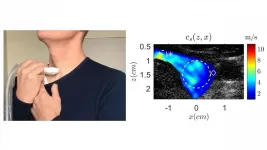
Singing a tumor test song
2021-01-12
WASHINGTON, January 12, 2021 -- Singing may be the next-generation, noninvasive approach to determining the health of a patient's thyroid.
Typically, a fine needle is used to detect the presence of a tumor in the thyroid, which most commonly affects children and younger women. However, this method can only detect about 5% of thyroid cancers.
Researchers from Université de Tours, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Dijon-Bourgogne, and Université Bourgogne Franche-Comté suggest a simpler approach: singing. They demonstrate the technique in the journal Applied Physics Letters, from AIP Publishing.
"Developing noninvasive methods would reduce the stress of patients during their medical exams," said Steve Beuve, one of the authors. "Having to sing during a medical ...
Suicide among individuals with autism spectrum disorder
2021-01-12
What The Study Did: National register data from Denmark were used to examine if people with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) have higher rates of suicide attempts and suicide compared to those without ASD and to identify potential risk factors.
Author: Kairi Kõlves, Ph.D., of Griffith University in Brisbane, Australia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.33565)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict ...
Higher live birth rates found after transferring fresh rather than frozen embryos...
2021-01-12
BOSTON -- For women hoping to achieve a pregnancy using freshly retrieved donor eggs, a new retrospective study led by researchers from Brigham and Women's Hospital may provide important insight. Brigham senior author Janis H. Fox, MD, had observed that when freshly retrieved donor eggs were used, pregnancy rates were higher for fresh compared to frozen embryo transfers. Fox and her colleagues were intrigued by this observation. The team set out to scientifically determine if this observation would be replicated in a larger sample of recipients. Leveraging national data from the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology (SART), the Brigham researchers found that, in cycles using freshly retrieved donor eggs, fresh embryo transfers were indeed ...
Hip fracture incidence expected to increase two-to-three fold in some Eurasian countries
2021-01-12
A detailed analysis of the burden of osteoporosis in eight Eurasian countries has found that osteoporosis is a significant and growing health problem in the region that will escalate in the future due to expected demographic changes.
The authors of the Audit report [1] carried out a review of the available literature and a survey of the representatives of the national osteoporosis societies in eight Eurasian countries. The Audit reviews both the burden and the differences between Armenia, Belarus, Georgia, Moldova, Kazakhstan, the Kyrgyz Republic, the Russian Federation, and Uzbekistan with regard to the prevalence of osteoporosis and incidence of osteoporotic fractures, future demographic changes, diagnostic resources, and treatment availability.
The findings ...
Researchers develop laser-based process to 3D print detailed glass objects
2021-01-12
WASHINGTON -- Researchers have developed a new laser-based process for 3D printing intricate parts made of glass. With further development, the new method could be useful for making complex optics for vision, imaging, illumination or laser-based applications.
"Most 3D printing processes build up an object layer by layer," said research team leader Laurent Gallais from The Fresnel Institute and Ecole Centrale Marseille in France. "Our new process avoids the limitations of these processes by using a laser beam to transform -- or polymerize -- a liquid precursor into solid glass."
In The Optical Society (OSA) journal Optics Letters, Gallais and research team members Thomas Doualle and Jean-Claude Andre demonstrate how they used the new technique to create detailed objects in ...
Scientists study use of abundant enzyme in tumor cells to monitor cancer treatment
2021-01-12
The abundant presence of an enzyme known as low molecular weight protein tyrosine phosphatase (LMWPTP) in tumor cells has long been considered an indicator of cancer aggressiveness and metastatic potential. It is also known to perform important functions in cells under normal conditions, participating in both the proliferation process and the regulation of intracellular systems. Research continues on its role in cancer progression.
In Brazil, a group of researchers at the University of Campinas’s In Vitro Bioassay and Signal Transduction Laboratory led by Professor Carmen Veríssima Ferreira-Halder are studying the possibility of inhibiting this protein phosphatase ...
