Spilling the beans on coffee's true identity
2021-01-13
People worldwide want their coffee to be both satisfying and reasonably priced. To meet these standards, roasters typically use a blend of two types of beans, arabica and robusta. But, some use more of the cheaper robusta than they acknowledge, as the bean composition is difficult to determine after roasting. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry have developed a new way to assess exactly what's in that cup of joe.
Coffee blends can have good quality and flavor. However, arabica beans are more desirable than other types, resulting in a higher market value for blends containing a higher proportion of this variety. In some cases, producers dilute their blends with the less expensive robusta beans, yet that is hard for consumers ...
The cancer microbiome reveals which bacteria live in tumors
2021-01-13
DURHAM, N.C. -- Biomedical engineers at Duke University have devised an algorithm to remove contaminated microbial genetic information from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). With a clearer picture of the microbiota living in various organs in both healthy and cancerous states, researchers will now be able to find new biomarkers of disease and better understand how numerous cancers affect the human body.
In the first study using the newly decontaminated dataset, the researchers have already discovered that normal and cancerous organ tissues have a slightly different microbiota composition, that bacteria from these diseased sites can enter the bloodstream, and that this bacterial information could help diagnose ...
Scoring system to redefine how U.S. patients prioritized for liver transplant
2021-01-13
Liver transplant priority in the U.S. goes to the sickest patients, which fails to consider other important factors, including how long patients are likely to survive post-transplant.
Researchers with Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine are collaborating with faculty at the University of Pennsylvania to develop a risk score that more comprehensively prioritizes liver cancer patients for transplantation.
Their paper documenting the development and validation of the LiTES-HCC score to predict post-transplant survival for hepatocellular carcinoma, or liver cancer, patients was published in the highly respected peer-reviewed Journal of Hepatology.
The ...
Mathematics explains how giant whirlpools form in developing egg cells
2021-01-13
Egg cells are among the largest cells in the animal kingdom. If moved only by the random jostlings of water molecules, a protein could take hours or even days to drift from one side of a forming egg cell to the other. Luckily, nature has developed a faster way: cell-spanning whirlpools in the immature egg cells of animals such as mice, zebrafish and fruit flies. These vortices enable cross-cell commutes that take just a fraction of the time. But until now, scientists didn't know how these crucial flows formed.
Using mathematical modeling, researchers now have an answer. The gyres result from the collective behavior of rodlike molecular ...
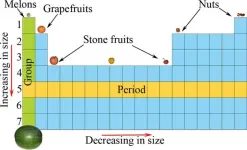
Superheroes, foods and apps bring a modern twist to the periodic table
2021-01-13
Many students, especially non-science majors, dread chemistry. The first lesson in an introductory chemistry course typically deals with how to interpret the periodic table of elements, but its complexity can be overwhelming to students with little or no previous exposure. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Journal of Chemical Education introduce an innovative way to make learning about the elements much more approachable -- by using "pseudo" periodic tables filled with superheroes, foods and apps.
One of the fundamental topics taught in first-year undergraduate chemistry courses is ...
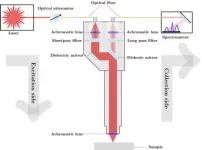
Raman spectroscopy shows promise for diagnosing oral cancer
2021-01-13
WASHINGTON -- In a new study, researchers show that a light-based analytical technique known as Raman spectroscopy could aid in early detection of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC).
OSCC is the most prevalent type of oral cancer and ranks among the most common cancers diagnosed worldwide. Although effective treatments are available, the cancer is often not detected until a late stage, resulting in overall poor prognosis.
"Raman spectroscopy is not only label-free and non-invasive, but it can potentially be used in ambient light conditions," says research team leader Levi Matthies from University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf in Germany. "This makes it promising for use as a potential screening tool ...
