Bacteria carried by mosquitos may protect them against pesticides
2021-01-13
A common bacterial species naturally infecting mosquitoes may actually be protecting them against specific mosquito pesticides, a study has found.
Wolbachia - a bacterium that occurs naturally and spreads between insects - has become more frequently used in recent years as a means of controlling mosquito populations.
Scientists at the University of Reading, and the INBIOTEC-CONICET and the National University of San Juan in Argentina, studied the effect of Wolbachia on a common mosquito species and found those carrying the bacteria were less susceptible to widely used pesticides.
Dr Alejandra Perotti, an Associate Professor in invertebrate biology at the University of Reading, and a co-author of the study, said: "This shows the importance of looking more ...
A 'ghastly future' unless extraordinary action is taken soon on sustainability
2021-01-13
Without immediate and drastic intervention, humans face a "ghastly future" -- including declining health, climate devastation, tens of millions of environmental migrants and more pandemics -- in the next several decades, according to an international team of 17 prominent scientists. ...
Blue-light stride in perovskite-based LEDs
2021-01-13
Researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, have developed efficient blue light-emitting diodes based on halide perovskites. "We are very excited about this breakthrough", says Feng Gao, professor at Linköping University. The new LEDs may open the way to cheap and energy-efficient illumination.
Illumination is responsible for approximately 20% of global electricity consumption, a figure that could be reduced to 5% if all light sources consisted of light-emitting diodes (LEDs). The blue-white LEDs currently in use, however, need complicated manufacturing methods and are expensive, which makes it more difficult to achieve ...
Limits of atomic nuclei predicted
2021-01-13
Atomic nuclei are held together by the strong interaction between neutrons and protons. About ten percent of all known nuclei are stable. Starting from these stable isotopes, nuclei become increasingly unstable as neutrons are added or removed, until neutrons can no longer bind to the nucleus and "drip" out. This limit of existence, the so-called neutron "dripline", has so far been discovered experimentally only for light elements up to neon. Understanding the neutron dripline and the structure of neutron-rich nuclei also plays a key role in the research program for the future accelerator facility FAIR at the GSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Research in Darmstadt.
In a new study, "Ab Initio Limits of Nuclei," ...
A new study identifies possible biomarkers of severe malaria in African children
2021-01-13
The levels of small molecules called microRNAs (miRNAs) circulating in blood could help identify early on children with life-threatening forms of malaria, according to a study led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health, an institution supported by "la Caixa" Foundation, in collaboration with the Manhiça Health Research Center (CISM) in Mozambique. The results, published in Emerging Infectious Diseases journal, could also help better understand the mechanisms underlying severe malaria.
Malaria mortality among young African children remains unacceptably high. To improve the outcome, it is important to rapidly identify and treat children with severe forms of the disease. ...
Seawater as an electrical cable !? Wireless power transfers in the ocean
2021-01-13
Overview:
Associate professor Masaya Tamura, Kousuke Murai (who has completed the first term of his master's program), and their research team from the Department of Electrical and Electronic Information Engineering at Toyohashi University of Technology have successfully transferred power and data wirelessly through seawater by using a power transmitter/receiver with four layers of ultra-thin, flat electrodes. In the field of wireless power transfers, seawater behaves as a dielectric with extremely high loss, and achievement through capacitive coupling is difficult. Up until now, it had been thought that wireless power transfers could only be achieved through magnetic coupling. ...
New molecular structures associated with ALS
2021-01-13
Researchers from the University of Seville and the University of Pavia have identified a link between Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) and the accumulation of DNA-RNA hybrids in the genome. The accumulation of these hybrids causes increased genomic damage and boosts genetic instability. This finding will make it possible to better understand the molecular basis of the disease, as well as to propose new solutions to curb it.
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) is a neurodegenerative disease of the central nervous system, characterised by progressive degeneration ...
Evolution in a test tube: these bacteria survive on deadly copper surfaces
2021-01-13
The descendants of regular wild-type bacteria can evolve to survive for a long time on metallic copper surfaces that would usually kill them within a few minutes. An international research team led by Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) and the Bundeswehr Institute of Microbiology was able to produce these tiny survivalists in the lab and has been able to study them more closely. The team reports on its findings in Applied and Environmental Microbiology.
Bacterial infections are usually treated with antibiotics. However, in recent decades many pathogenic bacteria have developed an increasing tolerance to common drugs. So-called multidrug-resistant bacteria are of particular concern as ...
How will we achieve carbon-neutral flight in future?
2021-01-13
It is politically agreed and necessary for climate protection reasons that our entire economy becomes climate-neutral in the coming decades - and that applies to air travel, too. This is a technically feasible goal, and there are numerous ways to achieve it. ETH Professor Marco Mazzotti and his team have now compared the options that appear to be the easiest to implement in the short and medium term and evaluated them according to factors such as cost-effectiveness.
The ETH researchers conclude that the most favourable option is to continue powering aircraft with fossil fuels in future, but then remove the associated CO2 emissions from the atmosphere ...