Formula predicts ideal dose of stem cells to cure HIV
2021-01-12
Scientists have determined the optimal conditions following a stem cell transplant that could control HIV without the need of an everyday pill, according to a study published today in eLife.
Finding the right balance of stem cell dose, cell type and timing of antiretroviral therapy (ART) could potentially lead to a spontaneous cure of HIV.
There are only two cases of HIV cure to date: the Berlin Patient and the London Patient, who both received stem cell transplants with stem cells from donors that lack a molecule called CCR5, which HIV is attracted to.
"The major obstacle to HIV eradication is a latent reservoir of long-lived infected cells, and cure strategies aim to eliminate all infected cells or permanently prevent viral reactivation ...
Study identifies immune response biomarkers, novel pathways in four marine mollusc species
2021-01-12
Understanding the immune systems of oysters and clams is important in monitoring the effects of pollution and climate change on the health of molluscan species and the potential impacts on the aquaculture industry. Their immune responses also can serve as indicators of changes in ocean environments.
A new study involving the University of Maine assessed immune responses in four economically important marine mollusc species -- the blue mussel, soft-shell clam, Eastern oyster, and Atlantic jackknife clam -- and identified new biomarkers relating to changes ...
Discovery of a new approach to inhibiting a highly treatment-refractory liver cancer
2021-01-12
BOSTON -- Reprogramming the rich connective tissue microenvironment of a liver cancer known as intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) inhibits its progression and resistance to standard chemotherapy in animal models, researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) have found. This new treatment for a disease with extremely poor outcomes uses antibodies to block placental growth factor (PlGF), a member of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family, which has been widely studied for its role in new vessel formation in cancers. PlGF is highly expressed ...
UCF researchers use advanced light to reveal how different biofuels behave
2021-01-12
ORLANDO, Jan. 12, 2021 -Vehicles have evolved to become more efficient and sophisticated, but their fuel hasn't necessarily evolved along with them. The Department of Energy is determined to identify cleaner burning and renewable alternatives to gasoline, and through the work of two UCF researchers, the DOE is one step closer to that goal.
Research engineer Anthony C. Terracciano and Associate Professor Subith Vasu have developed a model that will help engine designers, fuel chemists and federal agencies determine whether certain biofuels should be implemented as an alternative fuel ...
How many tests after vasectomy? Guideline update leads to change in practice
2021-01-12
January 12, 2021 - A change in evidence-based guidelines for vasectomy may have led to a reduction in the number of follow-up tests to confirm the procedure was successful, reports a study in Urology Practice®, an Official Journal of the American Urological Association (AUA). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
Originally published in 2012, and then updated in 2015, the AUA clinical guideline could significantly reduce the number of men undergoing multiple postvasectomy semen analyses (PVSAs) to confirm it's safe to stop using other methods of birth control, according to new research by Tony Chen, MD, of University of Washington, ...
Soil degradation costs U.S. corn farmers a half-billion dollars every year
2021-01-12
One-third of the fertilizer applied to grow corn in the U.S. each year simply compensates for the ongoing loss of soil fertility, leading to more than a half-billion dollars in extra costs to U.S. farmers every year, finds new research from the University of Colorado Boulder published last month in Earth's Future.
Long-term soil fertility is on the decline in agricultural lands around the world due to salinization, acidification, erosion and the loss of important nutrients in the soil such as nitrogen and phosphorus. Corn farmers in the U.S. offset these losses with nitrogen and ...
Enlightening dark ions
2021-01-12
Every field has its underlying principles. For economics it's the rational actor; biology has the theory of evolution; modern geology rests on the bedrock of plate tectonics.
Physics has conservation laws and symmetries. For instance, the law of conservation of energy - which holds that energy can neither be created nor destroyed -- has guided research in physics since antiquity, becoming more formalized as time went on. Likewise, parity symmetry suggests that switching an event for its mirror image shouldn't affect the outcome.
