public Policy, says that medicine alone is insufficient for the elimination of disease.
The World Health Organization declared India polio-free in 2014. ...
Research breakthrough in the fight against cancer
2021-05-06
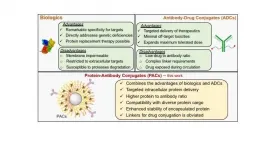
AMHERST, Mass. - A team of researchers at the Center for Bioactive Delivery at the University of Massachusetts Amherst's Institute for Applied Life Sciences has engineered a nanoparticle that has the potential to revolutionize disease treatment, including for cancer. This new research, which appears today in Angewandte Chemie, combines two different approaches to more precisely and effectively deliver treatment to the specific cells affected by cancer.
Two of the most promising new treatments involve delivery of cancer-fighting drugs via biologics or antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). Each has its own advantages and limitations. Biologics, such as protein-based ...
The COVID-19 pandemic: Even mild disease impacts mental health
2021-05-06
May 6, 2021 -- A significant level of symptoms of depression, anxiety and post-traumatic stress may follow COVID-19 independent of any previous psychiatric diagnoses, according to new research by Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health with colleagues at Universidade Municipal de São Caetano do Sul in Brazil. Exposure to increased symptomatic levels of COVID-19 may be associated with psychiatric symptoms after the acute phase of the disease. This is the largest study to evaluate depressive, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress symptoms in tandem among patients who had mild COVID-19 ...
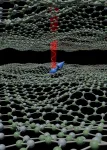
New boost in quantum technologies
2021-05-06
Quantum computers or quantum sensors consist of materials that are completely different to their classic predecessors. These materials are faced with the challenge of combining contradicting properties that quantum technologies entail, as for example good accessibility of quantum bits with maximum shielding from environmental influences. In this regard, so-called two-dimensional materials, which only consist of a single layer of atoms, are particularly promising.
Researchers at the new Center for Applied Quantum Technologies and the 3rd Institute of Physics at the University of Stuttgart have now succeeded in identifying promising quantum bits in these materials. They were able to show that the quantum bits can be generated, read out and coherently controlled in a very ...
Blocking viruses' exit strategy
2021-05-06
The Marburg virus, a relative of the Ebola virus, causes a serious, often-fatal hemorrhagic fever. Transmitted by the African fruit bat and by direct human-to-human contact, Marburg virus disease currently has no approved vaccine or antivirals to prevent or treat it.
A team of researchers is working to change that. In a new paper in the journal Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, investigators from Penn's School of Veterinary Medicine, working together with scientists from the Fox Chase Chemical Diversity Center and the Texas Biomedical Research Institute, report encouraging results from tests of an experimental ...
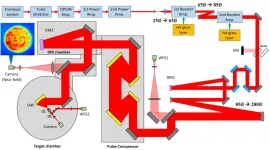
Researchers produce laser pulses with record-breaking intensity
2021-05-06
WASHINGTON -- Researchers have demonstrated a record-high laser pulse intensity of over 1023 W/cm2 using the petawatt laser at the Center for Relativistic Laser Science (CoReLS), Institute for Basic Science in the Republic of Korea. It took more than a decade to reach this laser intensity, which is ten times that reported by a team at the University of Michigan in 2004. These ultrahigh intensity light pulses will enable exploration of complex interactions between light and matter in ways not possible before.
The powerful laser can be used to examine phenomena believed to be responsible for ...
Realization of the highest laser intensity ever reached
2021-05-06
Recently, laser scientists at the Center for Relativistic Laser Science (CoReLS) within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) in South Korea realized the unprecedented laser intensity of 1023 W/cm2. This has been a milestone that has been pursued for almost two decades by many laser institutes around the world.
An ultrahigh intensity laser is an important research tool in several fields of science, including those which explore novel physical phenomena occurring under extreme physical conditions. Since the demonstration of the 1022 W/cm2 intensity laser by a team at the ...
Eating sardines regularly helps prevent type 2 diabetes
2021-05-06
The health benefits of sardines and oily fish are widely known: their high levels of unsaturated fats help to regulate cholesterol levels and prevent the onset of cardiovascular diseases. However, the benefits don't end there. A study led by Diana Diaz Rizzolo, lecturer and researcher of the Universitat Oberta de Catalunya's (UOC) Faculty of Health Sciences and the August Pi i Sunyer Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBAPS), has discovered that the regular consumption of sardines helps to prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes. Nutrients found in high quantities in sardines - such as taurine, omega 3, calcium and vitamin D - help to protect against this disease which, according to CIBERDEM's Di@betes study, affects around 14% of the Spanish population over the ...
Novavax COVID-19 vaccine trial results show efficacy against the B.1.351 variant in SA study
2021-05-06
The published data provide additional detail of an initial analysis conducted in January, while more robust data from a complete analysis of the study was subsequently shared in March 2021.
Publication of initial primary analysis highlights cross-protection by the Novavax Covid-19 vaccine against the B.1.351 variant prevalent in South Africa during the study.
This is the first published study to show protection against mild Covid-19 caused by the B.1.351 variant circulating in South Africa.
An updated analysis of the study indicated 100% protection against severe Covid-19 due to the B.1.351 variant.
"An efficacy of 50% is sufficient to meet the World ...