TalTech's neuroscientists investigate the causes of a widespread eye disease
2021-01-13
Fuchs' corneal dystrophy is one of the most common eye diseases diagnosed in almost 5% of the population of Europe aged 40 years or over. It is a hereditary eye disease that causes vision impairment and typically manifests in middle age. The first symptoms of the disease - blisters on the surface of your cornea - resemble cataract at first glance. The disease progresses from the centre of the cornea affecting all layers of the cornea. The progression of the disease varies from individual to individual and in severe cases results in vision loss.
The molecular neurobiology ...
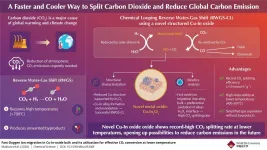
Copper-indium oxide: A faster and cooler way to reduce our carbon footprint
2021-01-13
With ever-worsening climate change, there is a growing need for technologies that can capture and use up the atmospheric CO2 (carbon dioxide) and reduce our carbon footprint. Within the realm of renewable energy, CO2-based e-fuels have emerged as a promising technology that attempts to convert atmospheric CO2 into clean fuels. The process involves production of synthetic gas or syngas (a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide (CO)). With the help of the reverse water-gas shift (RWGS) reaction, CO2 is broken down into the CO necessary for syngas. While promising in its conversion efficiency, the RWGS reaction requires incredibly high temperatures (>700°C) to proceed, while also generating ...
Lipid biomarkers in urine can determine the type of asthma
2021-01-13
In a new study, researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have used a urine test to identify and verify a patient's type of asthma. The study, which has been published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, lays the foundation for a more personalized diagnosis and may result in improved treatment of severe asthma in the future.
About 10 percent of the Swedish population suffers from asthma, a disease that has become increasingly widespread over the past 50 years, with annual global mortality of around 400,000 according to the World Health Organization. Asthma is characterized by chronic inflammation in the airways, which can result in symptoms including ...
New studies support blood test for early detection of Alzheimer's disease
2021-01-13
In three recent publications in Molecular Psychiatry, Brain and JAMA Neurology researchers from the University of Gothenburg provide convincing evidence that an in-house developed blood test for Alzheimer's disease can detect the disease early and track its course, which has major implications for a potential use in clinical practice and treatment trials.
"This is an extremely dynamic research field right now, thanks to the technological development and seminal scientific progress in the past years. The dream scenario is to have a blood test for the early detection and screening of Alzheimer's disease up and running. That would give significantly ...
Workaholism leads to mental and physical health problems
2021-01-13
Workaholism or work addiction risk is a growing public health concern that can lead to many negative mental and physical health outcomes such as depression, anxiety or sleep disorder. Perception of work (job demands and job control) may become a major cause of employees' work addiction. The international group of researchers including the HSE University scientist explored the link between work addiction risk and health-related outcomes using the framework of Job Demand Control Model. The results were published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.
Workaholics are people who usually work seven and more hours more than ...
High-sensitivity nanophotonic sensors with passive trapping of analyte molecules in hot-spots
2021-01-13
Optical sensors can quantitatively analyze chemical and biological samples by measuring and processing the optical signals produced by the samples. Optical sensors based on infrared absorption spectroscopy can achieve high sensitivity and selectivity in real time, and therefore play a crucial role in a variety of application areas such as environmental sensing, medical diagnostics, industrial process control and homeland security.
In a new paper published in Light: Science & Applications, a team of scientists, led by Dr. Peter Q. Liu from the Department of Electrical Engineering, the State University of New York at Buffalo, have demonstrated a new type of high-performance optical sensor which can utilize ...
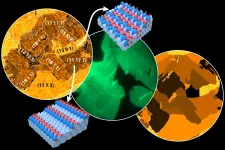
Catalysts: worth taking a closer look
2021-01-13
Metal surfaces play a role as catalysts for many important applications - from fuel cells to the purification of car exhaust gases. However, their behaviour is decisively affected by oxygen atoms incorporated into the surface.
This phenomenon has been known for a long time, but until now it has not been possible to precisely investigate the role of oxygen in complex surfaces point by point in order to understand the chemical background at the atomic level. This has now been achieved at TU Wien in cooperation with a team from the Elettra Synchrotron in Trieste. It became possible ...
Could we harness energy from black holes?
2021-01-13
A remarkable prediction of Einstein's theory of general relativity--the theory that connects space, time, and gravity--is that rotating black holes have enormous amounts of energy available to be tapped.
For the last 50 years, scientists have tried to come up with methods to unleash this power. Nobel physicist Roger Penrose theorized that a particle disintegration could draw energy from a black hole; Stephen Hawking proposed that black holes could release energy through quantum mechanical emission; while Roger Blandford and Roman Znajek suggested electromagnetic ...