As physicists have worked to understand the truly bizarre rules ...
Study of flowers with two types of anthers solves mystery that baffled Darwin
2021-01-12
Most flowering plants depend on pollinators such as bees to transfer pollen from the male anthers of one flower to the female stigma of another flower, enabling fertilization and the production of fruits and seeds. Bee pollination, however, involves an inherent conflict of interest, because bees are only interested in pollen as a food source.
"The bee and the plant have different goals, so plants have evolved ways to optimize the behavior of bees to maximize the transfer of pollen between flowers," explained Kathleen Kay, associate professor of ecology ...
High doses of saccharin don't lead to diabetes in healthy adults, study finds
2021-01-12
COLUMBUS, Ohio - For those trying to live a healthy lifestyle, the choice between sugar and artificial sweeteners such as saccharin can be confusing. A new study led by researchers at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and The Ohio State University College of Medicine found the sugar substitute saccharin doesn't lead to the development of diabetes in healthy adults as previous studies have suggested.
The study findings are published in the journal Microbiome.
"It's not that the findings of previous studies are wrong, they just didn't adequately control for things like ...
Scientists identify "immune cop" that detects SARS-CoV-2
2021-01-12
LA JOLLA, CALIF. - Jan 12, 2020 - Scientists at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute have identified the sensor in human lungs that detects SARS-CoV-2 and signals that it's time to mount an antiviral response. The study, published today in Cell Reports, provides insights into the molecular basis of severe disease and may enable new strategies for the treatment and prevention of COVID-19.
"Our research has shown that MDA-5 is the immune cop that's tasked to keep an eye out for SARS-CoV-2 and call for back-up," says Sumit Chanda, Ph.D., director of the Immunity and Pathogenesis Program at Sanford Burnham Prebys and senior author of ...
Family court decisions distorted by misuse of key research, say experts
2021-01-12
Family courts are misunderstanding and misusing research around how children form close relationships with their caregivers, say an international group of experts.
Seventy experts from across the globe argue that widespread misunderstandings around attachment research have hampered its accurate implementation, with potentially negative consequences for decisions in family courts.
In response, they have published an international consensus statement in Attachment & Human Development that aims "to counter misinformation and help steer family court applications of attachment theory in a supportive, evidence-based direction on matters related to child protection and custody decisions".
In the statement, the group sets out three principles from attachment research ...
Noted experts challenge conventional wisdom within the field of radiology
2021-01-12
Philadelphia, January 12, 2021 - A special issue of the Journal of the American College of Radiology (JACR), published by Elsevier, challenges conventional wisdom across the imaging community. This collection of articles, the "Provocative Issue," presents extreme opinions on pressing issues confronting radiologists with the deliberate aim of sparking positive dialog and debate that will lead to innovative solutions to improve patient care and imaging-related outcomes.
The issue is guest-edited by:
Caroline Chung, MD, MSc, Director of Advanced ...
Record drop in cancer mortality for second straight year due to improved lung cancer treatment
2021-01-12
ATLANTA - JANUARY 12, 2021 - Overall cancer death rates in the United States dropped continuously from 1991 through 2018 for a total decrease of 31%, including a 2.4% decline from 2017 to 2018. The news comes from the American Cancer Society's annual Cancer Statistics, 2021 article, appearing in CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, and its consumer version, Cancer Facts & Figures 2021. This year marks the American Cancer Society's 70th anniversary of reporting this data to inform the nation's fight against cancer.
The report estimates that in the U.S. in 2021, almost 1.9 million (1,898,160) new cancer cases will be diagnosed and 608,570 Americans will die from cancer. ...
Fossils' soft tissues helping to solve puzzle that vexed Darwin
2021-01-12
Remarkably well-preserved fossils are helping scientists unravel a mystery about the origins of early animals that puzzled Charles Darwin.