Twitter data unveils issues nursing mothers face, informs proposed interventions
2021-05-06
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Social media has become a platform for new mothers to openly share their experiences of the joys and challenges of parenthood. Researchers at Penn State and Dalhousie University have unraveled the sentiments in nursing mothers' tweets to better understand the factors influencing breastfeeding behaviors. They hope the findings can inform policies and interventions to support and improve resources for nursing mothers, such as breastfeeding support, workplace accommodations and technological aids such as apps.
"We are getting the raw sentiment of nursing mothers without putting them in a controlled experiment environment ...
Lancaster University team's 'eggstraordinary' paper revealed at major conference
2021-05-06
The world's first-ever 'academic paper which is not a paper' is due to be presented by a Lancaster University research team at the premier international conference on human-computer interaction.
Dr Joseph Lindley, a researcher at Lancaster University's ImaginationLancaster design-led research laboratory, Dr Miriam Sturdee, from the University's School of Computing and Communications, Senior Research Associate Dr David Green and Research Associate Hayley Alter have been invited to take part in the 2021 ACM CHI Virtual Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems in May.
Using the innovative 'Gather Town' online video-calling and conferencing platform, they have experimented in setting up a conference paper as an interactive but virtual ...
Better healthcare guidance needed for trans people
2021-05-06
Clinical practice guidelines for dealing with the physical and mental health of transgender people highlight the current lack of a solid research base which must be improved, according to a new study published in the journal BMJ Open.
A team of researchers from Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) and King's College London searched world literature for all international clinical practice guidelines on the healthcare needs of gender minority and trans people.
Results showed that higher quality guidelines tended to focus mainly on HIV, and most others were on transition-related interventions. There were noticeable gaps in the topics of guidelines, with none addressing ...
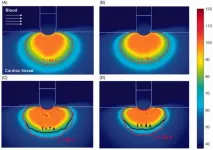
Greater effectiveness in the treatment of arrhythmia with radio frequency energy and catheterization
2021-05-06
An article published in International Journal of Hyperthermia proposes a more effective protocol for the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias when applying radiofrequency energy at the site of the arrhythmia by catheterization. The research results from the final year project (TFG) on the bachelor's degree in Biomedical Engineering by Sergi Coderch Navarro, supervised by Ana González Suárez and Oscar Camara, researchers with the PhySense group of the BCN MedTech Research Unit at the UPF Department of Information and Communication Technologies (DTIC). Sergi Coderch Navarro defended his TFG in July 2019 and was a runner-up in the 2019 Gemma Rossell i Romero Awards. Currently, Ana González Suárez is a postdoctoral ...
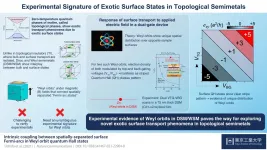
Unusual semimetal shows evidence of unique surface conduction states
2021-05-06
Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology experimentally verify the existence of exotic surface conduction states in topological semimetals (TSMs), materials that lie at the boundary between conductors and insulators, by performing voltage scans of these surface states on a thin film sample of a TSM. The findings can pave the way for future study and exploitation of such conduction states in realizing novel, quantum transport phenomena.
All of us are probably familiar with the idea of conductors and insulators. But what would you call a material that can conduct on the surface but insulate on the inside? Physicists call it a "topological insulator" (TI), a term that highlights the geometric aspect of its strange conduction behavior. Even stranger ...
Researchers unveil roadmap to expand NY solar energy, meet green goals
2021-05-06
ITHACA, N.Y. - Solar-power developers need to explore using lower-quality agricultural land for solar energy, incentivize dual-use (combined agriculture and solar) options, avoid concentrated solar development and engage communities early to achieve New York's green energy goals, according to forthcoming Cornell University research.
"As farmland is generally flat and cleared, agricultural land will be the prime target for future solar energy development," said Max Zhang, professor in the Sibley School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering. "Good farmland, however, is not ideal."
Zhang is senior author of "Strategic Land Use Analysis for Solar Energy Development in New York State," which will publish in August 2021 in Renewable Energy.
Under New York state's 2019 Climate ...
The natural brightness of the night sky
2021-05-06
A recent study analyses data collect4d at 44 of the darkest places in the world, including the Canary Island Observatories, to develop the first complete reference method to measure the natural brightness of the night sky using low-cost photometers.
Of the 44 photometers in the survey, the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory (Garafía, La Palma, Canary Islands) stands out at the darkest of all the skies analysed.
The night sky is not completely dark; even in the remotest places there is a glow in the sky produced by natural components, both terrestrial and extraterrestrial, ...
Just a few atoms thick: New functional materials developed
2021-05-06
They are 50,000 times thinner than a human hair, and just a few atoms thick: two-dimensional materials are the thinnest substances it is possible to make today. They have completely new properties and are regarded as the next major step in modern semiconductor technology. In the future they could be used instead of silicon in computer chips, light-emitting diodes and solar cells. Until now, the development of new two-dimensional materials has been limited to structures with layers of rigid chemical bonds in two spatial directions - like a sheet of paper in a stack. Now for the first time, a research team from the ...
[1] ... [2337]
[2338]
[2339]
[2340]
[2341]
[2342]
[2343]
[2344]
2345
[2346]
[2347]
[2348]
[2349]
[2350]
[2351]
[2352]
[2353]
... [8810]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.