UCI scientists measure local vibrational modes at individual crystalline faults
2021-01-13
Irvine, Calif., Jan. 11, 2021 - Often admired for their flawless appearance to the naked eye, crystals can have defects at the nanometer scale, and these imperfections may affect the thermal and heat transport properties of crystalline materials used in a variety of high-technology devices.
Employing newly developed electron microscopy techniques, researchers at the University of California, Irvine and other institutions have, for the first time, measured the spectra of phonons - quantum mechanical vibrations in a lattice - at individual crystalline faults, and they discovered the propagation of phonons near the flaws. The team's findings are the subject of a study published recently in Nature.
"Point defects, dislocations, stacking ...
UCI researchers use deep learning to identify gene regulation at single-cell level
2021-01-13
Irvine, Calif., Jan. 5, 2021 -- Scientists at the University of California, Irvine have developed a new deep-learning framework that predicts gene regulation at the single-cell level.
Deep learning, a family of machine-learning methods based on artificial neural networks, has revolutionized applications such as image interpretation, natural language processing and autonomous driving. In a study published recently in Science Advances, UCI researchers describe how the technique can also be successfully used to observe gene regulation at the cellular level. Until now, that process had ...
Research reveals how teeth functioned and evolved in giant mega-sharks
2021-01-13
A pioneering study by University of Bristol researchers finds that the evolution of teeth in the giant prehistoric shark Megalodon and its relatives was a by-product of becoming huge, rather than an adaptation to new feeding habits.
The iconic extinct Megalodon was the largest shark to ever roam the seas. Its name translates to 'big tooth', making reference to its massive teeth, which represent the most abundant fossil remains of the species. They are broad and triangular, nothing like the curved, blade-like teeth of the closest relatives of Megalodon.
The ...
Recurrent GBM brain tumors with few mutations respond best to immunotherapy
2021-01-13
DURHAM, N.C. - Glioblastoma brain tumors are especially perplexing. Inevitably lethal, the tumors occasionally respond to new immunotherapies after they've grown back, enabling up to 20% of patients to live well beyond predicted survival times.
What causes this effect has long been the pursuit of researchers hoping to harness immunotherapies to extend more lives.
New insights from a team led by Duke's Preston Robert Tisch Brain Tumor Center provide potential answers. The team found that recurring glioblastoma tumors with very few mutations are far more vulnerable ...
Upper ocean temperatures hit record high in 2020
2021-01-13
Even with the COVID-19-related small dip in global carbon emissions due to limited travel and other activities, the ocean temperatures continued a trend of breaking records in 2020. A new study, authored by 20 scientists from 13 institutes around the world, reported the highest ocean temperatures since 1955 from surface level to a depth of 2,000 meters.
The report was published on January 13 in Advances in Atmospheric Sciences and concluded with a plea to the policymakers and others to consider the lasting damage warmer oceans can cause as they attempt to mitigate the ...
Ukraine genome survey adds missing pieces to human diversity puzzle
2021-01-13
Today, the largest study of genetic diversity in Ukraine was published in the open science journal GigaScience. The project was an international effort, bringing together researchers in Ukraine, the US and China and is the first fruits of this collaboration to set up a new Central Europe Center for Genomic Research in Ukraine. Led by researchers at Uzhhorod National University and Oakland University in the US, the work provides genetic understanding of the historic and pre-historic migration settlements in one of the key intersections of human trade and migration between the Eurasian peoples as well as the identification of genetic variants of medical interest in the Ukrainian population that differ ...
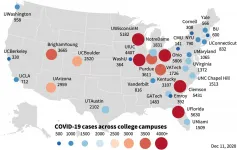
New study suggests that college campuses are COVID-19 superspreaders
2021-01-13
College campuses are at risk of becoming COVID-19 superspreaders for their entire county, according to a new vast study which shows the striking danger of the first two weeks of school in particular.
Looking at 30 campuses across the nation with the highest amount of reported cases, experts saw that over half of the institutions had spikes - at their peak - which were well above 1,000 coronavirus cases per 100,000 people per week within the first two weeks of class.
In some colleges, one in five students had been infected with the virus by the end of the fall term. Four institutions had over 5,000 ...
Ovarian cancer cells adapt to their surroundings to aid tumor growth
2021-01-13
A detailed description of how ovarian cancer cells adapt to survive and proliferate in the peritoneal cavity has been published in Frontiers in Oncology. Researchers show that structures inside the cells change as the disease progresses from benign to malignant, helping the cells to grow in an otherwise hostile environment of low nutrients and oxygen. Understanding how these cellular adaptations are regulated could herald new targeted treatment options against the fifth-leading cause of cancer-related deaths in women.
"Our study compared the structures inside cells representing different stages of ovarian cancer, including after aggregation, which enhances their survival," says Eva Schmelz, a Professor and Scientific Director at Virginia Tech University, USA, who led this research. "We found ...
[1] ... [2755]
[2756]
[2757]
[2758]
[2759]
[2760]
[2761]
[2762]
2763
[2764]
[2765]
[2766]
[2767]
[2768]
[2769]
[2770]
[2771]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.