Analysis of the 547 million-year-old remains has enabled researchers to trace the ancestry of some of the world's earliest animals further back than ever before.
Their study has uncovered the first known link between animals that evolved during the so-called Cambrian Explosion some 540 million-years-ago and one of their early ancestors.
Until recently, little was known about the origins of animals that evolved during the Cambrian event because of a lack of well-preserved fossil evidence.
The mysterious origins of animals that evolved at this time - when the diversity ...
DiosCURE to develop highly specific single-chain antibodies against SARS-CoV-2
2021-01-12
Core technology includes promising bivalent single-domain antibodies simultaneously targeting two surface structures of the viral spike protein.
Lead candidates DIOS-202 and DIOS-203 are engineered for high potency and their potential to avoid the emergence of escape mutants.
DIOS-202 and DIOS-203 entered into accelerated development to initiate clinical studies later this year.
BONN, Germany, January 12, 2021 - DiosCURE SE announced a publication in Science describing its core technology of multivalent single-chain antibodies with a unique molecular mode-of-action to inactivate ...
Healthcare Nutrition Council leads the way on medical food discussions
2021-01-12
While most people are able to eat a normal diet, many of those managing distinct nutritional requirements related to a disease or health condition rely on medical foods. Medical foods help patients meet their nutritional needs, often improving nutritional and health outcomes and quality of life. A recent publication in Current Developments in Nutrition, titled "Medical Foods: Science, Regulation, and Practical Aspects. Summary of a Workshop," shares the historical and regulatory context of medical foods and perspectives on their role in the future.
Medical foods help patients manage their nutritional needs, yet it can be very difficult for patients to have access to them. In August 2019, the Healthcare Nutrition Council (HNC), in partnership with the American Society ...
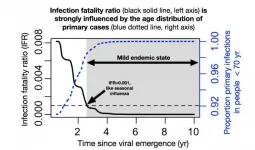
Another common cold virus? Modeling SARS-CoV-2's progress through the ages
2021-01-12
What is the endgame for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that is causing worldwide devastation? If it becomes endemic -- circulating in the general population -- and most people are exposed in childhood, SARS-CoV-2 may join the ranks of mild cold-causing coronaviruses that currently circulate in humans, according to a model developed by Emory and Penn State scientists.
The model, published January 12 in Science, draws upon studies of the four common cold coronaviruses and SARS-CoV-1. For those viruses, the term "herd immunity" is incomplete and possibly misleading, says ...
New promising antibodies against SARS-CoV-2
2021-01-12
Antibodies are an important weapon in the immune system's defense against infections. They bind to the surface structures of bacteria or viruses and prevent their replication. One strategy in the fight against disease is therefore to produce effective antibodies in large quantities and inject them into the patients. The outgoing US President Donald Trump probably owes his rapid recovery to this method. However, the antibodies used to treat him have a complex structure, do not penetrate very deeply into the tissue and may cause unwanted complications. Moreover, producing antibodies is difficult and time-consuming. They are therefore probably not suitable for widespread use.
Mass production in yeast or bacteria
"We focus on another group of molecules, the nanobodies," ...
New small antibodies show promising effects against COVID-19 infection
2021-01-12
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have developed, in collaboration with researchers in Germany and the U.S., new small antibodies, also known as nanobodies, which prevent the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus from entering human cells. The research study, published in Science, shows that a combined nanobody had a particularly good effect - even if the virus mutated. According to the researchers, the nanobodies have the potential to be developed into a treatment for COVID-19.
Specific proteins, spike proteins, on the surface of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus help the virus infect host cells. Therefore, antibodies that block the spike proteins and prevent them from binding to the cell can be a way to stop infection.
From the perspective ...
[1] ... [2746]
[2747]
[2748]
[2749]
[2750]
[2751]
[2752]
[2753]
2754
[2755]
[2756]
[2757]
[2758]
[2759]
[2760]
[2761]
[2762]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.