CVIA publishes selected abstracts from the 31st GW-ICC Conference
2021-01-13
Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications, publishes selected abstracts from the 31st Great Wall International Cardiology (GW-ICC) Conference, October 19 - 25, 2020
Beijing, January 13, 2021: Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications (CVIA), in its role as the official journal of the Great Wall International Cardiology Conference (GW-ICC), has published selected abstracts from the 31st GW-ICC. Abstracts are now online at https://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/cscript/cvia/2020/00000005/a00101s1/art00001
Co-Editors-in-Chief of CVIA Dr. C. Richard Conti, past president of the American College of Cardiology, and Dr Jianzeng Dong, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China commented that CVIA is delighted to be ...
Inferring human genomes at a fraction of the cost promises to boost biomedical research
2021-01-13
Thousands of genetic markers have already been robustly associated with complex human traits, such as Alzheimer's disease, cancer, obesity, or height. To discover these associations, researchers need to compare the genomes of many individuals at millions of genetic locations or markers, and therefore require cost-effective genotyping technologies. A new statistical method, developed by Olivier Delaneau's group at the SIB Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics and the University of Lausanne (UNIL), offers game-changing possibilities. For less than $1 in computational cost, GLIMPSE is able to statistically infer a complete human genome from a very small amount of data. The method offers ...
Researchers at Brazil's space institute discover why lightning branches and flickers
2021-01-13
Researchers at Brazil's National Space Research Institute (INPE), in partnership with colleagues in the United States, United Kingdom and South Africa, have recorded for the first time the formation and branching of luminous structures by lightning strikes.
Analyzing images captured by a super slow motion camera, they discovered why lightning strikes bifurcate and sometimes then form luminous structures interpreted by the human eye as flickers.
The study was supported by São Paulo Research Foundation - FAPESP. An article outlining its results is published in Scientific Reports.
"We managed to obtain the first optical observation of these phenomena and find a possible explanation for branching and flickering," Marcelo Magalhães Fares Saba, ...
Evolution: Speciation in the presence of gene flow
2021-01-13
Spatial isolation is known to promote speciation - but researchers at Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich have now shown that, at least in yeast, the opposite is also true. New ecological variants can also evolve within thoroughly mixed populations.
The idea that speciation is based on the selection of variants that are better adapted to the local environmental conditions is at the heart of Charles Darwin's theory of the origin of species - and it is now known to be a central component of biological evolution, and thus of biodiversity. Geographic isolation of populations is often regarded as a necessary condition for ecotypes to diverge ...
New research in JNCCN highlights dangerous disparities for life-saving cancer screening
2021-01-13
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [January 13, 2021] -- New research in the January 2021 issue of JNCCN--Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network finds more than a third of eligible people miss timely screening tests for colorectal cancer and at least a quarter appear to miss timely screening tests for breast and cervical cancers. The study comes from the University of Alberta, Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry in Alberta, Canada, with findings based on self-reported results from the Canadian Community Health Survey (CCHS) from 2007-2016. According to the author, the results also ...
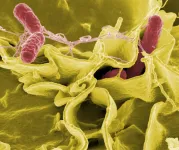
NIH scientists study salmonella swimming behavior as clues to infection
2021-01-13
WHAT:
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium bacteria (S. Typhimurium) commonly cause human gastroenteritis, inflammation of the lining of the intestines. The bacteria live inside the gut and can infect the epithelial cells that line its surface. Many studies have shown that Salmonella use a "run-and-tumble" method of short swimming periods (runs) punctuated by tumbles when they randomly change direction, but how they move within the gut is not well understood.
National Institutes of Health scientists and their colleagues believe they have identified a S. Typhimurium protein, McpC ...
Getting romantic at home wearing an EEG cap
2021-01-13
Research into the neuronal basis of emotion processing has so far mostly taken place in the laboratory, i.e. in unrealistic conditions. Bochum-based biopsychologists have now studied couples in more natural conditions. Using electroencephalography (EEG), they recorded the brain activity of romantic couples at home while they cuddled, kissed or talked about happy memories together. The results confirmed the theory that positive emotions are mainly processed in the left half of the brain.
A group led by Dr. Julian Packheiser, Gesa Berretz, Celine Bahr, Lynn Schockenhoff and Professor Sebastian Ocklenburg from the Department of Biopsychology at Ruhr-Universität Bochum ...
BU researchers uncover viral small RNAs in mosquito cells
2021-01-13
(Boston)--Researchers from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) provide a new genomics resource that details the small RNA transcriptomes (gene expression) of four bio-medically important mosquito species.
This is the first study to provide a platform for biologists to compare the characteristics of these small RNAs between these four mosquitoes as well as the most widely used insects for genetic experiments, the fruit fly, Drosophila. Although previous studies looked at each of the individual mosquito species separately, this study is the first to allow comparisons between all four species.
"Although ...
How to keep drones flying when a motor fails
2021-01-13
As anxious passengers are often reassured, commercial aircrafts can easily continue to fly even if one of the engines stops working. But for drones with four propellers - also known as quadcopters - the failure of one motor is a bigger problem. With only three rotors working, the drone loses stability and inevitably crashes unless an emergency control strategy sets in.
Researchers at the University of Zurich and the Delft University of Technology have now found a solution to this problem: They show that information from onboard cameras can be used to stabilize the drone and keep it flying autonomously after one rotor suddenly gives out.
Spinning like a ballerina
"When one rotor fails, the drone begins to spin ...
The meat of the matter: Environmental dissemination of beef cattle agrochemicals
2021-01-13
A recent Point of Reference article, "The meat of the matter: Environmental dissemination of beef cattle agrochemicals," published in Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, points at synthetic chemical cocktails being emitted from cattle feed yards into the environment and how they can impact our ecosystem and our health.
Industrial meat production facilities have a bad reputation for their impact on the environment. Concentrated animal feeding operations (CAFOs) are known to release greenhouse gases related to global warming and for discharge of manure to watersheds, which affects water quality. A less publicized impact of modern beef production is the excessive use of ...
Infection biology: How one pathogen evades the immune system
2021-01-13
Our immune system is never idle. Their task is to detect and eliminate invasive pathogens, and they have no time to lose. The adaptive immune system identifies infectious organisms by recognizing foreign proteins on the surfaces of bacteria, viruses and unicellular protozoans. The interaction of these antigens with immune cells triggers a series of downstream events, which in most cases leads to the elimination of the pathogen.
But pathogenic organisms have developed strategies that enable them to escape detection by the immune system, and the strategies employed by remotely related organisms are often remarkably similar to each other. One way of confusing the immune system is to increase the structural heterogeneity of the antigens it encounters. ...
Temple researchers identify cardiac protein that causes different types of heart failure
2021-01-13
(Philadelphia, PA) - Like a failing fuel pump that causes a loss of engine power in a car, a diseased heart can take a serious toll on the body's performance. For some patients, tasks like walking up a flight of stairs or walking across a room eventually turn into exhausting endeavors. This is because, over time, regardless of the underlying cause, heart damage typically progresses, owing to a constant barrage of oxidative stress and toxic lipids that alter heart cell energetics and, ultimately, the ability of the heart to function normally.
Oxidative stress occurs when harmful oxygen-containing molecules outnumber helpful antioxidants, leading to damaging reactions with proteins, DNA, and other cell components. ...
Impact of COVID lockdown on aeromedical retrievals in remote parts of Australia
2021-01-13
New data released this week by Australian researchers reveals the impact of the COVID-19 lockdown period on aeromedical retrievals in rural and remote regions.
Researchers say while the social isolation measures led to a reduction in overall aeromedical activity during the lockdown in 2020, once the restrictions were lifted, evacuations increased significantly.
These findings are published in the Internal Medicine Journal, comparing aeromedical evacuation trends in Australia during the pre-restriction, lockdown and post-restriction periods last ...
Perceptions of police using PPE during the pandemic - SFU study
2021-01-13
A Simon Fraser University study on public perceptions of police officers wearing personal protective equipment (PPE) during the current pandemic finds that most PPE renders positive perceptions of police, while some equipment, including full-face respirator masks, may be viewed more negatively. The research was published January 9 in the Journal of Experimental Criminology.
Led by SFU criminology assistant professor Rylan Simpson and MA student Ryan Sandrin, the online experimental study drew on a sample of 117 participants residing in North America. The participants were randomly assigned to read one of three fictitious news articles that were either pro-PPE (highlighting health benefits), neutral or anti-PPE (lacking health benefits). Participants were then asked to rate 12 ...
Scientists discover key enzyme responsible for skin blistering in the elderly
2021-01-13
The Granzyme B (GzmB) enzyme, which accumulates in certain tissues as we age, has been identified as a driver of itchy and sometimes life-threatening autoimmune conditions known as pemphigoid diseases (PDs), which cause blistering and skin erosion below the skin's surface.
New research led by University of British Columbia (UBC) and Vancouver Coastal Health Research Institute (VCHRI) scientists has found that a gel containing a specific and potent inhibitor of GzmB activity, VTI-1002, resulted in significant improvements on skin affected by PDs.
"Blisters caused by these conditions can be extremely discomforting, unsightly and ...
USTC obtains Pd-Pt tesseracts for oxygen reduction reaction
2021-01-13
A proton exchange membrane fuel cell is a chemical cell that converts energy released when a substance reacts into electrical energy with zero emission. It is an excellent substitute for fossil fuel.
However, low activity and stability of the Pt-based catalysts in the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) of the battery cathode restricted the output power and the number of charge and discharge cycles, thus increasing the cost of the whole fuel cells. The preparation of cathode catalysts with high activity and stability is a difficult problem.
In a study ...
Discovery of 'adolescent' skeletal stem cells might someday help prevent osteoporosis
2021-01-13
Durham, NC - A new study reported in STEM CELLS reveals a unique population of skeletal stem cells (SSCs) that function during the transitional period between rapid bone growth and bone maintenance. This discovery provides an opportunity to determine whether alterations in the SSCs' pattern might affect bone formation, as well as helps us understand the physiological factors that regulate its timing.
"This is particularly important given that anything that interferes with the proper development of bone mass during childhood and adolescence has long-lasting effects on our health, including the development of osteoporosis ...
Changes in political administration come with increased danger of international conflict
2021-01-13
BINGHAMTON, NY -- A new leader takes office and foreign rivals begin to test the waters. How tough is this new leader? Are they willing to risk war, or just full of bluster?
This testing can escalate crises, increasing the risk of war as international adversaries gauge the new leader's willingness to use force. A new paper co-written by faculty at Binghamton University, State University of New York shows that when this "turnover trap" occurs depends a good deal on the politics back home, and the nature of the leader's transition into office.
Binghamton University Associate Professor of Political Science Amanda Licht was among ...
CU Anschutz scientists reverse deadly impacts of asthma in mice
2021-01-13
AURORA, Colo. (Jan. 13, 2021) - Mucus in the lungs can be fatal for asthma patients, but scientists at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus have broken up those secretions at the molecular level and reversed their often deadly impacts.
In a study published Monday in the journal Nature Communications, the researchers explained how they created an inhaled treatment that disrupted the production of excess mucus by reducing disulfide bonds in mice and opening up their airways. The same treatment had similar impacts on human mucus samples.
"Currently about 10% of the population has asthma," said the study's lead author Christopher Evans, PhD, professor of Pulmonary Sciences & Critical ...
[1] ... [2754]
[2755]
[2756]
[2757]
[2758]
[2759]
[2760]
[2761]
2762
[2763]
[2764]
[2765]
[2766]
[2767]
[2768]
[2769]
[2770]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.